APB Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy
... When methane reacts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide, electrons end up farther away from the carbon atom and closer to their new covalent partners, the oxygen atoms, which are very electronegative. ...
... When methane reacts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide, electrons end up farther away from the carbon atom and closer to their new covalent partners, the oxygen atoms, which are very electronegative. ...
Pupmed Linked Abstracts
... killed and serum and kidneys were isolated for analysis. 3. Injection of CDDP resulted in a significant increase in serum creatinine, blood urea nitrogen (BUN), thiobarbituric acid-reactive substances (TBARS) and total nitrate/nitrite (NO(x)), as well as a significant decrease in reduced glutathione ...
... killed and serum and kidneys were isolated for analysis. 3. Injection of CDDP resulted in a significant increase in serum creatinine, blood urea nitrogen (BUN), thiobarbituric acid-reactive substances (TBARS) and total nitrate/nitrite (NO(x)), as well as a significant decrease in reduced glutathione ...
Ch2
... – 4.1 kcal/g; ~2,500 kcal stored in body – Primary ATP substrate for muscles, brain – Extra glucose stored as glycogen in liver, muscles ...
... – 4.1 kcal/g; ~2,500 kcal stored in body – Primary ATP substrate for muscles, brain – Extra glucose stored as glycogen in liver, muscles ...
Document
... ATP-Generating Steps C Enzymes attach a phosphate to the two PGAL, and transfer two electrons and a hydrogen ion from each PGAL to NAD+. Two PGA (phosphoglycerate) and two NADH are the result. D Enzymes transfer a phosphate group from each PGA to ADP. Thus, two ATP have formed by substratelevel phos ...
... ATP-Generating Steps C Enzymes attach a phosphate to the two PGAL, and transfer two electrons and a hydrogen ion from each PGAL to NAD+. Two PGA (phosphoglycerate) and two NADH are the result. D Enzymes transfer a phosphate group from each PGA to ADP. Thus, two ATP have formed by substratelevel phos ...
7 | cellular respiration
... Step 1. The first step in glycolysis (Figure 7.6) is catalyzed by hexokinase, an enzyme with broad specificity that catalyzes the phosphorylation of six-carbon sugars. Hexokinase phosphorylates glucose using ATP as the source of the phosphate, producing glucose-6-phosphate, a more reactive form of g ...
... Step 1. The first step in glycolysis (Figure 7.6) is catalyzed by hexokinase, an enzyme with broad specificity that catalyzes the phosphorylation of six-carbon sugars. Hexokinase phosphorylates glucose using ATP as the source of the phosphate, producing glucose-6-phosphate, a more reactive form of g ...
How Cells Release Chemical Energy
... ATP-Generating Steps C Enzymes attach a phosphate to the two PGAL, and transfer two electrons and a hydrogen ion from each PGAL to NAD+. Two PGA (phosphoglycerate) and two NADH are the result. D Enzymes transfer a phosphate group from each PGA to ADP. Thus, two ATP have formed by substratelevel phos ...
... ATP-Generating Steps C Enzymes attach a phosphate to the two PGAL, and transfer two electrons and a hydrogen ion from each PGAL to NAD+. Two PGA (phosphoglycerate) and two NADH are the result. D Enzymes transfer a phosphate group from each PGA to ADP. Thus, two ATP have formed by substratelevel phos ...
A Supramolecular Peptide Synthesizer
... after reaction with the activated amino acids. The condensation domain (C-domain) finally catalyzes the formation of the peptide, similar to the ribosome in RPS. Nevertheless, several differences between the two biosynthetic pathways are apparent. For instance, nonribosomal peptides (NRPs) are not r ...
... after reaction with the activated amino acids. The condensation domain (C-domain) finally catalyzes the formation of the peptide, similar to the ribosome in RPS. Nevertheless, several differences between the two biosynthetic pathways are apparent. For instance, nonribosomal peptides (NRPs) are not r ...
The Stimulatory Effect of Globular Adiponectin on Insulin
... from the rectus abdominus muscle was excised perpendicular to the direction of the muscle fibers, clipped at resting length, and placed in oxygenated ice-cold medium 199 (Sigma, Oakville, ON, Canada) for transport to the laboratory (⬃5 min). Then, 8 –12 muscle strips weighing ⬃25 mg were separated f ...
... from the rectus abdominus muscle was excised perpendicular to the direction of the muscle fibers, clipped at resting length, and placed in oxygenated ice-cold medium 199 (Sigma, Oakville, ON, Canada) for transport to the laboratory (⬃5 min). Then, 8 –12 muscle strips weighing ⬃25 mg were separated f ...
Lecture 13: Fighting Entropy II: Respiration
... cycle, NADH and FADH2 carry most of the energy extracted from food • These two molecules transport the high energy electrons generated by the breakdown of glucose to pyruvate (during glycolysis) and pyruvate to oxaloacetate and CO2 (during the citric acid cycle) and donate them to the electron trans ...
... cycle, NADH and FADH2 carry most of the energy extracted from food • These two molecules transport the high energy electrons generated by the breakdown of glucose to pyruvate (during glycolysis) and pyruvate to oxaloacetate and CO2 (during the citric acid cycle) and donate them to the electron trans ...
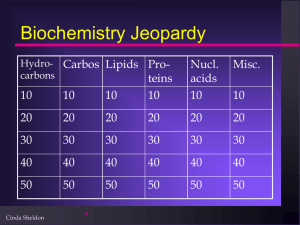
BIOCHEMISTRY
... 1. Cellulose A. polysacch. - plants 2. Glucose B. fiber from plants 3. Glycogen C. polysacch. - animals 4. Starch D. monosaccharide ...
... 1. Cellulose A. polysacch. - plants 2. Glucose B. fiber from plants 3. Glycogen C. polysacch. - animals 4. Starch D. monosaccharide ...
glucose-6-P - WordPress.com
... rate to provide glucose 6-phosphate to meet the cell's need. Liver cells also contain an isoenzyme of hexokinase, glucokinase, which has a Km very much higher than the normal intracellular concentration of glucose. The function of glucokinase in the liver is to remove glucose from the blood followin ...
... rate to provide glucose 6-phosphate to meet the cell's need. Liver cells also contain an isoenzyme of hexokinase, glucokinase, which has a Km very much higher than the normal intracellular concentration of glucose. The function of glucokinase in the liver is to remove glucose from the blood followin ...
Effects of oxygen on the growth and metabolism of Actinomyces
... enables the production of 1 mol of ATP per mol succinate formed [17]. Fermentation of 1 mol glucose would then yield 4 mol ATP. Since, with glucose as an electron donor oxygen was consumed with a high rate and affinity, it seems reasonable to assume that under aerobic conditions a very similar elect ...
... enables the production of 1 mol of ATP per mol succinate formed [17]. Fermentation of 1 mol glucose would then yield 4 mol ATP. Since, with glucose as an electron donor oxygen was consumed with a high rate and affinity, it seems reasonable to assume that under aerobic conditions a very similar elect ...
The Effect of Detergents on Amino Acid Liberation by
... required in small quantities in the cell and is undetectable as a free-pool amino acid by the methods employed in this study. Several factors may contribute to tryptophan overproduction, either singly or in combination : deregulation of aromatic amino acid biosynthesis at the prime branch point of t ...
... required in small quantities in the cell and is undetectable as a free-pool amino acid by the methods employed in this study. Several factors may contribute to tryptophan overproduction, either singly or in combination : deregulation of aromatic amino acid biosynthesis at the prime branch point of t ...
Cellular Respiration Harvesting Chemical Energy
... ATP accounting so far… Glycolysis 2 ATP Kreb’s cycle 2 ATP Life takes a lot of energy to run, need to extract more energy than 4 ATP! There’s got to be a better way! ...
... ATP accounting so far… Glycolysis 2 ATP Kreb’s cycle 2 ATP Life takes a lot of energy to run, need to extract more energy than 4 ATP! There’s got to be a better way! ...
4 Dr. M. Alzaharna 2016 Dr. M. Alzaharna 2016 II. REACTIONS OF
... CYCLE AND PYRUVATE DEHYDROGENASE COMPLEX ...
... CYCLE AND PYRUVATE DEHYDROGENASE COMPLEX ...
Biosketch - NC State University
... Deborah M. Muoio, and Gary D. Lopaschuk. Insulin-stimulated cardiac glucose oxidation is increased in high fat diet-induced obese mice lacking malonyl CoA decarboxylase. In revision. 37. Timothy R. Koves, Terry E. Jones, Dorothy Slentz, James Way, Ann Louise Olson, G. Lynis Dohm, and Deborah M. Muoi ...
... Deborah M. Muoio, and Gary D. Lopaschuk. Insulin-stimulated cardiac glucose oxidation is increased in high fat diet-induced obese mice lacking malonyl CoA decarboxylase. In revision. 37. Timothy R. Koves, Terry E. Jones, Dorothy Slentz, James Way, Ann Louise Olson, G. Lynis Dohm, and Deborah M. Muoi ...
Amino Acid Incorporation by in Vitro Tumor and
... amino acids, of the order of 800 @mo1es.The natural RNA's which have been shown to increase the incorporation of individual amino acids by 16—45per cent would raise the theoretical total incorporation to as much as 1150 j@moles. The addition of polyuridylic acid produces a seven-fold increase in p ...
... amino acids, of the order of 800 @mo1es.The natural RNA's which have been shown to increase the incorporation of individual amino acids by 16—45per cent would raise the theoretical total incorporation to as much as 1150 j@moles. The addition of polyuridylic acid produces a seven-fold increase in p ...
Essential amino acid
... invading bacteria, and enhances memory. – Nitric oxide is synthesized from oxygen and the amino acid arginine. – In blood vessels, NO activates reactions in smooth muscle cells that cause dilation and a resulting decrease in blood pressure. ...
... invading bacteria, and enhances memory. – Nitric oxide is synthesized from oxygen and the amino acid arginine. – In blood vessels, NO activates reactions in smooth muscle cells that cause dilation and a resulting decrease in blood pressure. ...
22: Peptides, Proteins, and α
... They are useful for analyzing only the first few amino acids at the C-terminal end of a peptide because they cleave different C-terminal amino acids at different rates. As a result, C-terminal amino acids of shortened chains formed during the analysis procedure may cleave more rapidly than those of ...
... They are useful for analyzing only the first few amino acids at the C-terminal end of a peptide because they cleave different C-terminal amino acids at different rates. As a result, C-terminal amino acids of shortened chains formed during the analysis procedure may cleave more rapidly than those of ...
Activities for the -Helix and -Sheet Construction Kit
... hydrogen bonds. Examine the two secondary structures. 1. What similarities are present between the two structures? 2. What differences are present between the two? 3. How is the amino-group of one amino acid positioned in relation to other amino groups? The carboxyl carbons? B. Add the hydrogen bond ...
... hydrogen bonds. Examine the two secondary structures. 1. What similarities are present between the two structures? 2. What differences are present between the two? 3. How is the amino-group of one amino acid positioned in relation to other amino groups? The carboxyl carbons? B. Add the hydrogen bond ...
Respiration Notes - Streetsboro City Schools
... Kreb’s cycle- the process in which pyruvic acid is broken down into carbon dioxide in a series of energy-releasing steps Electron transport chain- the process in which high-energy electrons convert ADP to ATP (a lot of it). ATP- the principal chemical compound that cells use to store and release ...
... Kreb’s cycle- the process in which pyruvic acid is broken down into carbon dioxide in a series of energy-releasing steps Electron transport chain- the process in which high-energy electrons convert ADP to ATP (a lot of it). ATP- the principal chemical compound that cells use to store and release ...
Lead (Pb) - American Nutrition Association
... Average daily intake is 50ug. Drinking water doesn’t contribute significantly BUT smoking does. One cigarette contains 1-2ug cadmiuim Cadmium occurs in only ONE valency state, Cd2+. -Does not form stable alkyl compounds or other organometallic compounds ABSORPTION -Cd is absorbed poorly in GI tract, ...
... Average daily intake is 50ug. Drinking water doesn’t contribute significantly BUT smoking does. One cigarette contains 1-2ug cadmiuim Cadmium occurs in only ONE valency state, Cd2+. -Does not form stable alkyl compounds or other organometallic compounds ABSORPTION -Cd is absorbed poorly in GI tract, ...
Lecture 4 Enzymes Catalytic proteins Enzymes Enzymes Enzymes
... • Eg: Adrenalin activates Phosphorylase kinase which phosphorylates Glycogen Phosphorylase. -This enzyme in turn breaks down glycogen to release glucose ...
... • Eg: Adrenalin activates Phosphorylase kinase which phosphorylates Glycogen Phosphorylase. -This enzyme in turn breaks down glycogen to release glucose ...