Chemical digestion
... • Enzymes provide site where reactants are brought together. • Reactants = substrate • Substrate binds to active site of enzyme; enzyme substrate complex • Reaction occurs. • Product released; enzyme freed for another reaction. ...
... • Enzymes provide site where reactants are brought together. • Reactants = substrate • Substrate binds to active site of enzyme; enzyme substrate complex • Reaction occurs. • Product released; enzyme freed for another reaction. ...
Slide 1
... forms a non-covalent homochiral octamer in a mass spectrometer via electrospray ionization Octamer was found to be chiroselective—formed from enantiopure samples, but not racemic ones! one L-serine selects to bind with 7 more L-enantiomers Also found that they could incorporate more than one type ...
... forms a non-covalent homochiral octamer in a mass spectrometer via electrospray ionization Octamer was found to be chiroselective—formed from enantiopure samples, but not racemic ones! one L-serine selects to bind with 7 more L-enantiomers Also found that they could incorporate more than one type ...
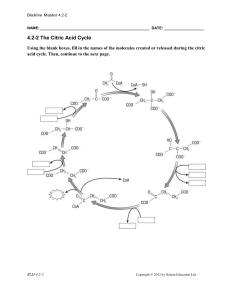
Blackline Master 4.2-2 NAME: DATE: 4.2
... Complete the summaries below by filling in the blanks. 1. Pyruvate oxidation ________________ enters the mitochondrion from the cytoplasm. One ________________ atom is removed via ___________________, and ________________ is removed using ________. ________________ becomes attached to the remaining ...
... Complete the summaries below by filling in the blanks. 1. Pyruvate oxidation ________________ enters the mitochondrion from the cytoplasm. One ________________ atom is removed via ___________________, and ________________ is removed using ________. ________________ becomes attached to the remaining ...
energy
... • Single sugar molecules are called monosaccharides • The large macromolecules formed from monosaccharides are known as polysaccharides ...
... • Single sugar molecules are called monosaccharides • The large macromolecules formed from monosaccharides are known as polysaccharides ...
Cellular Respiration
... 2> Kreb’s cycle: a series of chemical reactions using pyruvic acid to produce ATP and two types of reduced molecules. 3>Electron Transport Chain: the process of extracting ATP from NADH and FADH2 ...
... 2> Kreb’s cycle: a series of chemical reactions using pyruvic acid to produce ATP and two types of reduced molecules. 3>Electron Transport Chain: the process of extracting ATP from NADH and FADH2 ...
Glycolysis is the first step in the breakdown of glucose to
... Nearly all of the energy used by living cells comes to them from the energy in the bonds of the sugar glucose. Glucose enters heterotrophic cells in two ways. One method is through secondary active transport in which the transport takes place against the glucoseconcentration gradient. The other mech ...
... Nearly all of the energy used by living cells comes to them from the energy in the bonds of the sugar glucose. Glucose enters heterotrophic cells in two ways. One method is through secondary active transport in which the transport takes place against the glucoseconcentration gradient. The other mech ...
BIOCHEMISTRY NOTES
... 4. The force with which molecules collide depends upon their kinetic energy, which is usually not very high within a cell 5. Enzymes help the molecules perform the chemical reactions, since the molecules alone would take a long, long time (if ever) B. HOW ENZYMES FUNCTION 1. ENERGY OF ACTIVATION - I ...
... 4. The force with which molecules collide depends upon their kinetic energy, which is usually not very high within a cell 5. Enzymes help the molecules perform the chemical reactions, since the molecules alone would take a long, long time (if ever) B. HOW ENZYMES FUNCTION 1. ENERGY OF ACTIVATION - I ...
Paper - IndiaStudyChannel.com
... 12. In the pentose phosphate pathway : (A) Only the C-1 carbon of glucose are oxidized to CO2 (B) All the carbons of glucose are oxidized to CO2 (C) No decarboxylation occurs (D) C-4 and C-5 of glucose is oxidized to CO2 13. F1F0–ATPase in chloroplasts is located on the : (A) inner chloroplast membr ...
... 12. In the pentose phosphate pathway : (A) Only the C-1 carbon of glucose are oxidized to CO2 (B) All the carbons of glucose are oxidized to CO2 (C) No decarboxylation occurs (D) C-4 and C-5 of glucose is oxidized to CO2 13. F1F0–ATPase in chloroplasts is located on the : (A) inner chloroplast membr ...
Discussion Questions for Week 5: HWA Pages 167-177
... 9. In glycolysis, how many CO2 molecules are formed for each glucose molecule oxidized? 10. The ETC pumps protons from the matrix to the core of the mitochondria. The protons become concentrated in the intermembrane space and tend to diffuse back into the matrix. What two types of proteins discussed ...
... 9. In glycolysis, how many CO2 molecules are formed for each glucose molecule oxidized? 10. The ETC pumps protons from the matrix to the core of the mitochondria. The protons become concentrated in the intermembrane space and tend to diffuse back into the matrix. What two types of proteins discussed ...
FapR, a Bacterial Transcription Factor Involved in
... Bacterial cells exert exquisite control over the biosynthesis of their membrane lipids, but the mechanisms are obscure. We describe the identification and purification from Bacillus subtilis of a transcription factor, FapR, that controls the expression of many genes involved in fatty acid and phosph ...
... Bacterial cells exert exquisite control over the biosynthesis of their membrane lipids, but the mechanisms are obscure. We describe the identification and purification from Bacillus subtilis of a transcription factor, FapR, that controls the expression of many genes involved in fatty acid and phosph ...
chapter 5 the structure and function of macromolecules
... ○ Protein functions include structural support, storage, transport, cellular communication, movement, and defense against foreign substances. ○ Most important, protein enzymes function as catalysts in cells, regulating metabolism by selectively accelerating certain chemical reactions without being c ...
... ○ Protein functions include structural support, storage, transport, cellular communication, movement, and defense against foreign substances. ○ Most important, protein enzymes function as catalysts in cells, regulating metabolism by selectively accelerating certain chemical reactions without being c ...
Reece9e_Lecture_C05
... ○ A polymer is a long molecule consisting of many similar or identical building blocks linked by covalent bonds. ○ The repeated units are small molecules called monomers. ○ Some of the molecules that serve as monomers have other functions of their own. The chemical mechanisms which cells use to ma ...
... ○ A polymer is a long molecule consisting of many similar or identical building blocks linked by covalent bonds. ○ The repeated units are small molecules called monomers. ○ Some of the molecules that serve as monomers have other functions of their own. The chemical mechanisms which cells use to ma ...
Micro Lab Unit 1 Flashcards
... What is the body's least preferred source of energy? Why is protein one of the body's least preferred sources of energy? Why are proteins essential? ...
... What is the body's least preferred source of energy? Why is protein one of the body's least preferred sources of energy? Why are proteins essential? ...
Third Lecture - LSU School of Medicine
... Serotonin is a neurotransmitters that pass messages between nerve cells that are involved in depression. ...
... Serotonin is a neurotransmitters that pass messages between nerve cells that are involved in depression. ...
Биологическая химия
... from inorganic substances, thereby dealing a blow to the widespread vitalistic doctrine of a so-called life-force. ** Butlerov – the author of the theory of chemical structure of organic compounds. One of the streets nearby Russian Peoples’ Friendship University is called by his name. ...
... from inorganic substances, thereby dealing a blow to the widespread vitalistic doctrine of a so-called life-force. ** Butlerov – the author of the theory of chemical structure of organic compounds. One of the streets nearby Russian Peoples’ Friendship University is called by his name. ...
Curriculum for Excellence Higher Chemistry Unit 2 Nature`s Che
... Structural formulae for esters can be drawn given the name of the parent alcohol and the parent carboxylic acid or given the name of the ester. Esters have characteristic smells, and are used as flavourings. Esters are also used as industrial solvents. Esters can be made by reacting alcohols ...
... Structural formulae for esters can be drawn given the name of the parent alcohol and the parent carboxylic acid or given the name of the ester. Esters have characteristic smells, and are used as flavourings. Esters are also used as industrial solvents. Esters can be made by reacting alcohols ...
Amino Acid/Protein Structure
... https://www.khanacademy.org/science/biology/macromolecules/proteins-andamino-acids/a/orders-of-protein-structure Describe the 4 levels of protein structure: ...
... https://www.khanacademy.org/science/biology/macromolecules/proteins-andamino-acids/a/orders-of-protein-structure Describe the 4 levels of protein structure: ...
lecture7
... active. In starvation, the level of free fatty acids rises because hormones such as epinephrine and glucagon stimulate adipose-cell lipase. Insulin, in contrast, inhibits lipolysis. Acetyl CoA carboxylase also plays a role in the regulation of fatty acid degradation. Malonyl CoA, the product of the ...
... active. In starvation, the level of free fatty acids rises because hormones such as epinephrine and glucagon stimulate adipose-cell lipase. Insulin, in contrast, inhibits lipolysis. Acetyl CoA carboxylase also plays a role in the regulation of fatty acid degradation. Malonyl CoA, the product of the ...
Learning Objectives Week 8 – Digestion and Absorption (Part1) 1
... Carbohydrates, like lipids and proteins, can be very complex structures that require breakdown before they can be absorbed. Some forms of carbohydrates like cellulose (plant fiber) are too complex for the human digestive system to break down. Breakdown of carbohydrates begins in the mouth where an e ...
... Carbohydrates, like lipids and proteins, can be very complex structures that require breakdown before they can be absorbed. Some forms of carbohydrates like cellulose (plant fiber) are too complex for the human digestive system to break down. Breakdown of carbohydrates begins in the mouth where an e ...
CH 3 Biochemistry - Belle Vernon Area School District
... • Describe the structure of a water molecule. • How do polar compounds differ from nonpolar compounds? • What happens to ions when they are mixed in water? • Define cohesion and adhesion. ...
... • Describe the structure of a water molecule. • How do polar compounds differ from nonpolar compounds? • What happens to ions when they are mixed in water? • Define cohesion and adhesion. ...
Animal Nutrition - De Anza College
... intestine allows food to go out in squirts. Takes 2 to 6 hrs after a meal for the stomach to empty. ...
... intestine allows food to go out in squirts. Takes 2 to 6 hrs after a meal for the stomach to empty. ...
The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules 1. Polymers What are Polymers?
... vertebrate blood, transports oxygen from the lungs to other parts of the body. Other proteins transport molecules across cell membranes. ...
... vertebrate blood, transports oxygen from the lungs to other parts of the body. Other proteins transport molecules across cell membranes. ...
CITRIC ACID CYCLE
... It is the second of three metabolic pathways that are involved in fuel molecule catabolism and ATP production, the other two being glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation. The citric acid cycle also provides precursors for many compounds such as certain amino acids, and some of its reactions are th ...
... It is the second of three metabolic pathways that are involved in fuel molecule catabolism and ATP production, the other two being glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation. The citric acid cycle also provides precursors for many compounds such as certain amino acids, and some of its reactions are th ...