The Formation of Pyruvate from Citric Acid
... In studies to investigate the relationship of renal gluconeogenesis to ammonia production in isolated tubules from rat kidney cortex we observed the following: when phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase [GTP-oxaloacetate carboxy-lyase (transphosphorylating), EC 4.1 .I .32] is inhibited by 3-mercaptopico ...
... In studies to investigate the relationship of renal gluconeogenesis to ammonia production in isolated tubules from rat kidney cortex we observed the following: when phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase [GTP-oxaloacetate carboxy-lyase (transphosphorylating), EC 4.1 .I .32] is inhibited by 3-mercaptopico ...
Document
... – Are constructed from two types of smaller molecules, a single glycerol and usually three fatty acids – Vary in the length and number and locations of ...
... – Are constructed from two types of smaller molecules, a single glycerol and usually three fatty acids – Vary in the length and number and locations of ...
Anaerobic Respiration
... electron acceptor is reduced and used as the source of nutrient for cell growth. Dissimilative metabolism: A large amount of the electron acceptor is reduced for energy and the reduced product is excreted into the environment. ...
... electron acceptor is reduced and used as the source of nutrient for cell growth. Dissimilative metabolism: A large amount of the electron acceptor is reduced for energy and the reduced product is excreted into the environment. ...
Cytoplasmatic Bacterial Membrane Responses to Environmental
... gas treatment, bioremediation and biocatalysis. ...
... gas treatment, bioremediation and biocatalysis. ...
Aerobic Respiration - East Muskingum Schools
... produces 2 ATP. The Kreb's cycle produces 2 ATP, and the electron transport chain produces 34 ATP. That gives a total of ____ATP when ____________ is available to the cell during aerobic respiration. ...
... produces 2 ATP. The Kreb's cycle produces 2 ATP, and the electron transport chain produces 34 ATP. That gives a total of ____ATP when ____________ is available to the cell during aerobic respiration. ...
LESSON 2.5 WORKBOOK Blood glucose in sleep, a 5 mile
... During exercise the rate of the citric acid cycle can’t always keep up with the amount of glucose that is being supplied to the muscles. This is because the citric acid cycle requires oxygen to be delivered from the lungs via the blood. During anaerobic exercise like running or dancing you breathe h ...
... During exercise the rate of the citric acid cycle can’t always keep up with the amount of glucose that is being supplied to the muscles. This is because the citric acid cycle requires oxygen to be delivered from the lungs via the blood. During anaerobic exercise like running or dancing you breathe h ...
METABOLISM OF CARBOHYDRATES
... Metabolism – biochemical reactions that provide energy and cell growth Two types of metabolism: anabolism – synthesis of more complicated molecules from simple precursors (requires energy ...
... Metabolism – biochemical reactions that provide energy and cell growth Two types of metabolism: anabolism – synthesis of more complicated molecules from simple precursors (requires energy ...
File - Mr. Shanks` Class
... d) Dihydroxy – acetone phosphate, fructose – 1,6 biphosphate 5. What happens to the two carbons from acetyl – COA entering the Krebs cycle? a) Expelled as a gas b) Recycled in oxaloacetate c) Released as ethanol d) Converted into pyruvate 6. What is the name of the final product in Glycolysis? a) AT ...
... d) Dihydroxy – acetone phosphate, fructose – 1,6 biphosphate 5. What happens to the two carbons from acetyl – COA entering the Krebs cycle? a) Expelled as a gas b) Recycled in oxaloacetate c) Released as ethanol d) Converted into pyruvate 6. What is the name of the final product in Glycolysis? a) AT ...
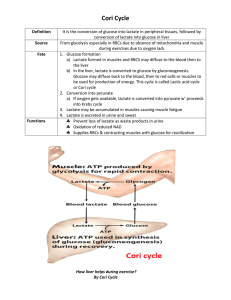
Cori Cycle - COFFEE BREAK CORNER
... It is the conversion of glucose into lactate in peripheral tissues, followed by conversion of lactate into glucose in liver From glycolysis especially in RBCs due to absence of mitochondria and muscle ...
... It is the conversion of glucose into lactate in peripheral tissues, followed by conversion of lactate into glucose in liver From glycolysis especially in RBCs due to absence of mitochondria and muscle ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Nerve activates contraction
... – Also known as functional proteins – Function as antibodies or enzymes – Can be denatured ...
... – Also known as functional proteins – Function as antibodies or enzymes – Can be denatured ...
midtermstudyguidehe325_2015
... Know what the three groups of complimentary proteins are and be able to list foods in each group as well as combinations that would fulfill the definition of a complimentary protein Be able to distinguish whether soy is similar in quality to animal protein Be able to distinguish between the v ...
... Know what the three groups of complimentary proteins are and be able to list foods in each group as well as combinations that would fulfill the definition of a complimentary protein Be able to distinguish whether soy is similar in quality to animal protein Be able to distinguish between the v ...
FUNCTIONS OF CELL ORGANELLES
... incapable of dividing to produce daughter cells. The best-known anucleated cell is the mammalian red blood cell, or erythrocyte, which also lacks other organelles such as mitochondria and serves primarily as a transport vessel to ferry oxygen from the lungs to the body's tissues. ...
... incapable of dividing to produce daughter cells. The best-known anucleated cell is the mammalian red blood cell, or erythrocyte, which also lacks other organelles such as mitochondria and serves primarily as a transport vessel to ferry oxygen from the lungs to the body's tissues. ...
functions of cell organelles
... incapable of dividing to produce daughter cells. The best-known anucleated cell is the mammalian red blood cell, or erythrocyte, which also lacks other organelles such as mitochondria and serves primarily as a transport vessel to ferry oxygen from the lungs to the body's tissues. ...
... incapable of dividing to produce daughter cells. The best-known anucleated cell is the mammalian red blood cell, or erythrocyte, which also lacks other organelles such as mitochondria and serves primarily as a transport vessel to ferry oxygen from the lungs to the body's tissues. ...
General pathways of amino acids transformation
... All aminotransferases require the prosthetic group pyridoxal phosphate (PLP), which is derived from pyridoxine (vitamin B6). Ping-pong kinetic mechanism First step: the amino group of amino acid is transferred to pyridoxal phosphate, forming pyridoxamine phosphate and releasing ketoacid. Second step ...
... All aminotransferases require the prosthetic group pyridoxal phosphate (PLP), which is derived from pyridoxine (vitamin B6). Ping-pong kinetic mechanism First step: the amino group of amino acid is transferred to pyridoxal phosphate, forming pyridoxamine phosphate and releasing ketoacid. Second step ...
Digestive System
... Used to synthesize glucose Converted to acetyl CoA and enters Krebs/Citric acid cycle (of cellular respiration) Stored in adipose tissue (insulation) Used in building cellular structures (cell and organelle membranes) Used to synthesize some hormones (steroid) Animation ...
... Used to synthesize glucose Converted to acetyl CoA and enters Krebs/Citric acid cycle (of cellular respiration) Stored in adipose tissue (insulation) Used in building cellular structures (cell and organelle membranes) Used to synthesize some hormones (steroid) Animation ...
Nutrition- Notes
... glucose. Excess glucose is converted into the complex carbohydrate glycogen and is stored in that form. When supplies of glucose are needed, the glycogen is broken down to glucose for transport through the body. 4. Lipids (fats_).(9_ cal/g)(fat, butter, oil, lard) (a) Use by the body. Fats are used ...
... glucose. Excess glucose is converted into the complex carbohydrate glycogen and is stored in that form. When supplies of glucose are needed, the glycogen is broken down to glucose for transport through the body. 4. Lipids (fats_).(9_ cal/g)(fat, butter, oil, lard) (a) Use by the body. Fats are used ...
BIO 210 Anatomy and Physiology Homework #9: Chs. 24
... 32) All of the following are true of beta-oxidation, except that A) it yields large amounts of ATP. B) lipids are converted into glycogen molecules. C) it requires coenzyme A, NAD, and FAD. D) fatty acids break down into two-carbon fragments that enter the TCA cycle. E) it occurs in the mitochondria ...
... 32) All of the following are true of beta-oxidation, except that A) it yields large amounts of ATP. B) lipids are converted into glycogen molecules. C) it requires coenzyme A, NAD, and FAD. D) fatty acids break down into two-carbon fragments that enter the TCA cycle. E) it occurs in the mitochondria ...
Major Metabolic Pathway
... •Organisms are divided into autotrophs and heterotrophs according to their energy pathways. •Autotrophs are those organisms that are able to make energy-containing organic molecules from inorganic raw material by using basic energy sources such as sunlight. Plants are the prime example of autotrophs ...
... •Organisms are divided into autotrophs and heterotrophs according to their energy pathways. •Autotrophs are those organisms that are able to make energy-containing organic molecules from inorganic raw material by using basic energy sources such as sunlight. Plants are the prime example of autotrophs ...
Chapter 2: Major Metabolic Pathway
... •Organisms are divided into autotrophs and heterotrophs according to their energy pathways. •Autotrophs are those organisms that are able to make energy-containing organic molecules from inorganic raw material by using basic energy sources such as sunlight. Plants are the prime example of autotrophs ...
... •Organisms are divided into autotrophs and heterotrophs according to their energy pathways. •Autotrophs are those organisms that are able to make energy-containing organic molecules from inorganic raw material by using basic energy sources such as sunlight. Plants are the prime example of autotrophs ...
Chapter 1 An Introduction to Phospholipids
... (Figure 1-II) in the liquid ordered phase. In the membrane this collective forms an organized lipid raft2 which is essential for signal transduction.3 As this classification to saponifiable and non-saponifiable lipids is historical, it is easy to find exceptions. For example, lipid 1 (Figure 1-III) ...
... (Figure 1-II) in the liquid ordered phase. In the membrane this collective forms an organized lipid raft2 which is essential for signal transduction.3 As this classification to saponifiable and non-saponifiable lipids is historical, it is easy to find exceptions. For example, lipid 1 (Figure 1-III) ...