biology
... in GCE Biology. They were finalised after detailed discussion at examiners' conferences by all the examiners involved in the assessment. The conferences were held shortly after the papers were taken so that reference could be made to the full range of candidates' responses, with photocopied scripts ...
... in GCE Biology. They were finalised after detailed discussion at examiners' conferences by all the examiners involved in the assessment. The conferences were held shortly after the papers were taken so that reference could be made to the full range of candidates' responses, with photocopied scripts ...
CH 2. CELLULAR RESPIRATION
... » the 6 carbon atoms leave as low energy CO2 molecules The Krebs Cycle produces: - 2 molecules of CO2 ...
... » the 6 carbon atoms leave as low energy CO2 molecules The Krebs Cycle produces: - 2 molecules of CO2 ...
RESPIRATION: SYNTHESIS OF ATP
... NADH, FADH2; citric acid cycle stops. ! Without air, some cells regenerate NAD+ (from glycolysis only) by passing e- (+ H+) to pyruvic acid ! Result: continued glycolysis, forming 2 ATP per ...
... NADH, FADH2; citric acid cycle stops. ! Without air, some cells regenerate NAD+ (from glycolysis only) by passing e- (+ H+) to pyruvic acid ! Result: continued glycolysis, forming 2 ATP per ...
06a Organic Acids 2
... Aim: Produce citrate from non-carbohydrate material e.g.: hydrocarbons, fatty acids, ethanol, acetate ...
... Aim: Produce citrate from non-carbohydrate material e.g.: hydrocarbons, fatty acids, ethanol, acetate ...
ch3a FA11 - Cal State LA
... Overcoming the activation energy barrier (EA) • Bunsen burner: CH4 + 2O2 --> CO2 + 2H2O – The spark adds enough E to exceed EA (not a catalyst) ...
... Overcoming the activation energy barrier (EA) • Bunsen burner: CH4 + 2O2 --> CO2 + 2H2O – The spark adds enough E to exceed EA (not a catalyst) ...
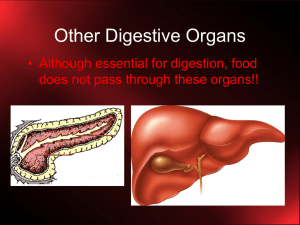
Other Digestive Organs
... molecules they break down • carbohydrates, protein, and fats are broken down with the addition of enzymes as well as water (hydrolyzation) • hydrolyzation is the opposite process of dehydrolysis synthesis (process that makes carbs, protein, fats) ...
... molecules they break down • carbohydrates, protein, and fats are broken down with the addition of enzymes as well as water (hydrolyzation) • hydrolyzation is the opposite process of dehydrolysis synthesis (process that makes carbs, protein, fats) ...
Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency
... NADP is reduced by G-6-PDH in the presence of G-6-P. The rate of formation of NADPH is directly proportional to the G-6-PDH activity and is measured spectrophotometrically as an increased in absorbance at 340nm. Prodution of asecond molar equivalant of NADPH by erythrocyte 6-phosphogluconate dehydro ...
... NADP is reduced by G-6-PDH in the presence of G-6-P. The rate of formation of NADPH is directly proportional to the G-6-PDH activity and is measured spectrophotometrically as an increased in absorbance at 340nm. Prodution of asecond molar equivalant of NADPH by erythrocyte 6-phosphogluconate dehydro ...
CH2O -OCH CH2O- - f.a. #1 f.a.#2 f.a.#3 f.a. = fatty acid.
... The cell membrane defines the volume of space occupied by a cell and ensures that the cell contents remain confined within that space. But in addition membranes confer a number of benefits upon cells: 1) An important function of a cell membranes is that of PROTECTION allowing the cell to maintain a ...
... The cell membrane defines the volume of space occupied by a cell and ensures that the cell contents remain confined within that space. But in addition membranes confer a number of benefits upon cells: 1) An important function of a cell membranes is that of PROTECTION allowing the cell to maintain a ...
A dietary supplement is intended to provide nutrients that may
... the body's natural glutamine stores are depleted during anaerobic exercise. Some studies have shown there to be no significant effect of glutamine on bench press strength, knee-extension torque ...
... the body's natural glutamine stores are depleted during anaerobic exercise. Some studies have shown there to be no significant effect of glutamine on bench press strength, knee-extension torque ...
Slides
... Only plants and microorganisms are able to obtain N from both air and soil.. N CYCLE Two ways plants convert available N to a biological useful form. I. Biological N Fixation: N2 ---.> NH3 II. NO3- Reduction: NO3- ---> NH4+ NH4+ --> Amides or Ureides --> Amino acids --> Proteins NITRATE REDUCTION Al ...
... Only plants and microorganisms are able to obtain N from both air and soil.. N CYCLE Two ways plants convert available N to a biological useful form. I. Biological N Fixation: N2 ---.> NH3 II. NO3- Reduction: NO3- ---> NH4+ NH4+ --> Amides or Ureides --> Amino acids --> Proteins NITRATE REDUCTION Al ...
energy - Wsfcs
... 2 molecules of ATP are used to start glycolysis and only 4 molecules of ATP are produced (therefore, there is a net gain of 2 ATP in the process) also makes 4 NADH molecules After glycolysis, there are 2 pathways for producing ATP; either fermentation, which also occurs in the cytoplasm of the ...
... 2 molecules of ATP are used to start glycolysis and only 4 molecules of ATP are produced (therefore, there is a net gain of 2 ATP in the process) also makes 4 NADH molecules After glycolysis, there are 2 pathways for producing ATP; either fermentation, which also occurs in the cytoplasm of the ...
No Slide Title
... ATP, NADH, and two pyruvates are the end products of glycolysis. It’s vital to know the reactants and products for each process of cellular respiration and photosynthesis! ...
... ATP, NADH, and two pyruvates are the end products of glycolysis. It’s vital to know the reactants and products for each process of cellular respiration and photosynthesis! ...
Note 4.2 - Aerobic Respiration
... After two turns of the citric acid cycle the original glucose molecule (6 carbons) has been completely broken down and 6 molecules of CO2 have been released. Acetyl-CoA + 3 NAD+ +FAD + ADP + Pi → 2 CO2 + 3 NADH + 3 H+ + FADH2 + ATP + CoA ...
... After two turns of the citric acid cycle the original glucose molecule (6 carbons) has been completely broken down and 6 molecules of CO2 have been released. Acetyl-CoA + 3 NAD+ +FAD + ADP + Pi → 2 CO2 + 3 NADH + 3 H+ + FADH2 + ATP + CoA ...
Toxicant Disposition and Metabolism
... – Makes less water-soluble and more readily absorbed. • Metal methylation; e.g., inorganic to methyl mercury. ...
... – Makes less water-soluble and more readily absorbed. • Metal methylation; e.g., inorganic to methyl mercury. ...
Phytanic acid omega-oxidation in human liver microsomes
... most active CYP450 but is not present in liver and therefore is not responsible for phytanic acid ωhydroxylation activity in liver. The other CYP450s ...
... most active CYP450 but is not present in liver and therefore is not responsible for phytanic acid ωhydroxylation activity in liver. The other CYP450s ...
Biochemistry 2EE3 Metabolism and Physiological Chemistry 2002
... Instructor: Dr. Boris S. Zhorov (HSC-4H29, ext. 22049; E- mail: [email protected]) Purpose: To provide a brief introduction to proteins, enzymes and gene expression followed by a more detailed treatment of energy and intermediary metabolism with emphasis on physiological chemistry Learning objectiv ...
... Instructor: Dr. Boris S. Zhorov (HSC-4H29, ext. 22049; E- mail: [email protected]) Purpose: To provide a brief introduction to proteins, enzymes and gene expression followed by a more detailed treatment of energy and intermediary metabolism with emphasis on physiological chemistry Learning objectiv ...
Lecture 6A/ Chapter 6 Protein
... Roles of Proteins • Structural (e.g. collagen) • Building blocks for most body structures • Replacement of dead or damaged cells • Enzymes (e.g. proteases, lipases) • Break down, build up, and transform substances • Catalysts for reactions Figure 6.9. Enzyme Action ...
... Roles of Proteins • Structural (e.g. collagen) • Building blocks for most body structures • Replacement of dead or damaged cells • Enzymes (e.g. proteases, lipases) • Break down, build up, and transform substances • Catalysts for reactions Figure 6.9. Enzyme Action ...
Cellular Respiration
... For example, 1 gram of glucose releases 3811 calories, on a food label 3.8 Calories ...
... For example, 1 gram of glucose releases 3811 calories, on a food label 3.8 Calories ...
Cellular Respiration
... tube). This reaction occurred very quickly. – A cell cannot use heat to do cellular work, not to mention the fact that this large increase in temp would be dangerous! ...
... tube). This reaction occurred very quickly. – A cell cannot use heat to do cellular work, not to mention the fact that this large increase in temp would be dangerous! ...
SBI 4U Unit 1 Questions
... All essential unit questions are to be handed in at the beginning of class on the day of our unit test. Please be sure to answer all questions in your own words. You are expected to use class notes and your text to answer all questions. Feel free to use additional internet sources to help with your ...
... All essential unit questions are to be handed in at the beginning of class on the day of our unit test. Please be sure to answer all questions in your own words. You are expected to use class notes and your text to answer all questions. Feel free to use additional internet sources to help with your ...