November 2003
... not be marked. 3. For each of the written-response questions, write your answer in ink unless otherwise instructed in the space provided in this booklet. 4. Ensure that you use language and content appropriate to the purpose and audience of this examination. Failure to comply may result in your pape ...
... not be marked. 3. For each of the written-response questions, write your answer in ink unless otherwise instructed in the space provided in this booklet. 4. Ensure that you use language and content appropriate to the purpose and audience of this examination. Failure to comply may result in your pape ...
Common Course Objective - Austin Community College
... to the cell when given the concentration of solutes in the environment and in the cell. 10. Determine which way water will move by osmosis and whether the cell will shrink, stay the same shape, or swell, when given the concentration of solutes in the cell and in the environment. K. Energy and Cells ...
... to the cell when given the concentration of solutes in the environment and in the cell. 10. Determine which way water will move by osmosis and whether the cell will shrink, stay the same shape, or swell, when given the concentration of solutes in the cell and in the environment. K. Energy and Cells ...
amino acids
... • The 1st AA(asparagine, Asp) was discovered in 1806 from asparagus (a green vegetable). • The last (threonine, Thr) was not identified until 1938! ...
... • The 1st AA(asparagine, Asp) was discovered in 1806 from asparagus (a green vegetable). • The last (threonine, Thr) was not identified until 1938! ...
prepex3
... Aminopterin, Methotrexate and purine and pyrimidine analogs such as arabinosides and AZT. GENERAL COMMENTS Some students will insist that “memorization” is absolutely essential to learning biochemistry. I will concur. But, I will not agree that ONLY memory can be used. The pathways of amino acids bu ...
... Aminopterin, Methotrexate and purine and pyrimidine analogs such as arabinosides and AZT. GENERAL COMMENTS Some students will insist that “memorization” is absolutely essential to learning biochemistry. I will concur. But, I will not agree that ONLY memory can be used. The pathways of amino acids bu ...
lecture11&12-RS_Major Metabolic Pathways of
... The severity of the hemolytic anemia depends on the degree of enzyme deficiency and the degree of RBC compensation by increasing the level of synthesis of 2,3-BPG to facilitate the release of Oxygen from hemoglobin to tissues. ...
... The severity of the hemolytic anemia depends on the degree of enzyme deficiency and the degree of RBC compensation by increasing the level of synthesis of 2,3-BPG to facilitate the release of Oxygen from hemoglobin to tissues. ...
Glycolysis is the major oxidative pathway for glucose
... The severity of the hemolytic anemia depends on the degree of enzyme deficiency and the degree of RBC compensation by increasing the level of synthesis of 2,3-BPG to facilitate the release of Oxygen from hemoglobin to tissues. ...
... The severity of the hemolytic anemia depends on the degree of enzyme deficiency and the degree of RBC compensation by increasing the level of synthesis of 2,3-BPG to facilitate the release of Oxygen from hemoglobin to tissues. ...
Ch 5
... – Operates with glycolysis – Use and production of 5 carbon sugars (na) – Bacillus subtilis, E. coli, Enterococcus faecalis ...
... – Operates with glycolysis – Use and production of 5 carbon sugars (na) – Bacillus subtilis, E. coli, Enterococcus faecalis ...
ester formation in brewery fermentations
... solvent-like flavours. They are also important in low alcohol beer production due to the low levels produced, which can result in beers with little flavour. The factors influencing ester production are reviewed, together with the ways in which they can be used to control ester synthesis. It is belie ...
... solvent-like flavours. They are also important in low alcohol beer production due to the low levels produced, which can result in beers with little flavour. The factors influencing ester production are reviewed, together with the ways in which they can be used to control ester synthesis. It is belie ...
Glycolysis Quiz
... 6. Where does glycolysis occur in the cell? (a) mitochondrial matrix (b) mitochondrial cristae (c) cytoplasm (d) chloroplast ...
... 6. Where does glycolysis occur in the cell? (a) mitochondrial matrix (b) mitochondrial cristae (c) cytoplasm (d) chloroplast ...
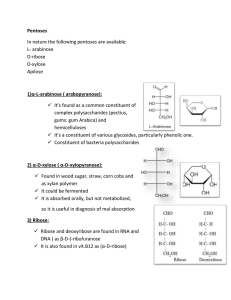
2) α-D-xylose
... * used as sweetners in liquid preparations *prepared by enzymatic conversion from glucose syrup, followed by glucose separation “usually produces HFCSs of 80-90%” 2) Fructose (Levulose): β-D-(-)-fructofuranose: Found free in fruits and honey and in polysaccharides It’s a furanose “in polysacch.” ...
... * used as sweetners in liquid preparations *prepared by enzymatic conversion from glucose syrup, followed by glucose separation “usually produces HFCSs of 80-90%” 2) Fructose (Levulose): β-D-(-)-fructofuranose: Found free in fruits and honey and in polysaccharides It’s a furanose “in polysacch.” ...
question
... shown (separately) on a nutritional label, but whose amounts are shown in total lipids and total carbs? •What carb doesn’t have calories (because it is not broken down, it passes through the large intestine ...
... shown (separately) on a nutritional label, but whose amounts are shown in total lipids and total carbs? •What carb doesn’t have calories (because it is not broken down, it passes through the large intestine ...
biol 161 aerobic cellular respiration
... C. Name the folds of the inner membrane that jut into the matrix. D. Within the mitochondrion, where do preparatory reaction and citric acid cycle occur? E. Where does the electron transport chain occur? ...
... C. Name the folds of the inner membrane that jut into the matrix. D. Within the mitochondrion, where do preparatory reaction and citric acid cycle occur? E. Where does the electron transport chain occur? ...
Cellular Respiration Part V: Anaerobic Respiration and Fermentation
... • All use glycolysis (net ATP = 2) to oxidize glucose and harvest chemical energy of food • In all three, NAD+ is the oxidizing agent that accepts electrons during glycolysis • The processes have different final electron acceptors: an organic molecule (such as pyruvate or acetaldehyde) in fermentati ...
... • All use glycolysis (net ATP = 2) to oxidize glucose and harvest chemical energy of food • In all three, NAD+ is the oxidizing agent that accepts electrons during glycolysis • The processes have different final electron acceptors: an organic molecule (such as pyruvate or acetaldehyde) in fermentati ...
how cells obtain energy from food
... grow. This is thermodynamically possible only because of a continual input of energy, part of which must be released from the cells to their environment as heat that disorders the surroundings. The only chemical reactions possible are those that increase the total amount of disorder in the universe. ...
... grow. This is thermodynamically possible only because of a continual input of energy, part of which must be released from the cells to their environment as heat that disorders the surroundings. The only chemical reactions possible are those that increase the total amount of disorder in the universe. ...
Intracellular Respiration
... 1. oxidation – the loss of electrons (usually pulled by electronegative oxygen) a. in respiration Glucose is oxidized, releasing energy b. Oxygen, in turn, is reduced 2.reduction the addition of electrons 3. hydrocarbons, and molecules that have a lot of Hydrogen(sugars, fats) are sources of electro ...
... 1. oxidation – the loss of electrons (usually pulled by electronegative oxygen) a. in respiration Glucose is oxidized, releasing energy b. Oxygen, in turn, is reduced 2.reduction the addition of electrons 3. hydrocarbons, and molecules that have a lot of Hydrogen(sugars, fats) are sources of electro ...
Chapter 14 Glycolysis and the catabolism of hexoses
... the cell. This is done by enzymes attached to the outer surface of the intestinal epithelial cells. Lactose intolerance come from the disappearance of lactase activity from the intestinal epithelial. When the undigested lactose hit the large intestine bacteria convert it to toxic product that cause ...
... the cell. This is done by enzymes attached to the outer surface of the intestinal epithelial cells. Lactose intolerance come from the disappearance of lactase activity from the intestinal epithelial. When the undigested lactose hit the large intestine bacteria convert it to toxic product that cause ...
Chapter 9 Presentation
... The Citric Acid Cycle • Upon entering the citric acid cycle, acetyl CoA adds its 2 carbon acetyl group to oxaloacetate, which creates citrate. • Citrate now undergoes a series of steps that creates 1 ATP molecule, 3NADH and 1FADH2. In the process, 2CO2 are given off, and oxaloacetate is regenerated ...
... The Citric Acid Cycle • Upon entering the citric acid cycle, acetyl CoA adds its 2 carbon acetyl group to oxaloacetate, which creates citrate. • Citrate now undergoes a series of steps that creates 1 ATP molecule, 3NADH and 1FADH2. In the process, 2CO2 are given off, and oxaloacetate is regenerated ...
Chemotropism of Achlya ambisexualis to Methionine
... activity in A. ambisexualis. Among individual amino acids only L-methionine induced a tropic response (Table 1a). The reorientation of hyphal tips (Fig. 1d) in response to changed positions of methionine-containing donor blocks is consistent with the conclusion that this compound is chemotropically ...
... activity in A. ambisexualis. Among individual amino acids only L-methionine induced a tropic response (Table 1a). The reorientation of hyphal tips (Fig. 1d) in response to changed positions of methionine-containing donor blocks is consistent with the conclusion that this compound is chemotropically ...
glucose
... • Citric acid (6C) is gradually converted back to the 4carbon compound -ready to start the cycle once more • The carbons removed are released as CO2 ...
... • Citric acid (6C) is gradually converted back to the 4carbon compound -ready to start the cycle once more • The carbons removed are released as CO2 ...
Chapter 3: Bioenergetics
... • Oxidation and reduction are always coupled reactions • In cells often involve the transfer of hydrogen atoms rather than free electrons – Hydrogen atom contains one electron – A molecule that loses a hydrogen also loses an electron, and therefore is oxidized ...
... • Oxidation and reduction are always coupled reactions • In cells often involve the transfer of hydrogen atoms rather than free electrons – Hydrogen atom contains one electron – A molecule that loses a hydrogen also loses an electron, and therefore is oxidized ...
Guidelines for the Investigation of Hyperammonaemia
... collection or a delay in analysis. (see Appendix –Measurement of Ammonia in Blood/Plasma) Hyperammonaemia can be caused by inherited deficiencies of the enzymes of the urea cycle. They are individually rare disorders but have a combined estimated incidence of approximately 1:30,000. The commonest di ...
... collection or a delay in analysis. (see Appendix –Measurement of Ammonia in Blood/Plasma) Hyperammonaemia can be caused by inherited deficiencies of the enzymes of the urea cycle. They are individually rare disorders but have a combined estimated incidence of approximately 1:30,000. The commonest di ...
Energy Systems - Mrs N Benedict
... re-synthesise three molecules of ATP but the process of glycolysis itself requires energy (one molecule) The lactic acid system provides energy for high-intensity activities lasting up to 3 minutes but peaking at 1 minute, for example the 400m ...
... re-synthesise three molecules of ATP but the process of glycolysis itself requires energy (one molecule) The lactic acid system provides energy for high-intensity activities lasting up to 3 minutes but peaking at 1 minute, for example the 400m ...
NHM 555 - Pennington Biomedical Research Center
... glycolysis is shuttled to the mitochondria and further metabolized into carbon dioxide and water in a series of reactions. Although the aerobic pathway supplies ATP more slowly than does the anaerobic pathway, it releases more energy. ...
... glycolysis is shuttled to the mitochondria and further metabolized into carbon dioxide and water in a series of reactions. Although the aerobic pathway supplies ATP more slowly than does the anaerobic pathway, it releases more energy. ...
12_Lecture
... fatty acids funnel into and out of the citric acid cycle. • The citric acid cycle degrades two-carbon acetyl groups from acetyl CoA into CO2 and generates the high-energy molecules NADH and FADH2. • The initial reaction is a condensation reaction between acetyl CoA and the four-carbon molecule oxalo ...
... fatty acids funnel into and out of the citric acid cycle. • The citric acid cycle degrades two-carbon acetyl groups from acetyl CoA into CO2 and generates the high-energy molecules NADH and FADH2. • The initial reaction is a condensation reaction between acetyl CoA and the four-carbon molecule oxalo ...
Digestion Review Answer Key
... When your body has too much energy, or saturated fat, the liver tends to put fats into the LDL’s . When the body needs the energy from the fat, the liver tends to send it to the cells in ...
... When your body has too much energy, or saturated fat, the liver tends to put fats into the LDL’s . When the body needs the energy from the fat, the liver tends to send it to the cells in ...