12_Lecture
... fatty acids funnel into and out of the citric acid cycle. • The citric acid cycle degrades two-carbon acetyl groups from acetyl CoA into CO2 and generates the high-energy molecules NADH and FADH2. • The initial reaction is a condensation reaction between acetyl CoA and the four-carbon molecule oxalo ...
... fatty acids funnel into and out of the citric acid cycle. • The citric acid cycle degrades two-carbon acetyl groups from acetyl CoA into CO2 and generates the high-energy molecules NADH and FADH2. • The initial reaction is a condensation reaction between acetyl CoA and the four-carbon molecule oxalo ...
4. AMINO ACIDS
... because it reacts with the basic amino group to form zwitterions that are not decomposed completely at the end of alkaline indicators (phenolphthalein, thymolphtahalein). • But when formaldehyde is added to the solution of an amino acid it binds to the amino group as dimethylol and the amino acid ca ...
... because it reacts with the basic amino group to form zwitterions that are not decomposed completely at the end of alkaline indicators (phenolphthalein, thymolphtahalein). • But when formaldehyde is added to the solution of an amino acid it binds to the amino group as dimethylol and the amino acid ca ...
Answer Key for the Supplemental Problem Set #1
... 4 ADP molecules are converted into ATP. There is a net gain of only 2 ATP molecules because 2 are consumed during the first stage of glycolysis. 3. What are the three metabolically irreversible steps of glycolysis? What general type of reaction is catalyzed by these enzymes? Why are these reactions ...
... 4 ADP molecules are converted into ATP. There is a net gain of only 2 ATP molecules because 2 are consumed during the first stage of glycolysis. 3. What are the three metabolically irreversible steps of glycolysis? What general type of reaction is catalyzed by these enzymes? Why are these reactions ...
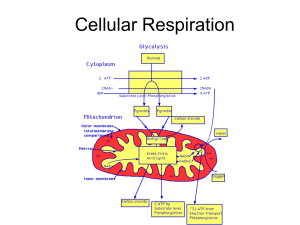
Cellular Respiration
... 7. The electrons from step 2 enter step 3 and make how many ATP? 8. From splitting 1 glucose how many total ATP are produced in cell respiration? 9. Anaerobic respiration is a type of cell respiration that requires no oxygen and only produces ___ ATP. 10. Alcoholic fermentation is used in ___ and la ...
... 7. The electrons from step 2 enter step 3 and make how many ATP? 8. From splitting 1 glucose how many total ATP are produced in cell respiration? 9. Anaerobic respiration is a type of cell respiration that requires no oxygen and only produces ___ ATP. 10. Alcoholic fermentation is used in ___ and la ...
Cellular respiration - how cells make energy
... now need to deal with all the NADH's (and an FADH2 or two) - We already discussed the basics of this - we use chemiosmosis. - several proteins are embedded in the inside membrane of mitochondria [OVERHEAD, fig. 6.10, p. 98 / 4th: 6.12, p. 100] - these proteins function in the electron transport chai ...
... now need to deal with all the NADH's (and an FADH2 or two) - We already discussed the basics of this - we use chemiosmosis. - several proteins are embedded in the inside membrane of mitochondria [OVERHEAD, fig. 6.10, p. 98 / 4th: 6.12, p. 100] - these proteins function in the electron transport chai ...
AP Biology - Richfield Public Schools
... electrons, protons and neutrons. Draw an electron shell diagram for each atom, label the valence electrons and identify how many bonds this atom can make. Using the structural formula draw a molecule of these atoms bonded together to complete their valence electrons. (Hint: you may have to use m ...
... electrons, protons and neutrons. Draw an electron shell diagram for each atom, label the valence electrons and identify how many bonds this atom can make. Using the structural formula draw a molecule of these atoms bonded together to complete their valence electrons. (Hint: you may have to use m ...
From Amino Acids to Proteins - in 4 Easy Steps
... A. Hydrophobic amino acids are buried in the interior of a globular protein. • Hydrophobic amino acids are composed primarily of carbon atoms, which cannot form hydrogen bonds with water. In order to form a hydrogen bond with water, a polar molecule, the amino acid side chains must also be polar, o ...
... A. Hydrophobic amino acids are buried in the interior of a globular protein. • Hydrophobic amino acids are composed primarily of carbon atoms, which cannot form hydrogen bonds with water. In order to form a hydrogen bond with water, a polar molecule, the amino acid side chains must also be polar, o ...
Aerobic vs. Anaerobic respiration
... down glucose when oxygen is absent. Produces CO2 and alcohol Live yeast: undergoing anaerobic fermentation Breaking down glucose to form 2ATP ...
... down glucose when oxygen is absent. Produces CO2 and alcohol Live yeast: undergoing anaerobic fermentation Breaking down glucose to form 2ATP ...
Mitochondria and energy production
... Mitochondrial b-oxidation of fatty acids Although peroxisomes contribute to the oxidation of fatty acids (particularly that of very-long-chain fatty acids), fatty acid oxidation mainly occurs within mitochondria. Unlike medium-chain or short-chain fatty acids, long-chain fatty acids cannot directly ...
... Mitochondrial b-oxidation of fatty acids Although peroxisomes contribute to the oxidation of fatty acids (particularly that of very-long-chain fatty acids), fatty acid oxidation mainly occurs within mitochondria. Unlike medium-chain or short-chain fatty acids, long-chain fatty acids cannot directly ...
Cellular Energy
... First step of photosynthesis that traps sunlight and makes electrons and ATP to run the dark reaction split and oxygen is released Water is _____ as a by product ...
... First step of photosynthesis that traps sunlight and makes electrons and ATP to run the dark reaction split and oxygen is released Water is _____ as a by product ...
Chapter 5 Notes (Biomolecules)
... 2. List the 3 different types of carbohydrates and give an example of each. 3. Which carbohydrate is found in plant cells? ...
... 2. List the 3 different types of carbohydrates and give an example of each. 3. Which carbohydrate is found in plant cells? ...
A Comparative Genomic Method for Computational
... Conservation of candidate DnaA binding sites across species is additional evidence of regulatory functionality If a regulator is conserved in several genomes ...
... Conservation of candidate DnaA binding sites across species is additional evidence of regulatory functionality If a regulator is conserved in several genomes ...
Amino acids and peptide bonds
... Here are some amino acids that are found in proteins, but are comparatively rare. They are not synthesized by ribosomal processes; most typically arise from post-translational modifications to the protein, which are catalyzed by specific enzymes. Common post-translational modifications include hydro ...
... Here are some amino acids that are found in proteins, but are comparatively rare. They are not synthesized by ribosomal processes; most typically arise from post-translational modifications to the protein, which are catalyzed by specific enzymes. Common post-translational modifications include hydro ...
Electron Transport Chain
... (including plant and animal cells) have mitochondria _______________ for cellular respiration Prokaryotes All __________________ (bacteria) have their electron transport enzymes attached to their Cell membranes _____________________ ...
... (including plant and animal cells) have mitochondria _______________ for cellular respiration Prokaryotes All __________________ (bacteria) have their electron transport enzymes attached to their Cell membranes _____________________ ...
Glucose Metabolism Glycolysis Expectations
... • Previous concepts: Redox and dehydrogenase • Pathway logic: Utilizes negative free energy of _____________ to drive nonspontaneous formation of ___________________ ...
... • Previous concepts: Redox and dehydrogenase • Pathway logic: Utilizes negative free energy of _____________ to drive nonspontaneous formation of ___________________ ...
Outline - Utexas
... 2. Acetyl-CoA enters the Krebs cycle a. glucose completely dismantled b. CO2 produced c. 2 ATP, 6 NADH and 2 FADH2 generated ...
... 2. Acetyl-CoA enters the Krebs cycle a. glucose completely dismantled b. CO2 produced c. 2 ATP, 6 NADH and 2 FADH2 generated ...
Name Date Period 1. What are the end products of aerobic cell
... Pyruvate joining with coenzyme A to produce CO2 and NADH + H+ ...
... Pyruvate joining with coenzyme A to produce CO2 and NADH + H+ ...
Chapter 20 TCA Cycle Bridging Reaction: Pyruvate → Acetyl-CoA
... • Mechanism involves two covalent intermediates with the enzyme: • Addition of pyruvate to TPP and loss of CO2 forms hydroxyethyl TPP. • (This same intermediate is formed by pyruvate decarboxylase in yeast alcoholic fermentation). ...
... • Mechanism involves two covalent intermediates with the enzyme: • Addition of pyruvate to TPP and loss of CO2 forms hydroxyethyl TPP. • (This same intermediate is formed by pyruvate decarboxylase in yeast alcoholic fermentation). ...
protein, glutathione, essential oils, energy, weight loss
... act to shape proteins or oxidize poisons and carcinogens such as pollutants, DDT and tobacco smoke, changing them into less toxic forms that the body can eliminate. The second category includes pancreatic digestive enzymes, of which there are about 22 in number. Secreted into the alkaline duodenum ...
... act to shape proteins or oxidize poisons and carcinogens such as pollutants, DDT and tobacco smoke, changing them into less toxic forms that the body can eliminate. The second category includes pancreatic digestive enzymes, of which there are about 22 in number. Secreted into the alkaline duodenum ...
Chapter 20 TCA Cycle Bridging Reaction: Pyruvate → Acetyl-CoA
... • Mechanism involves two covalent intermediates with the enzyme: • Addition of pyruvate to TPP and loss of CO2 forms hydroxyethyl TPP. • (This same intermediate is formed by pyruvate decarboxylase in yeast alcoholic fermentation). ...
... • Mechanism involves two covalent intermediates with the enzyme: • Addition of pyruvate to TPP and loss of CO2 forms hydroxyethyl TPP. • (This same intermediate is formed by pyruvate decarboxylase in yeast alcoholic fermentation). ...
Metabolic Patterns in Acetic Acid Bacteria
... For manometric work with suspensions of organisms, these were grown as described by Brown & Rainbow (1956)except that the glycophiles were grown on the same lactate-containingmedium as were the lactaphiles, in order to ensure as far as possible that differencesin the enzyme make-up of the organisms ...
... For manometric work with suspensions of organisms, these were grown as described by Brown & Rainbow (1956)except that the glycophiles were grown on the same lactate-containingmedium as were the lactaphiles, in order to ensure as far as possible that differencesin the enzyme make-up of the organisms ...
Bioelectrochemical Determination of Citric Acid in Real Samples
... better mixing with the sample solution. In the absence of TPP no response was observed while for concentrations higher than 0.8 mm TPP the response became constant; subsequent work used 1mM TPP. Several cations were examined as activators of POD. In addition to sensitivity, the criterion for the fin ...
... better mixing with the sample solution. In the absence of TPP no response was observed while for concentrations higher than 0.8 mm TPP the response became constant; subsequent work used 1mM TPP. Several cations were examined as activators of POD. In addition to sensitivity, the criterion for the fin ...