Amino Acid and Protein Structure
... The primary structure is the covalent "backbone" of the polypeptide formed by the specific amino acid sequence. 1. This sequence is coded for by DNA and determines the final three-dimensional form adopted by the protein in its native state. 2. By convention, peptide sequences are written from left t ...
... The primary structure is the covalent "backbone" of the polypeptide formed by the specific amino acid sequence. 1. This sequence is coded for by DNA and determines the final three-dimensional form adopted by the protein in its native state. 2. By convention, peptide sequences are written from left t ...
MC 2
... which is the ability of water molecules to rise up a narrow tube. Vascular plants, which include nearly all the plants important to animal life, depend on capillary action to lift water from the soil and roots to leaves, flowers, and fruits. 2. Coenzymes and cofactors do not act as enzymes by themse ...
... which is the ability of water molecules to rise up a narrow tube. Vascular plants, which include nearly all the plants important to animal life, depend on capillary action to lift water from the soil and roots to leaves, flowers, and fruits. 2. Coenzymes and cofactors do not act as enzymes by themse ...
APcarbonandmacromols2015 16
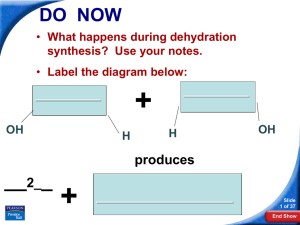
... 1. Is this a condensation or hydrolysis reaction? 2. What are the reactants? What are the products? 3. Is this an anabolic or catabolic reaction? 4. Is energy required or released? ...
... 1. Is this a condensation or hydrolysis reaction? 2. What are the reactants? What are the products? 3. Is this an anabolic or catabolic reaction? 4. Is energy required or released? ...
Megaloblastic Anemias
... atom situated in the middle of a corrin ring. It cannot be synthesized in the human body & must be taken in diet (only animal products) Daily req = 2.5 mg In stomach it is released from diet, then binds R protein (glycoprotein found in saliva, milk, gastric juice & bile). Cobalamin-R in duodenum is ...
... atom situated in the middle of a corrin ring. It cannot be synthesized in the human body & must be taken in diet (only animal products) Daily req = 2.5 mg In stomach it is released from diet, then binds R protein (glycoprotein found in saliva, milk, gastric juice & bile). Cobalamin-R in duodenum is ...
Cellular Respiration Packet
... (2) At end of the chain an enzyme combines electrons from the electron chain with H + ions and oxygen to form ______________ (3) Each time 2 high-energy electrons transport down the electron chain, their energy is used to transport ______________across the membrane (4) H+ ions build up in __________ ...
... (2) At end of the chain an enzyme combines electrons from the electron chain with H + ions and oxygen to form ______________ (3) Each time 2 high-energy electrons transport down the electron chain, their energy is used to transport ______________across the membrane (4) H+ ions build up in __________ ...
Ch - Paint Valley Local Schools
... The four macromolecules are proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids. 17. Which type of macromolecule do DNA and RNA belong to? They are nucleic acids. Know what each of these molecules function to do in the human body. DNA functions to provide one’s genetic code (instructions). RNA functi ...
... The four macromolecules are proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids. 17. Which type of macromolecule do DNA and RNA belong to? They are nucleic acids. Know what each of these molecules function to do in the human body. DNA functions to provide one’s genetic code (instructions). RNA functi ...
H - IS MU
... Fructose-1-P accumulates in the liver cells to such an extent that most of the inorganic phosphate is removed from the cytosol. Phosphate is needed for function of glycogen phosphorylase, oxidative phosphorylation is inhibited and hypoglycaemia also appears (Fru-1-P inhibits both glycolysis and gluc ...
... Fructose-1-P accumulates in the liver cells to such an extent that most of the inorganic phosphate is removed from the cytosol. Phosphate is needed for function of glycogen phosphorylase, oxidative phosphorylation is inhibited and hypoglycaemia also appears (Fru-1-P inhibits both glycolysis and gluc ...
AMINO ACID PROFILE
... mild flavor and digestibility. To be used in protein blends, energy shakes, energy and snack bars, and to enrich other food and bakery formulas. • As a stand-alone natural protein powder, ready to mix with water, juices or in bakery recipes. • In cosmetic applications as a texturizing i ...
... mild flavor and digestibility. To be used in protein blends, energy shakes, energy and snack bars, and to enrich other food and bakery formulas. • As a stand-alone natural protein powder, ready to mix with water, juices or in bakery recipes. • In cosmetic applications as a texturizing i ...
File
... Many lipids are formed from glycerol and a. fatty acids. b. monosaccharides. c. amino acids. ...
... Many lipids are formed from glycerol and a. fatty acids. b. monosaccharides. c. amino acids. ...
Physiology of metabolic processes in the body. Composition of diet
... These steps actually require energy, in the form of two ATPs per glucose. The fructose is then cleaved to yield two glyceraldehyde phosphates (GPs). Finally, two more ATPs are produced as the phosphoglycerates are oxidized to pyruvate. ...
... These steps actually require energy, in the form of two ATPs per glucose. The fructose is then cleaved to yield two glyceraldehyde phosphates (GPs). Finally, two more ATPs are produced as the phosphoglycerates are oxidized to pyruvate. ...
Glycolysis, Krebs Cycle, and other Energy
... Fats consist of a glycerol backbone with two or three fatty acids connected to it The body absorbs fats and then breaks off the fatty acids from the glycerol Glycerol is converted to glyceraldehyde phosphate, an intermediate of glycolysis The fatty acids are broken down into two-carbon units ...
... Fats consist of a glycerol backbone with two or three fatty acids connected to it The body absorbs fats and then breaks off the fatty acids from the glycerol Glycerol is converted to glyceraldehyde phosphate, an intermediate of glycolysis The fatty acids are broken down into two-carbon units ...
Lab Module 8: Phenol-Red Carbohydrate Fermentation Broths
... There are many different kinds of fermentable carbohydrates. Not all bacteria can ferment all of these carbs. The ability (or inability) of a particular species to ferment a particular carbohydrate depends on the presence (or absence) of an enzyme system to convert that carb to glucose (Step One, ab ...
... There are many different kinds of fermentable carbohydrates. Not all bacteria can ferment all of these carbs. The ability (or inability) of a particular species to ferment a particular carbohydrate depends on the presence (or absence) of an enzyme system to convert that carb to glucose (Step One, ab ...
Ch - Paint Valley Local Schools
... The four macromolecules are proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids. 17. Which type of macromolecule do DNA and RNA belong to? They are nucleic acids. Know what each of these molecules function to do in the human body. DNA functions to provide one’s genetic code (instructions). RNA functi ...
... The four macromolecules are proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids. 17. Which type of macromolecule do DNA and RNA belong to? They are nucleic acids. Know what each of these molecules function to do in the human body. DNA functions to provide one’s genetic code (instructions). RNA functi ...
Preview from Notesale.co.uk Page 3 of 6
... pigments but has no enzymes. Thus, it does not digest but emulsifies fats. The bile is released via the bile duct into the small intestine. The bile salts emulsify the salts, which mean that fats are broken down into tiny fats droplets suspended in water forming an emulsion, so that the surface a ...
... pigments but has no enzymes. Thus, it does not digest but emulsifies fats. The bile is released via the bile duct into the small intestine. The bile salts emulsify the salts, which mean that fats are broken down into tiny fats droplets suspended in water forming an emulsion, so that the surface a ...
File
... - huge organic molecs composed of smaller organic molecs - made up of smaller molecs called monomers - made via a process called polymerization • there are 4 groups of organic cmpds found in living things: (in no particular order) #1 carbs #2 lipids #3 nucleic acids #4 proteins ...
... - huge organic molecs composed of smaller organic molecs - made up of smaller molecs called monomers - made via a process called polymerization • there are 4 groups of organic cmpds found in living things: (in no particular order) #1 carbs #2 lipids #3 nucleic acids #4 proteins ...
univERsity oF copEnhAGEn
... are partly used as substrates for energy production when there is reduced pyruvate availability due to hypercapnia. It is proposed that amino acid carbon is made available for oxidation via transamination (aspartate aminotransferase reaction) and deamination (glutamate dehydrogenase reaction) and th ...
... are partly used as substrates for energy production when there is reduced pyruvate availability due to hypercapnia. It is proposed that amino acid carbon is made available for oxidation via transamination (aspartate aminotransferase reaction) and deamination (glutamate dehydrogenase reaction) and th ...
Carbohydrate metabolism
... "protein phsophatase-1", which in turn is inhibited by c-AMP dependant protein kinase via the protein "Inhibitor-1". Thus, glycogenolysis can be ...
... "protein phsophatase-1", which in turn is inhibited by c-AMP dependant protein kinase via the protein "Inhibitor-1". Thus, glycogenolysis can be ...
9/2/08 Transcript I - UAB School of Optometry
... Utilized in "Fight or Flight"- If confronted by a lion then you will fight or flee and use this type of process because it does not require any set up time or oxygen. There are 10 rxns which are the same in all cells, but may not happen at same rate. 2 Phases: 1. Converts glucose to two Glycer ...
... Utilized in "Fight or Flight"- If confronted by a lion then you will fight or flee and use this type of process because it does not require any set up time or oxygen. There are 10 rxns which are the same in all cells, but may not happen at same rate. 2 Phases: 1. Converts glucose to two Glycer ...
basic biochemistry - Personal Webspace for QMUL
... These are at the two positions where ATP is formed 1: The 1,3-Bisphosphoglycerate to 3-Phosphoglycerate The 1,3-BPG passes a phosphate to ADP This is known as substrate-level phosphorylation ...
... These are at the two positions where ATP is formed 1: The 1,3-Bisphosphoglycerate to 3-Phosphoglycerate The 1,3-BPG passes a phosphate to ADP This is known as substrate-level phosphorylation ...