RESPIRATION Metabolic processes that need energy include
... converted to glucose, and respired. Fatty acids cannot be respired. Fatty acids = long-chain hydrocarbons with a carboxylic acid group. In each molecule there is carbons and hydrogen atoms – source of many protons for oxidative phosphorylation so they produce a lot of ATP: Each fatty acid is c ...
... converted to glucose, and respired. Fatty acids cannot be respired. Fatty acids = long-chain hydrocarbons with a carboxylic acid group. In each molecule there is carbons and hydrogen atoms – source of many protons for oxidative phosphorylation so they produce a lot of ATP: Each fatty acid is c ...
2106lecture 2b powerpoint
... -lipases -proteases -carbohydrases -absorption which ultimately leads to transport within the bodysignificance for metabolism? -ileocecal valve-controls dumping into colon ...
... -lipases -proteases -carbohydrases -absorption which ultimately leads to transport within the bodysignificance for metabolism? -ileocecal valve-controls dumping into colon ...
BioH_Cellular Respiration
... Upon entering the mitochondria, the pyruvates formed during glycolysis are modified to make them more reactive to participate in the Krebs Cycle. The modifications include: a) Carbon atoms are removed from the 2 pyruvic acid molecules & given off as 2CO 2. b) The remaining 2-carbon fragment is oxidi ...
... Upon entering the mitochondria, the pyruvates formed during glycolysis are modified to make them more reactive to participate in the Krebs Cycle. The modifications include: a) Carbon atoms are removed from the 2 pyruvic acid molecules & given off as 2CO 2. b) The remaining 2-carbon fragment is oxidi ...
Analysis of Whole-Body Branched-Chain Amino Acid Metabolism in
... Utilizing a custom-designed 20% leucine 13C6 and 20% valine 13C5 mouse feed diet, we specifically labeled short- or long-term sources of plasma BCAAs in mice. These approaches also relied on the unique status of BCAAs as the only amino acids whose plasma levels are not regulated by the liver (Brosna ...
... Utilizing a custom-designed 20% leucine 13C6 and 20% valine 13C5 mouse feed diet, we specifically labeled short- or long-term sources of plasma BCAAs in mice. These approaches also relied on the unique status of BCAAs as the only amino acids whose plasma levels are not regulated by the liver (Brosna ...
Glycolysis & Fermentation
... across membrane to Mitochondrial matrix & forms Acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl CoA) ...
... across membrane to Mitochondrial matrix & forms Acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl CoA) ...
Chlorophyll – Protein complex + H* _ OH – (Ground state)
... exported from cells, most probably by facilitated diffusion and subsequently taken up by the phloem complex by a specific sucrose/H+ co transport mechanism Once in the phloem complex sucrose is transported to cells in heterotrophic “sink“ tissues. At least two distinct classes of sink tissues can be ...
... exported from cells, most probably by facilitated diffusion and subsequently taken up by the phloem complex by a specific sucrose/H+ co transport mechanism Once in the phloem complex sucrose is transported to cells in heterotrophic “sink“ tissues. At least two distinct classes of sink tissues can be ...
Cell Respiration Key
... 2. Fermentation enables cells to make ATP in the absence of Oxygen. 3. For every molecule of glucose consumed, glycolysis produces 2 pyruvate, 2 ATP and NADH. 4. The products of alcoholic fermentation are alcohol and CO2. ...
... 2. Fermentation enables cells to make ATP in the absence of Oxygen. 3. For every molecule of glucose consumed, glycolysis produces 2 pyruvate, 2 ATP and NADH. 4. The products of alcoholic fermentation are alcohol and CO2. ...
BS3050 Physiology of Sport and Exercise
... Glycogen depletion is generally accepted as a major cause of fatigue although this may take as long as 2 hours or more while exercising at high intensity for a prolonged period. Glycogen stores will therefore last just about the time it takes to complete a marathon Hypoglycaemia - the body generally ...
... Glycogen depletion is generally accepted as a major cause of fatigue although this may take as long as 2 hours or more while exercising at high intensity for a prolonged period. Glycogen stores will therefore last just about the time it takes to complete a marathon Hypoglycaemia - the body generally ...
Chapter 5- Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules
... Animals store a polysaccharide called glycogen, a polymer of glucose that is like amylopectin but more extensively ' branched (Figure 5.6b). Humans and other vertebrates store glycogen mainly in liver and muscle cells. Hydrolysis of glycogen in these cells releases glucose when the demand for sugar ...
... Animals store a polysaccharide called glycogen, a polymer of glucose that is like amylopectin but more extensively ' branched (Figure 5.6b). Humans and other vertebrates store glycogen mainly in liver and muscle cells. Hydrolysis of glycogen in these cells releases glucose when the demand for sugar ...
Cellular Respiration
... People say you can’t live without love, but I say oxygen is more important. ...
... People say you can’t live without love, but I say oxygen is more important. ...
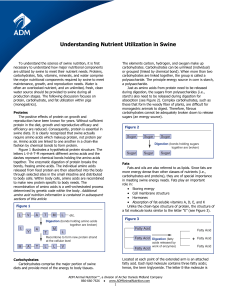
Nutrient Utilization in Swine
... When compared to carbohydrates and fats, the use of amino acids as an energy source is expensive. Not only is it economically inefficient, but biologically inefficient as well. To understand the inefficiency of using amino acids as an energy source, it is first important to examine the general struc ...
... When compared to carbohydrates and fats, the use of amino acids as an energy source is expensive. Not only is it economically inefficient, but biologically inefficient as well. To understand the inefficiency of using amino acids as an energy source, it is first important to examine the general struc ...
05 Cell Respiration Fermentation Anaerobic and
... • All use glycolysis (net ATP = 2) to oxidize glucose and harvest chemical energy of food • In all three, NAD+ is the oxidizing agent that accepts electrons during glycolysis • The processes have different final electron acceptors: an organic molecule (such as pyruvate or acetaldehyde) in fermentati ...
... • All use glycolysis (net ATP = 2) to oxidize glucose and harvest chemical energy of food • In all three, NAD+ is the oxidizing agent that accepts electrons during glycolysis • The processes have different final electron acceptors: an organic molecule (such as pyruvate or acetaldehyde) in fermentati ...
Generation of Virtual Amino Acid Libraries for Multiple Applications
... amino acid’s side chains as partially ordered set. This order can be used to describe the set of molecular formulas defined by a fuzzy formula. For instance the fuzzy formula C2−11H5−14N1−4O2−4S includes all molecular formulas f that fulfill the inclusions C2H5NO2 ≤ f ≤ C11H14N4O4S. ...
... amino acid’s side chains as partially ordered set. This order can be used to describe the set of molecular formulas defined by a fuzzy formula. For instance the fuzzy formula C2−11H5−14N1−4O2−4S includes all molecular formulas f that fulfill the inclusions C2H5NO2 ≤ f ≤ C11H14N4O4S. ...
Cancer-causing-Foods-MJ
... • "healthy" cells mainly generate energy from oxidative breakdown of pyruvate which is an end-product of glycolysis, and is oxidized within the mitochondria • In contrast, cancer cells show signs of glycolysis, (the process of sugar breakdown) with lactate secretion even in the presence of oxygen • ...
... • "healthy" cells mainly generate energy from oxidative breakdown of pyruvate which is an end-product of glycolysis, and is oxidized within the mitochondria • In contrast, cancer cells show signs of glycolysis, (the process of sugar breakdown) with lactate secretion even in the presence of oxygen • ...
Digestive System
... Fat molecules can be difficult to break down because large fat droplets do not mix well with water-based enzymes such as lipase. For lipase to work, it helps if the fat is emulsified into tiny droplets. This is done with the help of bile, which is stored in the gallbladder. 5. Observe: Now look at t ...
... Fat molecules can be difficult to break down because large fat droplets do not mix well with water-based enzymes such as lipase. For lipase to work, it helps if the fat is emulsified into tiny droplets. This is done with the help of bile, which is stored in the gallbladder. 5. Observe: Now look at t ...
Chapter 18 Metabolic Pathways and Energy Production
... Reaction 5 Isomerization Because dihydroxyacetone phosphate is a ketone, it cannot react further. It undergoes isomerization to provide a second molecule of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate, which can be oxidized. Now all six-carbon atoms from glucose are contained in two identical triose phosphates. ...
... Reaction 5 Isomerization Because dihydroxyacetone phosphate is a ketone, it cannot react further. It undergoes isomerization to provide a second molecule of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate, which can be oxidized. Now all six-carbon atoms from glucose are contained in two identical triose phosphates. ...
metabolism of amino acids
... • Negative nitrogen balance – output exceeds intakeduring surgery, advanced cancer or malnutrition ...
... • Negative nitrogen balance – output exceeds intakeduring surgery, advanced cancer or malnutrition ...
PROTEIN METABOLISM
... but many liver enzymes turn over in a couple of days. Some regulatory enzymes have half-lives measured in hours or minutes. The majority of the amino acids released during protein degradation are promptly reincorporated into fresh proteins. ...
... but many liver enzymes turn over in a couple of days. Some regulatory enzymes have half-lives measured in hours or minutes. The majority of the amino acids released during protein degradation are promptly reincorporated into fresh proteins. ...