28.1 Digestion of Protein
... because the volume of water needed to accomplish this safely would cause dehydration. Mammals must first convert ammonia, in solution as ammonium ion, to nontoxic urea via the urea cycle. • Urea formation begins with an energy investment, Ammonium ion, bicarbonate ion, and ATP combine to form ...
... because the volume of water needed to accomplish this safely would cause dehydration. Mammals must first convert ammonia, in solution as ammonium ion, to nontoxic urea via the urea cycle. • Urea formation begins with an energy investment, Ammonium ion, bicarbonate ion, and ATP combine to form ...
Methods of industrial production
... oxygen, the production of L‐glutamate oxygen, the production of L glutamate is poor and lactic acid as well as succinic is poor and lactic acid as well as succinic acid accumulates, whereas with an excess oxygen supply the amount of α‐ ketoglutarate as a by‐product accumulates. ...
... oxygen, the production of L‐glutamate oxygen, the production of L glutamate is poor and lactic acid as well as succinic is poor and lactic acid as well as succinic acid accumulates, whereas with an excess oxygen supply the amount of α‐ ketoglutarate as a by‐product accumulates. ...
Seminario Glúcidos 3 y lípidos 1. Comente los mecanismos de
... of mitochondria which had been sedimented once in 10 volumes of 0.88 M sucrose as described above, and subjecting the suspension at this point to two or three preliminary sedimentations at low speed (2000 X g), each of 5 minutes duration. The main bulk of the mitochondria, now freed of red blood cel ...
... of mitochondria which had been sedimented once in 10 volumes of 0.88 M sucrose as described above, and subjecting the suspension at this point to two or three preliminary sedimentations at low speed (2000 X g), each of 5 minutes duration. The main bulk of the mitochondria, now freed of red blood cel ...
AMINO ACIDS IN THE ASTEROIDAL WATER - USRA
... chondrites suggests that amino acids may be formed through Fischer-Tropsch type (FTT) gas-grain reactions after the meteorite parent body cooled to lower temperatures. β-alanine, which is a n-ω-amino acid [9], is also one of the most abundant amino acids in Zag, and its presence is consistent with i ...
... chondrites suggests that amino acids may be formed through Fischer-Tropsch type (FTT) gas-grain reactions after the meteorite parent body cooled to lower temperatures. β-alanine, which is a n-ω-amino acid [9], is also one of the most abundant amino acids in Zag, and its presence is consistent with i ...
Essentials of Medical Biochemistry. Edition No. 2 Brochure
... biochemistry, emphasizing relevant physiologic and pathophysiologic biochemical concepts. Pivotal clinical case studies aid in understanding basic science in the context of diagnosis and treatment of human diseases, and the text illuminates key topics in molecular immunology and hemostasis. Users wi ...
... biochemistry, emphasizing relevant physiologic and pathophysiologic biochemical concepts. Pivotal clinical case studies aid in understanding basic science in the context of diagnosis and treatment of human diseases, and the text illuminates key topics in molecular immunology and hemostasis. Users wi ...
CLN Carbohydrat es part3
... synthesized from tissue by glycogenolysis. Glycogensis: process if glycogen is converted back to glucose-6-phosphate for entry into glycolytic path. 2 major hormones involved: Insulin and glucagon; these hormones allow the body to respond on as needed bases. ...
... synthesized from tissue by glycogenolysis. Glycogensis: process if glycogen is converted back to glucose-6-phosphate for entry into glycolytic path. 2 major hormones involved: Insulin and glucagon; these hormones allow the body to respond on as needed bases. ...
Chapter 23 Digestive System
... – To be absorbed, fats must be broken down into fatty acids and glycerol. – Fats are digested by enzymes called lipases. Fats are first emulsified by bile. ...
... – To be absorbed, fats must be broken down into fatty acids and glycerol. – Fats are digested by enzymes called lipases. Fats are first emulsified by bile. ...
Oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate
... Only about 7 % of the total potential energy present in glucose is released in glycolysis. ...
... Only about 7 % of the total potential energy present in glucose is released in glycolysis. ...
Lesson (1) Chemical structure of living organisms` bodies
... organisms which consist from hydrogen and carbon basically (such as carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids). Carbohydrates: They are biological macromolecules formed from simple molecules (monosaccharides) which include starches, sugars and fibres. They consist of carbon, hydrogen and oxy ...
... organisms which consist from hydrogen and carbon basically (such as carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids). Carbohydrates: They are biological macromolecules formed from simple molecules (monosaccharides) which include starches, sugars and fibres. They consist of carbon, hydrogen and oxy ...
Cholesterol And Sterol Metabolism
... Glucagon stimulates adenyl cyclase producing cAMP cAMP activates protein kinase A Inactivates HMG-CoA reductase ...
... Glucagon stimulates adenyl cyclase producing cAMP cAMP activates protein kinase A Inactivates HMG-CoA reductase ...
Lesson (1) Chemical structure of living organisms` bodies
... organisms which consist from hydrogen and carbon basically (such as carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids). Carbohydrates: They are biological macromolecules formed from simple molecules (monosaccharides) which include starches, sugars and fibres. They consist of carbon, hydrogen and oxy ...
... organisms which consist from hydrogen and carbon basically (such as carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids). Carbohydrates: They are biological macromolecules formed from simple molecules (monosaccharides) which include starches, sugars and fibres. They consist of carbon, hydrogen and oxy ...
Review Report
... of life debate because they provide non-solar energy sources like hydrogen and carbon monoxide, which along with proton gradients could have been essential for life at its beginnings. Page 3, Lines 93–94: “Binding of these … was unlikely to provide … derived peptides”. Why not? Please elaborate. Res ...
... of life debate because they provide non-solar energy sources like hydrogen and carbon monoxide, which along with proton gradients could have been essential for life at its beginnings. Page 3, Lines 93–94: “Binding of these … was unlikely to provide … derived peptides”. Why not? Please elaborate. Res ...
Specialty Chemicals and Food Additives
... greater expenditure of energy than does that of any other amino acid (l). The yield of tryptophan from a given carbon source, therefore, will be lower than the yield for other amino acids. The yield of product from glucose is an important factor in determining production cost in a bioprocess. Inform ...
... greater expenditure of energy than does that of any other amino acid (l). The yield of tryptophan from a given carbon source, therefore, will be lower than the yield for other amino acids. The yield of product from glucose is an important factor in determining production cost in a bioprocess. Inform ...
Lecture 21
... Isozymes: Enzymes that catalyze the same reaction but are different in their kinetic behavior Tissue specific Glucokinase- Liver controls blood glucose levels. Hexokinase in muscle - allosteric inhibition by ATP Hexokinase in brain - NO allosteric inhibition by ATP ...
... Isozymes: Enzymes that catalyze the same reaction but are different in their kinetic behavior Tissue specific Glucokinase- Liver controls blood glucose levels. Hexokinase in muscle - allosteric inhibition by ATP Hexokinase in brain - NO allosteric inhibition by ATP ...
Aerobic respiration - Wesleyan
... Glycerol products enter glycolysis Fatty acids are converted to acetyl Co-A and enter the Krebs cycle ...
... Glycerol products enter glycolysis Fatty acids are converted to acetyl Co-A and enter the Krebs cycle ...
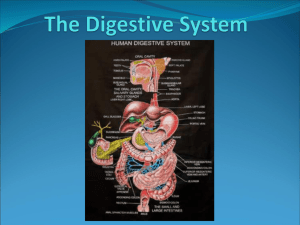
The Digestive System
... the packaged fats are absorbed into the lacteals in the interior of the villi, and are transported through the ...
... the packaged fats are absorbed into the lacteals in the interior of the villi, and are transported through the ...
Learning Outcome I: The Digestive System
... mitochondria because active transport is often required for absorption. • The ‘lumen’ of the villi is the ECF between the villi cells and the capillaries/lacteals. • The villi cells also produce three enzymes and release them into their lumen just prior to absorption in order to complete digestion. ...
... mitochondria because active transport is often required for absorption. • The ‘lumen’ of the villi is the ECF between the villi cells and the capillaries/lacteals. • The villi cells also produce three enzymes and release them into their lumen just prior to absorption in order to complete digestion. ...
Chemical Biology - Chem 370 (3 credits)
... b. Connecting sugars by an ethers linkage at the hemiketal carbon to form disacharides. c. More complex carbohydrate polymers: energy storage and altered protein function 9. Lipids and Membranes a. Review of carboxylic acids, aliphatic chains, and esters. b. Stereochemistry of carbon-carbon double b ...
... b. Connecting sugars by an ethers linkage at the hemiketal carbon to form disacharides. c. More complex carbohydrate polymers: energy storage and altered protein function 9. Lipids and Membranes a. Review of carboxylic acids, aliphatic chains, and esters. b. Stereochemistry of carbon-carbon double b ...
Document
... Chemical properties of monosaccharides Reductive properties –only when free aldehyde or ketone group in saccharide molecule is present. In alkaline environment saccharides have reductive properties and ring can be opened In acidic environment saccharides are in cyclic form and there is no =CO gro ...
... Chemical properties of monosaccharides Reductive properties –only when free aldehyde or ketone group in saccharide molecule is present. In alkaline environment saccharides have reductive properties and ring can be opened In acidic environment saccharides are in cyclic form and there is no =CO gro ...