I. ATP is Universal
... e) Phosphate groups are added to the C3 molecules. f) This stimulates the synthesis of ATP via substrate level ATP synthesis. An enzyme passes a high-energy phosphate to ADP. This is an example of the coupling of an energy-releasing reaction to an energy-requiring one. g) Oxidation of the resultant ...
... e) Phosphate groups are added to the C3 molecules. f) This stimulates the synthesis of ATP via substrate level ATP synthesis. An enzyme passes a high-energy phosphate to ADP. This is an example of the coupling of an energy-releasing reaction to an energy-requiring one. g) Oxidation of the resultant ...
Teacher shi 18940209087 Email: QQ
... (B) A total of six high-energy phosphate bonds are cleaved during production of one molecule of urea (C) N-acetylglutamate is a positive allosteric effector of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I (D) The enzyme arginase releases fumarate from argininosuccinate (E) Glutamine is the substrate that direct ...
... (B) A total of six high-energy phosphate bonds are cleaved during production of one molecule of urea (C) N-acetylglutamate is a positive allosteric effector of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I (D) The enzyme arginase releases fumarate from argininosuccinate (E) Glutamine is the substrate that direct ...
Ch. 9 - Crestwood Local Schools
... use these as energy sources as well! Proteins first broken down into AA’s Amino group (containing N) is removed from each AA by deamination Converts ...
... use these as energy sources as well! Proteins first broken down into AA’s Amino group (containing N) is removed from each AA by deamination Converts ...
Biosynthesis of Amino Acids
... In bacteria ammonia is the nitrogen source for this reaction. In mammals the nitrogen source for this reaction is derived from the hydolysis of glutamine into glutamate. The ammonia produced in this reaction is channeled to the aspartyl-adenylate intermediate to from asparagine. ...
... In bacteria ammonia is the nitrogen source for this reaction. In mammals the nitrogen source for this reaction is derived from the hydolysis of glutamine into glutamate. The ammonia produced in this reaction is channeled to the aspartyl-adenylate intermediate to from asparagine. ...
PowerPoint 簡報
... tissues and in other organisms that carry out lactic acid fermentation. Acetaldehyde is the product of this reaction. ...
... tissues and in other organisms that carry out lactic acid fermentation. Acetaldehyde is the product of this reaction. ...
Transcriptome analysis reveals unique C4
... These findings provided a molecular basis for the research and possibly economic exploitation of this ArA-rich microalga. Keywords: Myrmecia incisa Reisigl H4301, 454 Pyrosequencing, C4-Like photosynthesis, Arachidonic acid, Microalga, Lipid metabolism, Oil body, Carotenoids ...
... These findings provided a molecular basis for the research and possibly economic exploitation of this ArA-rich microalga. Keywords: Myrmecia incisa Reisigl H4301, 454 Pyrosequencing, C4-Like photosynthesis, Arachidonic acid, Microalga, Lipid metabolism, Oil body, Carotenoids ...
Respiration
... 2. Where in the cell does glycolysis occur? 3. What are the reactants and products of glycolysis? 4. Which has more energy available: a. ADP or ATP? b. NAD+ or NADH? c. FAD+ or FADH2? ...
... 2. Where in the cell does glycolysis occur? 3. What are the reactants and products of glycolysis? 4. Which has more energy available: a. ADP or ATP? b. NAD+ or NADH? c. FAD+ or FADH2? ...
Albumin from bovine serum (A4919) - Product - Sigma
... 40 mg/mL and obtains clear to very slightly hazy, faint yellow solutions. The solution stability of BSA is very good (especially if the solutions are stored as frozen aliquots). In fact, albumins are frequently used as stabilizers for other solubilized proteins (e.g., labile enzymes). However, album ...
... 40 mg/mL and obtains clear to very slightly hazy, faint yellow solutions. The solution stability of BSA is very good (especially if the solutions are stored as frozen aliquots). In fact, albumins are frequently used as stabilizers for other solubilized proteins (e.g., labile enzymes). However, album ...
7.2 Glycolysis
... Glycolysis is the first stage of cellular respiration Glycolysis occurs with or without oxygen (during both aerobic and anaerobic respiration) Glycolysis takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell During glycolysis glucose is split in two to form 2 pyruvate molecules ...
... Glycolysis is the first stage of cellular respiration Glycolysis occurs with or without oxygen (during both aerobic and anaerobic respiration) Glycolysis takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell During glycolysis glucose is split in two to form 2 pyruvate molecules ...
Renal tubular reabsorption
... remains similar to that of plasma) • 65% of water and solute reabsorption occurs in the proximal tubule • 90% of bicarbonate • 99% of glucose & amino acids ...
... remains similar to that of plasma) • 65% of water and solute reabsorption occurs in the proximal tubule • 90% of bicarbonate • 99% of glucose & amino acids ...
amino acid
... Defense. А wide variety of proteins have а protective role. Examples found in vertebrates include keratin, the protein found in skin cells that aids in protecting the organism against mechanical and chemical injury. The blood-clotting proteins fibrinogen and thrombin prevent blood loss when blood ve ...
... Defense. А wide variety of proteins have а protective role. Examples found in vertebrates include keratin, the protein found in skin cells that aids in protecting the organism against mechanical and chemical injury. The blood-clotting proteins fibrinogen and thrombin prevent blood loss when blood ve ...
Part a
... Each pyruvic acid is converted to acetyl CoA 1. Decarboxylation: removal of 1 C to produce acetic acid and CO2 2. Oxidation: H+ is removed from acetic acid and picked up by NAD+ 3. Acetic acid + coenzyme A forms acetyl CoA ...
... Each pyruvic acid is converted to acetyl CoA 1. Decarboxylation: removal of 1 C to produce acetic acid and CO2 2. Oxidation: H+ is removed from acetic acid and picked up by NAD+ 3. Acetic acid + coenzyme A forms acetyl CoA ...
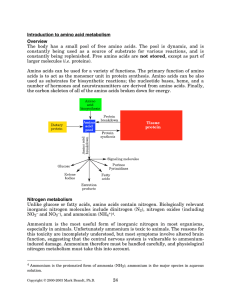
Introduction to amino acid metabolism Overview - Rose
... process of attaching ammonium ions to carbon compounds. The reactions used for this purpose are discussed below. Unlike plants, animals use organic nitrogen derived from their diet for essentially all of their nitrogen requirements. Animals require nitrogen in reduced form and release most nitrogen ...
... process of attaching ammonium ions to carbon compounds. The reactions used for this purpose are discussed below. Unlike plants, animals use organic nitrogen derived from their diet for essentially all of their nitrogen requirements. Animals require nitrogen in reduced form and release most nitrogen ...
CERTIFICATE OF HIGHER EDUCATION IN COSMETIC SCIENCE
... stabilise the colloidal dispersion. Give two examples of how this could be achieved. ( 6 Marks) d) Linear block copolymers (surfactants) comprised of alternating hydrophobic and hydrophilic groups are often used to stabilise the dispersion. Describe how the polymer can adsorb onto the surface of the ...
... stabilise the colloidal dispersion. Give two examples of how this could be achieved. ( 6 Marks) d) Linear block copolymers (surfactants) comprised of alternating hydrophobic and hydrophilic groups are often used to stabilise the dispersion. Describe how the polymer can adsorb onto the surface of the ...
126 EFFECT OF ULTRAVIOLET-B IRRADIATION ON FATTY ACIDS
... decrease in PUFA (polyunsaturated fatty acids) upon UVR (e.g. Wang & Chai, 1994), two papers reported no significant differences in the fatty acid profile between UVBR treatments and the control (Skerratt et al., 1998), and other reported an increase in UFA after UVR exposure (Gupta et al., 2008). R ...
... decrease in PUFA (polyunsaturated fatty acids) upon UVR (e.g. Wang & Chai, 1994), two papers reported no significant differences in the fatty acid profile between UVBR treatments and the control (Skerratt et al., 1998), and other reported an increase in UFA after UVR exposure (Gupta et al., 2008). R ...
1495/Chapter 03
... are the sites where ATP synthesis occurs. More mitochondria are found in cells that require more energy, such as muscle and liver cells. The two mitochondrial membranes have important differences in their biochemical composition. The outer membrane contains a transport protein called porin that make ...
... are the sites where ATP synthesis occurs. More mitochondria are found in cells that require more energy, such as muscle and liver cells. The two mitochondrial membranes have important differences in their biochemical composition. The outer membrane contains a transport protein called porin that make ...
Gastrointestinal Secretions
... cholesterol-derived “core” in yellow. (b) A space-filling model of a bile salt. The non-polar surface helps emulsify fats, The polar surface promotes water solubility. ...
... cholesterol-derived “core” in yellow. (b) A space-filling model of a bile salt. The non-polar surface helps emulsify fats, The polar surface promotes water solubility. ...
Metabolic Pathways and Energy Production
... B. In humans, there is no β (1-4) glucosidase that can digest such bonds. So cellulose passes as such in stool. C. Cellulose helps water retention during the passage of food along the intestine producing larger and softer feces ...
... B. In humans, there is no β (1-4) glucosidase that can digest such bonds. So cellulose passes as such in stool. C. Cellulose helps water retention during the passage of food along the intestine producing larger and softer feces ...
Cellular Respiration
... - Kinases transfer phosphate groups from one molecule to another (whether it be a phosphate group from ATP or from FBP) - Substrate-level phosphorylation uses enzymes (like kinases) to phosphorylate molecules. The source of phosphate groups can be from ATP or FBP. In cellular respiration, Kinase ...
... - Kinases transfer phosphate groups from one molecule to another (whether it be a phosphate group from ATP or from FBP) - Substrate-level phosphorylation uses enzymes (like kinases) to phosphorylate molecules. The source of phosphate groups can be from ATP or FBP. In cellular respiration, Kinase ...
幻灯片 1
... cholesterol-derived “core” in yellow. (b) A space-filling model of a bile salt. The non-polar surface helps emulsify fats, The polar surface promotes water solubility. ...
... cholesterol-derived “core” in yellow. (b) A space-filling model of a bile salt. The non-polar surface helps emulsify fats, The polar surface promotes water solubility. ...
Alcoholic fermentation
... The fate of the pyruvate depends on …………………… availability. In the absence of oxygen, alcoholic fermentation or lactic fermentation takes place. 2 x PYRUVATE (….C) ...
... The fate of the pyruvate depends on …………………… availability. In the absence of oxygen, alcoholic fermentation or lactic fermentation takes place. 2 x PYRUVATE (….C) ...
The molecules of life - Breakthrough Science Society
... endless diversity of the protein molecules is the basis of the chemistry of life. Such variations have made it possible to evolve different protein molecules for different activities of our body. Moreover, there is obviously no limit to the generation of new variety every day. The function of differ ...
... endless diversity of the protein molecules is the basis of the chemistry of life. Such variations have made it possible to evolve different protein molecules for different activities of our body. Moreover, there is obviously no limit to the generation of new variety every day. The function of differ ...