BIOCHEMISTRY Carbohydrate Metabolism
... • The glucose unit of UDP-glucose is attached to the end of a glycogen chain & UDP is produced, which reacts with ATP to reform UTP. • Adding 1 glucose to a growing glycogen chain requires the investment of 2 ATP – 1ATP to form Glucose 6-phosphate & 1ATP to regenerate UTP. • Catalyzed by Glycogen sy ...
... • The glucose unit of UDP-glucose is attached to the end of a glycogen chain & UDP is produced, which reacts with ATP to reform UTP. • Adding 1 glucose to a growing glycogen chain requires the investment of 2 ATP – 1ATP to form Glucose 6-phosphate & 1ATP to regenerate UTP. • Catalyzed by Glycogen sy ...
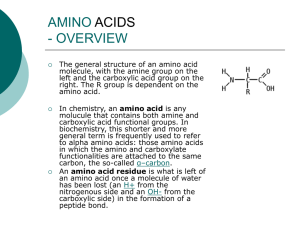
amino acids - UniMAP Portal
... least two others are also coded by DNA in a nonstandard manner as follows: Selenocysteine is incorporated into some proteins at a UGA codon, which is normally a stop codon. Pyrrolysine is used by some methanogens in enzymes that they use to produce methane. It is coded for similarly to selenocystein ...
... least two others are also coded by DNA in a nonstandard manner as follows: Selenocysteine is incorporated into some proteins at a UGA codon, which is normally a stop codon. Pyrrolysine is used by some methanogens in enzymes that they use to produce methane. It is coded for similarly to selenocystein ...
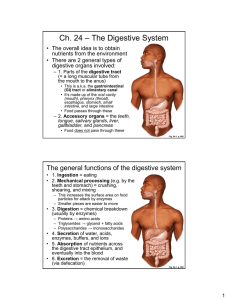
Ch. 24 – The Digestive System
... mucus (to protect the stomach’s epithelium from the HCl) – G cells secrete gastrin (a hormone), which: • ↑ Stomach motility • ↑ The secretion of gastric juice Fig. 24-13b, p. 899 ...
... mucus (to protect the stomach’s epithelium from the HCl) – G cells secrete gastrin (a hormone), which: • ↑ Stomach motility • ↑ The secretion of gastric juice Fig. 24-13b, p. 899 ...
Digestion - Part Two
... from the acid. If the mucus were not present, the hydrochloric acid would actually digest the tissue that ...
... from the acid. If the mucus were not present, the hydrochloric acid would actually digest the tissue that ...
BIOMOLECULES
... disturbed, globules unfold and helix gets uncoiled therefore protein loses its biological activity. This is called denaturation of proteins. ...
... disturbed, globules unfold and helix gets uncoiled therefore protein loses its biological activity. This is called denaturation of proteins. ...
Cellular Respiration
... Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) the short-term energy store of all cells easily transported and is therefore the universal energy carrier formed from the nucleotide adenosine monophosphate by the addition of two further phosphate molecules a metabolically active cell may require up to 2 million AT ...
... Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) the short-term energy store of all cells easily transported and is therefore the universal energy carrier formed from the nucleotide adenosine monophosphate by the addition of two further phosphate molecules a metabolically active cell may require up to 2 million AT ...
Cell Respiration
... increase the surface area for the electron transport chain and oxidative phosphorylation. Fluid matrix – contains enzymes for link reaction and Kreb’s cycle. Intermembrane space – the space between inner and outer membranes is small to allow for accumulation of protons for chemiosmosis. ...
... increase the surface area for the electron transport chain and oxidative phosphorylation. Fluid matrix – contains enzymes for link reaction and Kreb’s cycle. Intermembrane space – the space between inner and outer membranes is small to allow for accumulation of protons for chemiosmosis. ...
Chapter 9 from Mrs Chou
... Pyruvate Ethanol + CO2 Pyruvate Lactate Ex. bacteria, yeast Ex. fungi, bacteria, human Used in brewing, muscle cells winemaking, baking Used to make cheese, yogurt, acetone, methanol Note: Lactate build-up does NOT causes muscle fatigue and pain (old idea) ...
... Pyruvate Ethanol + CO2 Pyruvate Lactate Ex. bacteria, yeast Ex. fungi, bacteria, human Used in brewing, muscle cells winemaking, baking Used to make cheese, yogurt, acetone, methanol Note: Lactate build-up does NOT causes muscle fatigue and pain (old idea) ...
Warm-Up
... Pyruvate Ethanol + CO2 Pyruvate Lactate Ex. bacteria, yeast Ex. fungi, bacteria, human Used in brewing, muscle cells winemaking, baking Used to make cheese, yogurt, acetone, methanol Note: Lactate build-up does NOT causes muscle fatigue and pain (old idea) ...
... Pyruvate Ethanol + CO2 Pyruvate Lactate Ex. bacteria, yeast Ex. fungi, bacteria, human Used in brewing, muscle cells winemaking, baking Used to make cheese, yogurt, acetone, methanol Note: Lactate build-up does NOT causes muscle fatigue and pain (old idea) ...
Kofaktörler - mustafaaltinisik.org.uk
... often participate in substrate binding. • Metal ions of metalloenzymes – cations that are tightly bound to enzyme and participate directly in catalysis (Fe, Zn, Cu, Co). • Metal activated enzymes – require or are stimulated by addition of metal ions (i.e. Mg2+, is required by many ATP requiring enzy ...
... often participate in substrate binding. • Metal ions of metalloenzymes – cations that are tightly bound to enzyme and participate directly in catalysis (Fe, Zn, Cu, Co). • Metal activated enzymes – require or are stimulated by addition of metal ions (i.e. Mg2+, is required by many ATP requiring enzy ...
Amino acid - Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research
... aminoglycoside antibiotic (e.g streptomycin in which they first latch onto surface receptor on the bacteria before exerting their action) . Other uses of tannins are to stop haemorrhage, to treat diarrhea, as well as local burns treatment where they precipitate proteins in the burned area, thus form ...
... aminoglycoside antibiotic (e.g streptomycin in which they first latch onto surface receptor on the bacteria before exerting their action) . Other uses of tannins are to stop haemorrhage, to treat diarrhea, as well as local burns treatment where they precipitate proteins in the burned area, thus form ...
Ch 9 (primary ppt) - Phillips Scientific Methods
... 2. Where in the cell does glycolysis occur? 3. What are the reactants and products of glycolysis? ...
... 2. Where in the cell does glycolysis occur? 3. What are the reactants and products of glycolysis? ...
File - Ms. Richards IB Biology HL
... 1. Covalent electrons of methane are equally shared because carbon and hydrogen have similar electronegativities 2. As methane reacts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide, electrons shift away from carbon and hydrogen to the more electronegative oxygen 3. Since electrons lose potential energy when the ...
... 1. Covalent electrons of methane are equally shared because carbon and hydrogen have similar electronegativities 2. As methane reacts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide, electrons shift away from carbon and hydrogen to the more electronegative oxygen 3. Since electrons lose potential energy when the ...
2105Lecture 5a powerpoint
... Oxidation of LDL results in the binding of monocytes to the endothelial cells lining the vessel wall. These monocytes are activated and migrate into the endothelial space where they are transformed into macrophages, leading to further oxidation of the LDL. The oxidized LDL is taken up through the sc ...
... Oxidation of LDL results in the binding of monocytes to the endothelial cells lining the vessel wall. These monocytes are activated and migrate into the endothelial space where they are transformed into macrophages, leading to further oxidation of the LDL. The oxidized LDL is taken up through the sc ...
Alternative routes of acetyl-CoA synthesis identified
... genes in oleaginous strains Based on the ability of yeasts and fungi to produce different amounts of lipids, genome comparisons between oleaginous and non-oleaginous strains were undertaken to unravel cellular metabolic processes that might participate in oleaginicity. In this work, the genome seque ...
... genes in oleaginous strains Based on the ability of yeasts and fungi to produce different amounts of lipids, genome comparisons between oleaginous and non-oleaginous strains were undertaken to unravel cellular metabolic processes that might participate in oleaginicity. In this work, the genome seque ...
The metabolic advantage of tumor cells Open Access Maurice Israël
... spite of an increased glycolysis! Moreover, in tumors, one finds a particular PK, the M2 embryonic enzyme [2,9,10] the dimeric, phosphorylated form is inactive, leading to a “bottleneck “. The M2 PK has to be activated by fructose 1-6 bis P its allosteric activator, whereas the M1 adult enzyme is a ...
... spite of an increased glycolysis! Moreover, in tumors, one finds a particular PK, the M2 embryonic enzyme [2,9,10] the dimeric, phosphorylated form is inactive, leading to a “bottleneck “. The M2 PK has to be activated by fructose 1-6 bis P its allosteric activator, whereas the M1 adult enzyme is a ...
Finals Practice Exam answers
... homogenate, paying specific attention to separating Pyruvate Dehydrogenase from -ketoglutarate Dehydrogenase, Aconitase from Malate Dehydrogenase, and Succinyl-CoA Thiokinase from Fumarase in their native states, using affinity chromatography only as a last resort. : Size exclusion chromatography ...
... homogenate, paying specific attention to separating Pyruvate Dehydrogenase from -ketoglutarate Dehydrogenase, Aconitase from Malate Dehydrogenase, and Succinyl-CoA Thiokinase from Fumarase in their native states, using affinity chromatography only as a last resort. : Size exclusion chromatography ...
The Digestive System (PowerPoint)
... • Defecation reflex takes place when wastes build up in the large intestine, receptors in the wall of the intestine provide information to the central nervous system which, in turn, prompts a bowel movement. The bowel movement ensures the removal of potentially toxic wastes from the body. Individual ...
... • Defecation reflex takes place when wastes build up in the large intestine, receptors in the wall of the intestine provide information to the central nervous system which, in turn, prompts a bowel movement. The bowel movement ensures the removal of potentially toxic wastes from the body. Individual ...
Methods of industrial production
... oxygen, the production of L‐glutamate oxygen, the production of L glutamate is poor and lactic acid as well as succinic is poor and lactic acid as well as succinic acid accumulates, whereas with an excess oxygen supply the amount of α‐ ketoglutarate as a by‐product accumulates. ...
... oxygen, the production of L‐glutamate oxygen, the production of L glutamate is poor and lactic acid as well as succinic is poor and lactic acid as well as succinic acid accumulates, whereas with an excess oxygen supply the amount of α‐ ketoglutarate as a by‐product accumulates. ...