Pyruvate Dehydrogenase
... acetyl-CoA, providing another way the 2 major products of Pyruvate Dehydrogenase reaction inhibit the complex. ...
... acetyl-CoA, providing another way the 2 major products of Pyruvate Dehydrogenase reaction inhibit the complex. ...
Pharos university Faculty of Allied Medical SCIENCE Biochemistry 1
... There are 20 different amino acids that make up human proteins. Groups of two amino acids are called di-peptides ,whereas three amino acids ...
... There are 20 different amino acids that make up human proteins. Groups of two amino acids are called di-peptides ,whereas three amino acids ...
Chapter Twenty Three
... mobilized, and acetylSCoA molecules derived from breakdown of lipids accumulate. ►Acetyl-SCoA begins to be removed by a new series of metabolic reactions that transform it into ketone bodies. Prentice Hall © 2007 ...
... mobilized, and acetylSCoA molecules derived from breakdown of lipids accumulate. ►Acetyl-SCoA begins to be removed by a new series of metabolic reactions that transform it into ketone bodies. Prentice Hall © 2007 ...
Lecture 27
... Spontaneous cyclization is prevented by acetylation of amino group by Nacetylglutamate synthase. N-acetylglutamate-5-semialdehyde is converted to amine by transamination. Hydrolysis of protecting group yields ornithine which can be converted to arginine. In humans it is direct from glutamate-5-semia ...
... Spontaneous cyclization is prevented by acetylation of amino group by Nacetylglutamate synthase. N-acetylglutamate-5-semialdehyde is converted to amine by transamination. Hydrolysis of protecting group yields ornithine which can be converted to arginine. In humans it is direct from glutamate-5-semia ...
Notes: Enzymes
... This disorder is named after a physician, Dr Bernard Sachs, who noted in 1887 that a number of children of Central and Eastern Europe (Ashkenazic) Jewish ancestry, who were born with no apparent problems, degenerated physically and mentally and died by the age of about four. The affected children we ...
... This disorder is named after a physician, Dr Bernard Sachs, who noted in 1887 that a number of children of Central and Eastern Europe (Ashkenazic) Jewish ancestry, who were born with no apparent problems, degenerated physically and mentally and died by the age of about four. The affected children we ...
Document
... • when acetoacetate reduces to b-hydroxybutyrate or loses CO2 to form acetone, both ketone bodies. ...
... • when acetoacetate reduces to b-hydroxybutyrate or loses CO2 to form acetone, both ketone bodies. ...
19 Dr. Nafez Abu Tarboosh Qusai Al Sharef
... carbonyl ketone group (on C 2) so the bonds around this carbon will be weaken (between c1 and c2) and C1 will leave as a carboxylic group and this is why we call it decarboxylation reaction. Thiamine is rapidly converted to its active form thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP) in the brain and liver. ...
... carbonyl ketone group (on C 2) so the bonds around this carbon will be weaken (between c1 and c2) and C1 will leave as a carboxylic group and this is why we call it decarboxylation reaction. Thiamine is rapidly converted to its active form thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP) in the brain and liver. ...
Amino Acid Transport Systems in Animal Cells
... L (1). Another Na+-dependent system almost completely specific t o glycine is not seen in the Ehrlich cell but has been described for nucleated and reticulated red blood cells, and may occur in a variant form with broader specificity in the intestine and kidney (Summaries, Refs. 2, 3). A third Na+-d ...
... L (1). Another Na+-dependent system almost completely specific t o glycine is not seen in the Ehrlich cell but has been described for nucleated and reticulated red blood cells, and may occur in a variant form with broader specificity in the intestine and kidney (Summaries, Refs. 2, 3). A third Na+-d ...
Chapter 2
... 1. ____________________ (1o) – amino acid sequence; this determines the next 3 levels 2. ____________________ (2o) – the amino acid chains coils and folds 3. ____________________ (3o) – the 2o structure folds on itself 4. ____________________ (4o) – one or more polypeptide chains are added; a.k.a. g ...
... 1. ____________________ (1o) – amino acid sequence; this determines the next 3 levels 2. ____________________ (2o) – the amino acid chains coils and folds 3. ____________________ (3o) – the 2o structure folds on itself 4. ____________________ (4o) – one or more polypeptide chains are added; a.k.a. g ...
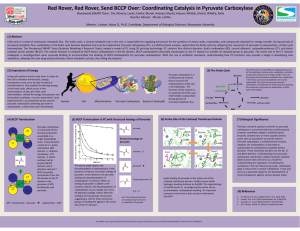
Poster
... undergoes a reconfiguration upon pyruvate binding to accommodate the docking of BCCP-carboxybiotin for pyruvate carboxylation. With the rise in antibiotic resistance, understanding how PC functions may provide a target in developing new antibiotics, whereby the new drug would eliminate critical meta ...
... undergoes a reconfiguration upon pyruvate binding to accommodate the docking of BCCP-carboxybiotin for pyruvate carboxylation. With the rise in antibiotic resistance, understanding how PC functions may provide a target in developing new antibiotics, whereby the new drug would eliminate critical meta ...
Base Foreign Students 2015
... of blood. What acidic substance that came to blood caused this phenomenon? A.*Lactate. B.Pyruvate. C.1,3-bisphosphoglycerate. D.3-phosphoglycerate. E. -. 5.After a sprint an untrained person develops muscle hypoxi This leads to the accumulation of the following metabolite in muscles: A.*Lactate. B.K ...
... of blood. What acidic substance that came to blood caused this phenomenon? A.*Lactate. B.Pyruvate. C.1,3-bisphosphoglycerate. D.3-phosphoglycerate. E. -. 5.After a sprint an untrained person develops muscle hypoxi This leads to the accumulation of the following metabolite in muscles: A.*Lactate. B.K ...
Metabolic diseases
... The clinical features of the disease ten to fall into two categories, acute and chronic. In the so-called acute form of the disease, abnormalities appear in the first month of life. Babies may show poor weight gain, an enlarged liver and spleen, a distended abdomen, swelling of the legs, and an incr ...
... The clinical features of the disease ten to fall into two categories, acute and chronic. In the so-called acute form of the disease, abnormalities appear in the first month of life. Babies may show poor weight gain, an enlarged liver and spleen, a distended abdomen, swelling of the legs, and an incr ...
Nutritional Requirements in Fermentation
... S, go into making up the molecules of living matter. All living cells on earth contain water as their predominant constituent. The remainder of the cell consists largely of proteins, nucleic acids, lipids, and carbohydrates, along with a few common salts. A few smaller compounds are very ubiquitous ...
... S, go into making up the molecules of living matter. All living cells on earth contain water as their predominant constituent. The remainder of the cell consists largely of proteins, nucleic acids, lipids, and carbohydrates, along with a few common salts. A few smaller compounds are very ubiquitous ...
PPT Nts Cellular Respiration
... 1. ATP : matrix intermembrane space 2. ADP : intermembrane space matrix ATP molecules diffuse through large pores in outer mitochondrial membrane and into cytosol ...
... 1. ATP : matrix intermembrane space 2. ADP : intermembrane space matrix ATP molecules diffuse through large pores in outer mitochondrial membrane and into cytosol ...
artículo - Anales de la Real Academia Nacional de Farmacia
... Comparative gerontological studies have already unveiled two traits that can explain the different (maximum) longevity of different mammals: long-‐lived animal species have a low rate of mitochondrial reactive ...
... Comparative gerontological studies have already unveiled two traits that can explain the different (maximum) longevity of different mammals: long-‐lived animal species have a low rate of mitochondrial reactive ...
Ontario`s Expanded Screening Program
... Medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (MCAD) deficiency Very long-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency (VLCAD) Long-chain L-3-OH acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency (LCHAD) Trifunctional protein deficiency (TFP) catalyzes 3 steps in mitochondrial betaoxidation of fatty acids ...
... Medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (MCAD) deficiency Very long-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency (VLCAD) Long-chain L-3-OH acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency (LCHAD) Trifunctional protein deficiency (TFP) catalyzes 3 steps in mitochondrial betaoxidation of fatty acids ...
Cellular Respiration - Cathedral High School
... for glycolysis • Proteins can be digested to amino acids, which are chemically altered and then used in the Krebs cycle • Fats are broken up and fed into glycolysis and the Krebs cycle Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... for glycolysis • Proteins can be digested to amino acids, which are chemically altered and then used in the Krebs cycle • Fats are broken up and fed into glycolysis and the Krebs cycle Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
Nucleic Acids Research
... suggestions, these do not form part of the present recommendations. First, we consider the uncertainty as to whether a base exists at a certain position or not. A symbol denoting "G or A or T or C or no nucleotide", for example ? or +, might be used to define regions of uncertainty of limited variab ...
... suggestions, these do not form part of the present recommendations. First, we consider the uncertainty as to whether a base exists at a certain position or not. A symbol denoting "G or A or T or C or no nucleotide", for example ? or +, might be used to define regions of uncertainty of limited variab ...
B. True or False/Edit
... Question: Why do we eat? Answer: To survive, right? Yet the answer is more complex than simply survival. As we learned in chapters 2-5, we eat primarily for two reasons: 1) to supply our tissue cells with the necessary carbohydrate, lipid (fat), and protein nutrients as fuel for cell respiration and ...
... Question: Why do we eat? Answer: To survive, right? Yet the answer is more complex than simply survival. As we learned in chapters 2-5, we eat primarily for two reasons: 1) to supply our tissue cells with the necessary carbohydrate, lipid (fat), and protein nutrients as fuel for cell respiration and ...
10-Urea cycle
... that undergoes rapid oxidative deamination Oxidative deamination of glutamate will ...
... that undergoes rapid oxidative deamination Oxidative deamination of glutamate will ...
Mock Exam 2 BY 123 – Dr. Biga Supplemental Instruction 1. Which
... 13. How many ATPs are generated through oxidative phosphorylation by the Oxidation of pyruvate? A) 7 ATP B) 4 ATP C) 5 ATP D) 8 ATP 14. How many ATP’s are generated by oxidative phosphorylation only if 7 Acetly COA’s were added to the mitochondria of a cell? A) 52.5 B) 63 C) 57.5 D) 70 15. The compl ...
... 13. How many ATPs are generated through oxidative phosphorylation by the Oxidation of pyruvate? A) 7 ATP B) 4 ATP C) 5 ATP D) 8 ATP 14. How many ATP’s are generated by oxidative phosphorylation only if 7 Acetly COA’s were added to the mitochondria of a cell? A) 52.5 B) 63 C) 57.5 D) 70 15. The compl ...
inhibition of protein synthesis in cell-free systems by
... vessel was used containing non-labeled leucine and the 21 other amino acids. If a significant deacylation occurred during the incubation, then the specific activity or the total counts incorporated into the protein should be greatly lowered. From the results of this experiment, it can be seen that H ...
... vessel was used containing non-labeled leucine and the 21 other amino acids. If a significant deacylation occurred during the incubation, then the specific activity or the total counts incorporated into the protein should be greatly lowered. From the results of this experiment, it can be seen that H ...
IR L Pre» Limited, Oxford, England. 3021
... numbered as recommended [24-26], although for the present purpose this has the disadvantage of giving discordant numbers to the corresponding positions . 3.5 Guanine or cytosine: S The choice of this symbol is discussed above in section 3.4. 3.6 Adenine or cytosine: M There are few common features b ...
... numbered as recommended [24-26], although for the present purpose this has the disadvantage of giving discordant numbers to the corresponding positions . 3.5 Guanine or cytosine: S The choice of this symbol is discussed above in section 3.4. 3.6 Adenine or cytosine: M There are few common features b ...