EOC Review Part 4
... Double helix with a backbone alternating between sugar (deoxyribose) and phosphate. The nitrogenous bases (A,T,G,C) on the two strands are bound to one another via hydrogen bonds (A w/ T; G w/ C). For the single DNA strand below, what do the black pentagons represent? Deoxyribose What kinds of bonds ...
... Double helix with a backbone alternating between sugar (deoxyribose) and phosphate. The nitrogenous bases (A,T,G,C) on the two strands are bound to one another via hydrogen bonds (A w/ T; G w/ C). For the single DNA strand below, what do the black pentagons represent? Deoxyribose What kinds of bonds ...
1.2 Differences between necrosis and apoptosis
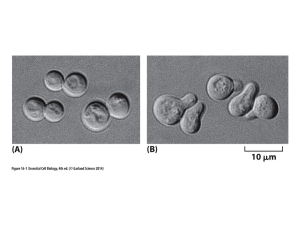
... There are many observable morphological (Figure 1, Table 1) and biochemical differences (Table 1) between necrosis and apoptosis2. Necrosis occurs when cells are exposed to extreme variance from physiological conditions (e.g., hypothermia, hypoxia) which may result in damage to the plasma membrane. ...
... There are many observable morphological (Figure 1, Table 1) and biochemical differences (Table 1) between necrosis and apoptosis2. Necrosis occurs when cells are exposed to extreme variance from physiological conditions (e.g., hypothermia, hypoxia) which may result in damage to the plasma membrane. ...
Model Description Sheet
... pathway, small RNAs derived from viruses are used by Ago-2 to slice virus mRNA, protecting the cells from infection. In the miRNA pathway, Ago-2 utilizes naturally occurring miRNA to slice cellular mRNAs to control protein production. Ago-2 works by binding small (~22 nucleotide) regulatory RNAs (si ...
... pathway, small RNAs derived from viruses are used by Ago-2 to slice virus mRNA, protecting the cells from infection. In the miRNA pathway, Ago-2 utilizes naturally occurring miRNA to slice cellular mRNAs to control protein production. Ago-2 works by binding small (~22 nucleotide) regulatory RNAs (si ...
Buffers - Philadelphia University
... • (H,C,N,O,P,S,Mn, Fe, Co, Cu, Zn, Na, Mg, Cl, K, Ca). – Chemical makeup appears to be determined partly by the availability of raw materials and the specific roles of of molecules in life processes. – Do not reflect the composition of the biosphere – Examples on per atom basis, H in organisms = 49% ...
... • (H,C,N,O,P,S,Mn, Fe, Co, Cu, Zn, Na, Mg, Cl, K, Ca). – Chemical makeup appears to be determined partly by the availability of raw materials and the specific roles of of molecules in life processes. – Do not reflect the composition of the biosphere – Examples on per atom basis, H in organisms = 49% ...
@ tin Scruppsfusrencu Iusrnurs
... According to Tainer, "Defectsin cell cycle control is a commontrait of all cancers. Understandingthe structureand function of this protein could be a first step in leading us to the developmentof more effective anti-cancertherapiesand/or an enhancementof those currently utilized." ...
... According to Tainer, "Defectsin cell cycle control is a commontrait of all cancers. Understandingthe structureand function of this protein could be a first step in leading us to the developmentof more effective anti-cancertherapiesand/or an enhancementof those currently utilized." ...
Bonding is more than attraction
... - It is a long chain of smaller molecules called nucleotides. • What is a nucleotide? - A nucleotide has three parts: a sugar, a base, and a phosphate group, which contains phosphorus and oxygen atoms. ...
... - It is a long chain of smaller molecules called nucleotides. • What is a nucleotide? - A nucleotide has three parts: a sugar, a base, and a phosphate group, which contains phosphorus and oxygen atoms. ...
Cells Use DNA and RNA to Make Proteins
... DNA provides the code for each protein Proteins and Amino Acids 1. 20 different aa’s 2. some small proteins and some very large 3. cells put together sequences of aa’s 4. DNA provides the info to sequence aa’s ...
... DNA provides the code for each protein Proteins and Amino Acids 1. 20 different aa’s 2. some small proteins and some very large 3. cells put together sequences of aa’s 4. DNA provides the info to sequence aa’s ...
Chapter 3 The Plasma Membrane: transport across cell membrane
... Process by which most molecules are secreted from a eucaryotic cell. These molecules are packaged into membrane-bounded vesicles that fuse with the plasma membrane and release their contents to the extracellular space. ...
... Process by which most molecules are secreted from a eucaryotic cell. These molecules are packaged into membrane-bounded vesicles that fuse with the plasma membrane and release their contents to the extracellular space. ...
diffusion
... Transport: move molecules or ions from one side of the membrane to the other. Receptors: bind substances secreted by other cells which trigger changes in the receiving cell. Anchors proteins: help cells stick to each other and stay positioned; found in cell junctions ...
... Transport: move molecules or ions from one side of the membrane to the other. Receptors: bind substances secreted by other cells which trigger changes in the receiving cell. Anchors proteins: help cells stick to each other and stay positioned; found in cell junctions ...
Chapter 6 fill-in-the Blank
... 22. Secretory proteins are packaged into _______________________ ______________________. 23. Rough ER is a ___________________ factory for the cell. Membrane-bound proteins are synthesized directly into the ER membrane. 24. Enzymes in rough ER also synthesize _________________________ from precurso ...
... 22. Secretory proteins are packaged into _______________________ ______________________. 23. Rough ER is a ___________________ factory for the cell. Membrane-bound proteins are synthesized directly into the ER membrane. 24. Enzymes in rough ER also synthesize _________________________ from precurso ...
Electron micrographs of E. coli. Reproduction of prokaryotic cells by
... flagella - structures protruding from the cell wall with a corkscrew shape, using energy, they can be rotated, to propel the cell from on area to another unlike eukaryotic flagella, they are solid and inflexible, working like a propeller ...
... flagella - structures protruding from the cell wall with a corkscrew shape, using energy, they can be rotated, to propel the cell from on area to another unlike eukaryotic flagella, they are solid and inflexible, working like a propeller ...
2.2 Prokaryotic CellsDaniel - DAVIS-DAIS
... flagella - structures protruding from the cell wall with a corkscrew shape, using energy, they can be rotated, to propel the cell from on area to another unlike eukaryotic flagella, they are solid and inflexible, working like a propeller ...
... flagella - structures protruding from the cell wall with a corkscrew shape, using energy, they can be rotated, to propel the cell from on area to another unlike eukaryotic flagella, they are solid and inflexible, working like a propeller ...
Ch. 5 Biochemistry
... 3 (phosphate group) • ‘Tails’ hydrophobic; ‘heads’ hydrophilic • Micelle (phospholipid droplet in water) • Bilayer (double layer); cell membranes ...
... 3 (phosphate group) • ‘Tails’ hydrophobic; ‘heads’ hydrophilic • Micelle (phospholipid droplet in water) • Bilayer (double layer); cell membranes ...
Omnis cellula e cellula, that each cell derives from a pre
... 3.5 billion years ago. Since that time, cells have continuously divided. At first they existed as single cells. Over time they got together and formed ever more complex organisms, culminating in man. Each of us starts life by the joining of one cell from our father and one cell from our mother. Like ...
... 3.5 billion years ago. Since that time, cells have continuously divided. At first they existed as single cells. Over time they got together and formed ever more complex organisms, culminating in man. Each of us starts life by the joining of one cell from our father and one cell from our mother. Like ...
Essential Cell Biology
... cells respond with a normal biological response to the appropriate first messenger. In mutated cells, however, no response was evoked, because the cells lacked the G-protein. The function could be restored by G-protein derived from another tissue such as brain. ...
... cells respond with a normal biological response to the appropriate first messenger. In mutated cells, however, no response was evoked, because the cells lacked the G-protein. The function could be restored by G-protein derived from another tissue such as brain. ...
Answers - AP BIOLOGY!
... Phospholipids are amphipathic (maintain dual properties) in that they have a hydrophilic head regions composed of a phosphate group and two hydrophobic fatty acid tails. Together , in aqueous environments, phospholipid molecules will form bilayers where their polar heads shield their polar tails fro ...
... Phospholipids are amphipathic (maintain dual properties) in that they have a hydrophilic head regions composed of a phosphate group and two hydrophobic fatty acid tails. Together , in aqueous environments, phospholipid molecules will form bilayers where their polar heads shield their polar tails fro ...
Fun with Cells with the Amoeba Sisters
... But, wait. There are basically 2 kinds of cells, right? One that is found in simple life forms like amoeba. And such cells are called as prokaryotes. And the other that is found in complex life forms like humans, for example. We call them eukaryotes. Let us hear their differences first. ...
... But, wait. There are basically 2 kinds of cells, right? One that is found in simple life forms like amoeba. And such cells are called as prokaryotes. And the other that is found in complex life forms like humans, for example. We call them eukaryotes. Let us hear their differences first. ...
organic compounds outline
... ____________________ – a segment of DNA that codes for the production of a specific protein Controls cell activities by what proteins (enzymes) they code for Order of bases determine what amino acids sequence is used in protein function of individual proteins _____________________ – copyin ...
... ____________________ – a segment of DNA that codes for the production of a specific protein Controls cell activities by what proteins (enzymes) they code for Order of bases determine what amino acids sequence is used in protein function of individual proteins _____________________ – copyin ...
Biology StaAr review
... An amino acid may have more than one codon There are 20 amino acids, but 64 possible codons Some codons tell the ribosome to stop translating ...
... An amino acid may have more than one codon There are 20 amino acids, but 64 possible codons Some codons tell the ribosome to stop translating ...
Hydrophobic signal molecules
... The receptor protein performs the first step in a series of transduction processes by converting the incoming extra-cellular signal to an intracellular signal that directs the cells behaviour ...
... The receptor protein performs the first step in a series of transduction processes by converting the incoming extra-cellular signal to an intracellular signal that directs the cells behaviour ...
chapter 7 membranes
... Held together mostly by hydrophobic interactions Most lipids and some proteins drift randomly in the plane of the membrane Rarely flip-flop from one side to the other Must be fluid to work properly Fluid mosaic model – arrangement of phospholipid layer(s) with proteins immersed throughout ...
... Held together mostly by hydrophobic interactions Most lipids and some proteins drift randomly in the plane of the membrane Rarely flip-flop from one side to the other Must be fluid to work properly Fluid mosaic model – arrangement of phospholipid layer(s) with proteins immersed throughout ...
Cells
... Lipid bilayer with hydrophobic core and hydrophilic face Plasma (cell) membrane: Hydrophobic barrier between inside (cytoplasm) and outside of the cell Internal membranes for eucaryote ...
... Lipid bilayer with hydrophobic core and hydrophilic face Plasma (cell) membrane: Hydrophobic barrier between inside (cytoplasm) and outside of the cell Internal membranes for eucaryote ...
Cell-penetrating peptide

Cell-penetrating peptides (CPPs) are short peptides that facilitate cellular uptake of various molecular cargo (from nanosize particles to small chemical molecules and large fragments of DNA). The ""cargo"" is associated with the peptides either through chemical linkage via covalent bonds or through non-covalent interactions. The function of the CPPs are to deliver the cargo into cells, a process that commonly occurs through endocytosis with the cargo delivered to the endosomes of living mammalian cells.CPPs hold great potential as in vitro and in vivo delivery vectors for use in research and medicine. Current use is limited by a lack of cell specificity in CPP-mediated cargo delivery and insufficient understanding of the modes of their uptake.CPPs typically have an amino acid composition that either contains a high relative abundance of positively charged amino acids such as lysine or arginine or has sequences that contain an alternating pattern of polar/charged amino acids and non-polar, hydrophobic amino acids. These two types of structures are referred to as polycationic or amphipathic, respectively. A third class of CPPs are the hydrophobic peptides, containing only apolar residues, with low net chargeor have hydrophobic amino acid groups that are crucial for cellular uptake.The first CPP was discovered independently by two laboratories in 1988, when it was found that the trans-activating transcriptional activator (TAT) from human immunodeficiency virus 1 (HIV-1) could be efficiently taken up from the surrounding media by numerous cell types in culture. Since then, the number of known CPPs has expanded considerably and small molecule synthetic analogues with more effective protein transduction properties have been generated.