The Cell
... Drives mechanical, transport, and chemical work in cells works by transferring phosphate group ...
... Drives mechanical, transport, and chemical work in cells works by transferring phosphate group ...
Ch 3 Cells - Review Cell theory The cell is the smallest unit of life
... summary of protein synthesis: DNA is made of nucleotides (A, T, G, C), in sets of 3 = triplet mRNA is made of nucleotides, in sets of 3 = codon tRNA contains 3 nucleotides, the anticodon, and one amino acid (AA) protein is made of many amino acids in a specific order. A gene is a piece of DNA with a ...
... summary of protein synthesis: DNA is made of nucleotides (A, T, G, C), in sets of 3 = triplet mRNA is made of nucleotides, in sets of 3 = codon tRNA contains 3 nucleotides, the anticodon, and one amino acid (AA) protein is made of many amino acids in a specific order. A gene is a piece of DNA with a ...
News Release
... ‘LEGO-Like’ Building Blocks to Halt Cell Growth Wins Kaye Prize for Hebrew University Ph.D. Student Jerusalem, June 7, 2006—A method for delivery of drugs to targeted cells through the design of specific molecular structures called SIB (Small Integrated Building Blocks) has won a prestigious scienti ...
... ‘LEGO-Like’ Building Blocks to Halt Cell Growth Wins Kaye Prize for Hebrew University Ph.D. Student Jerusalem, June 7, 2006—A method for delivery of drugs to targeted cells through the design of specific molecular structures called SIB (Small Integrated Building Blocks) has won a prestigious scienti ...
abstract form
... repeats in DNA damage induced by cytostatic bleomycin (BLM). The investigation was performed with Comet-FISH, combination of Comet-assay (single cell gel electrophoresis) with FISH (Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization) technique. This approach permits to detect in the individual cell simultaneously th ...
... repeats in DNA damage induced by cytostatic bleomycin (BLM). The investigation was performed with Comet-FISH, combination of Comet-assay (single cell gel electrophoresis) with FISH (Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization) technique. This approach permits to detect in the individual cell simultaneously th ...
Rapidly discover receptors and druggable targets
... primary receptors and secondary targets by screening for interactions against >4,000 human plasma membrane proteins that are individually over-expressed in their native context in human cells. Test molecules are allowed to bind and then specific interactions with target receptors are identified and ...
... primary receptors and secondary targets by screening for interactions against >4,000 human plasma membrane proteins that are individually over-expressed in their native context in human cells. Test molecules are allowed to bind and then specific interactions with target receptors are identified and ...
DNA Function II - Complete Vocab with
... General Transcription Factors: Other enzymes/proteins that are required for RNA Polymerase to function Transcription Activators: Proteins that bind to enhancers to stimulate transcription Transcription Repressors: Proteins that bind to enhancers to shut down transcription Enhancer: A sequence of DNA ...
... General Transcription Factors: Other enzymes/proteins that are required for RNA Polymerase to function Transcription Activators: Proteins that bind to enhancers to stimulate transcription Transcription Repressors: Proteins that bind to enhancers to shut down transcription Enhancer: A sequence of DNA ...
Quiz Next Tuesday (09/18) - Chemistry at Winthrop University
... 5.1 - What Is the Fundamental Structural Pattern in Proteins? ...
... 5.1 - What Is the Fundamental Structural Pattern in Proteins? ...
04-05 Biochem review sheet answers ws
... 1. Main elements found in living things are: CHON 2. What are organic chemicals? contain carbon bound to hydrogen 3. List the four classes of organic compounds. carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids 4. Which atoms does carbon almost always share electrons with? CHON 5. Explain how carbon’s ...
... 1. Main elements found in living things are: CHON 2. What are organic chemicals? contain carbon bound to hydrogen 3. List the four classes of organic compounds. carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids 4. Which atoms does carbon almost always share electrons with? CHON 5. Explain how carbon’s ...
Membrane Structure and Function
... carbohydrates on external side of membrane vary from species to species, within same species and even between cells ...
... carbohydrates on external side of membrane vary from species to species, within same species and even between cells ...
Prokaryotes, Eukaryotes and Viruses
... • Are they a type of cell? • No! Viruses are just genetic information surrounded by a protein coat ...
... • Are they a type of cell? • No! Viruses are just genetic information surrounded by a protein coat ...
Chapter 4 Study Guide
... 1. The outer living boundary of the cell is the ______________________. 2. The cell membrane regulates the _____________ of molecules into and out of the cell 3. The cell membrane is largely responsible for maintaining cellular ________________. 4. _______________ bilayer determines the basic struct ...
... 1. The outer living boundary of the cell is the ______________________. 2. The cell membrane regulates the _____________ of molecules into and out of the cell 3. The cell membrane is largely responsible for maintaining cellular ________________. 4. _______________ bilayer determines the basic struct ...
Methods for Detection of Small Molecule
... small molecules. In this thesis, novel detection methods for molecular interactions are shown. First, a simple detection paradigm based on reflectance interferometry is shown. This method is simple, low cost and can be easily applied for protein array detection. Second, a label-free charge sensitive ...
... small molecules. In this thesis, novel detection methods for molecular interactions are shown. First, a simple detection paradigm based on reflectance interferometry is shown. This method is simple, low cost and can be easily applied for protein array detection. Second, a label-free charge sensitive ...
Cells All living things are made up of cells. The cell theory says that
... All living things are made up of cells. The cell theory says that 1. all living things are made up of cells 2. cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things 3. all cells come from preexisting cells Cells are made up of smaller parts called organelles (just as you are made up of ...
... All living things are made up of cells. The cell theory says that 1. all living things are made up of cells 2. cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things 3. all cells come from preexisting cells Cells are made up of smaller parts called organelles (just as you are made up of ...
Oct_7
... Different types of membrane lipids (we talked about this last time) [ chart of Phospholipid composition of organelles ] o Note that sphingomyelin high in plasma membrane [ Inner / Outer membranes - curvature stress - phosphatidyl choline, big methyl group on outer membranes. Which ones on the insi ...
... Different types of membrane lipids (we talked about this last time) [ chart of Phospholipid composition of organelles ] o Note that sphingomyelin high in plasma membrane [ Inner / Outer membranes - curvature stress - phosphatidyl choline, big methyl group on outer membranes. Which ones on the insi ...
MEMBRANES Fluid mosaic of phopholipid bilayer, cholesterol
... Active Transport: facilitated movement against concentration gradient Requires not only Carrier Proteins, but also E in form of ATP In what class of macromolecule is ATP ...
... Active Transport: facilitated movement against concentration gradient Requires not only Carrier Proteins, but also E in form of ATP In what class of macromolecule is ATP ...
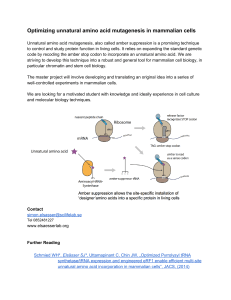
Optimizing unnatural amino acid mutagenesis in mammalian cells
... Unnatural amino acid mutagenesis, also called amber suppression is a promising technique to control and study protein function in living cells. It relies on expanding the standard genetic code by recoding the amber stop codon to incorporate an unnatural amino acid. We are striving to develop this ...
... Unnatural amino acid mutagenesis, also called amber suppression is a promising technique to control and study protein function in living cells. It relies on expanding the standard genetic code by recoding the amber stop codon to incorporate an unnatural amino acid. We are striving to develop this ...
Proteins and Nucleic Acids Proteins (pp.46-48) Monomer
... Proteins (pp.46-48) Monomer-basic structure Types of proteins and their functions Number of amino acids o what makes them different from one another o what's responsible for giving them their chemical properties Polymers o Bond responsible for linking amino acids together o Levels of Protein ...
... Proteins (pp.46-48) Monomer-basic structure Types of proteins and their functions Number of amino acids o what makes them different from one another o what's responsible for giving them their chemical properties Polymers o Bond responsible for linking amino acids together o Levels of Protein ...
Chemistry of Life - Haughton Science
... together in protein molecules dipeptide bond = two connected amino acids polypeptide bond = 3 or more connected amino acids ...
... together in protein molecules dipeptide bond = two connected amino acids polypeptide bond = 3 or more connected amino acids ...
Cell-penetrating peptide

Cell-penetrating peptides (CPPs) are short peptides that facilitate cellular uptake of various molecular cargo (from nanosize particles to small chemical molecules and large fragments of DNA). The ""cargo"" is associated with the peptides either through chemical linkage via covalent bonds or through non-covalent interactions. The function of the CPPs are to deliver the cargo into cells, a process that commonly occurs through endocytosis with the cargo delivered to the endosomes of living mammalian cells.CPPs hold great potential as in vitro and in vivo delivery vectors for use in research and medicine. Current use is limited by a lack of cell specificity in CPP-mediated cargo delivery and insufficient understanding of the modes of their uptake.CPPs typically have an amino acid composition that either contains a high relative abundance of positively charged amino acids such as lysine or arginine or has sequences that contain an alternating pattern of polar/charged amino acids and non-polar, hydrophobic amino acids. These two types of structures are referred to as polycationic or amphipathic, respectively. A third class of CPPs are the hydrophobic peptides, containing only apolar residues, with low net chargeor have hydrophobic amino acid groups that are crucial for cellular uptake.The first CPP was discovered independently by two laboratories in 1988, when it was found that the trans-activating transcriptional activator (TAT) from human immunodeficiency virus 1 (HIV-1) could be efficiently taken up from the surrounding media by numerous cell types in culture. Since then, the number of known CPPs has expanded considerably and small molecule synthetic analogues with more effective protein transduction properties have been generated.