ppt
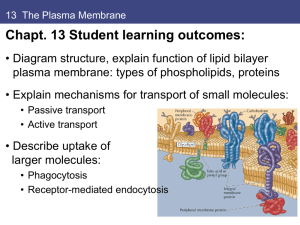
... Fundamental structure is phospholipid bilayer: • Proteins embedded in bilayer carry out functions: Mammalian red blood cells (erythrocytes) good model • no nuclei or internal membranes, • easy to isolate pure plasma membranes. Fig. 13.1 ...
... Fundamental structure is phospholipid bilayer: • Proteins embedded in bilayer carry out functions: Mammalian red blood cells (erythrocytes) good model • no nuclei or internal membranes, • easy to isolate pure plasma membranes. Fig. 13.1 ...
Document
... of movement (from high to low). • Transmembrane proteins take polar and charged molecules across membrane • Carrier proteins bind molecules on one side; undergo conformational change to allow molecule to pass through membrane to other side. ...
... of movement (from high to low). • Transmembrane proteins take polar and charged molecules across membrane • Carrier proteins bind molecules on one side; undergo conformational change to allow molecule to pass through membrane to other side. ...
Prokaryotic cell
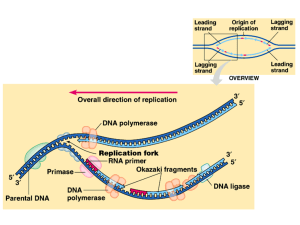
... to the next Contains 4 types of nucleotides Makes up genes Codes for proteins Genetic code is virtually universal. ...
... to the next Contains 4 types of nucleotides Makes up genes Codes for proteins Genetic code is virtually universal. ...
Early Earth and the Origin of Life
... Interaction between RNA and the proteins it made. Proteins formed may serve as RNA replication ...
... Interaction between RNA and the proteins it made. Proteins formed may serve as RNA replication ...
chapter20
... Chemical evolution leads to the formation and survival of the most stable of the more complex compounds. ...
... Chemical evolution leads to the formation and survival of the most stable of the more complex compounds. ...
lecture_ch03_for website_updated 11_12_14
... size to prokaryotic cells. 2. Chloroplasts and mitochondria have small amounts of circular DNA similar to those found in prokaryotes 3. Chloroplast and mitochondria divide by splitting (binary fission) 4. Chloroplast and mitochondria have small internal structure called ribosomes. ...
... size to prokaryotic cells. 2. Chloroplasts and mitochondria have small amounts of circular DNA similar to those found in prokaryotes 3. Chloroplast and mitochondria divide by splitting (binary fission) 4. Chloroplast and mitochondria have small internal structure called ribosomes. ...
File - Wildcat Biology Review
... RNA: single stranded ribonucleic acid (ribose sugar) Restriction Enzymes: unzips DNA so it can be read and copied Replication: copies DNA makes a complimentary strand occurs in nucleus mRNA: messenger RNA, end product of transcription (messenger RNA)carries a copy of genetic information instructions ...
... RNA: single stranded ribonucleic acid (ribose sugar) Restriction Enzymes: unzips DNA so it can be read and copied Replication: copies DNA makes a complimentary strand occurs in nucleus mRNA: messenger RNA, end product of transcription (messenger RNA)carries a copy of genetic information instructions ...
DNA-origami in Boston
... Impression of a NBS internship by Sjors Wijnands For six months I worked as a student researcher in the group of William Shih at the Wyss Institute in Boston, USA. This institute was founded in 2009 at Harvard University with the financial support of Hansjörg Wyss and its mission is to develop biolo ...
... Impression of a NBS internship by Sjors Wijnands For six months I worked as a student researcher in the group of William Shih at the Wyss Institute in Boston, USA. This institute was founded in 2009 at Harvard University with the financial support of Hansjörg Wyss and its mission is to develop biolo ...
Figure S1: 3xFLAG-tag cloning primers. Listed are primers used to
... were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde and stained with an anti-3xFLAG rabbit polyclonal antibody (Sigma-Aldrich) and the bicyclic peptide, phalloidin, to stain f-actin as a marker of the cell surface. Quantitative colocalization analysis in 3 dimensions was performed between the two channels and coloc ...
... were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde and stained with an anti-3xFLAG rabbit polyclonal antibody (Sigma-Aldrich) and the bicyclic peptide, phalloidin, to stain f-actin as a marker of the cell surface. Quantitative colocalization analysis in 3 dimensions was performed between the two channels and coloc ...
Pathophysiology
... Important metabolic processes occur here Organelles – membrane bound structures Membranes provide compartments for separation of chemical reactions ...
... Important metabolic processes occur here Organelles – membrane bound structures Membranes provide compartments for separation of chemical reactions ...
Week 12 – Basic Chemical Structures of Important Organic
... protein molecules of about 10 000 different types. Typical examples of these proteins are: Primary – e.g. the order of amino acids joined together in a single chain; Secondary – e.g. keratin found in skin, hair and nails; silk fibres of a spider web; Tertiary – e.g. some enzymes such as lipase and s ...
... protein molecules of about 10 000 different types. Typical examples of these proteins are: Primary – e.g. the order of amino acids joined together in a single chain; Secondary – e.g. keratin found in skin, hair and nails; silk fibres of a spider web; Tertiary – e.g. some enzymes such as lipase and s ...
prokaryotic cell
... • are organic molecules with the general formula of CHO in 1:2:1 ratio. Although carbohydrates constitute only 1 to 2 percent of cell mass, they provide the raw fuel for cellular energy production. • Carbohydrates are classified according to molecular size and solubility. In general, the smaller mol ...
... • are organic molecules with the general formula of CHO in 1:2:1 ratio. Although carbohydrates constitute only 1 to 2 percent of cell mass, they provide the raw fuel for cellular energy production. • Carbohydrates are classified according to molecular size and solubility. In general, the smaller mol ...
Unit 4 ~ Learning Guide Name
... 5. What factors influence the rate at which specific molecules diffuse across the cell membrane? (3 marks) Answer should include any 3 of the following: = surface area…greater surface are = faster diffusion = temperature…higher temperature = faster diffusion = concentration gradient…greater gradient ...
... 5. What factors influence the rate at which specific molecules diffuse across the cell membrane? (3 marks) Answer should include any 3 of the following: = surface area…greater surface are = faster diffusion = temperature…higher temperature = faster diffusion = concentration gradient…greater gradient ...
B2 revision questions
... 1. Glucose and oxygen diffuse from capillaries into respiring cells 2. Carbon dioxide diffuses from respiring cells into capillaries The movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration The use of oxygen to release energy from glucose, producing water and carb ...
... 1. Glucose and oxygen diffuse from capillaries into respiring cells 2. Carbon dioxide diffuses from respiring cells into capillaries The movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration The use of oxygen to release energy from glucose, producing water and carb ...
Similarities and Differences Among Living Things
... When the concentration in one area is higher than another the molecules will move from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration to even out the distribution. It requires no outside energy source ...
... When the concentration in one area is higher than another the molecules will move from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration to even out the distribution. It requires no outside energy source ...
The nuclear envelope
... Nucleoli are typically composed of three morphologically distinct regions which can be visualized by electron microscopy(EM): Fibrillar center(FC):it is highly stained inner most region of nucleolus composed of fibrils that occupies 1-2% of the total volume. The RNA genes of nucleolar organizer of c ...
... Nucleoli are typically composed of three morphologically distinct regions which can be visualized by electron microscopy(EM): Fibrillar center(FC):it is highly stained inner most region of nucleolus composed of fibrils that occupies 1-2% of the total volume. The RNA genes of nucleolar organizer of c ...
Similarities and Differences Among Living Things
... When the concentration in one area is higher than another the molecules will move from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration to even out the distribution. It requires no outside energy source ...
... When the concentration in one area is higher than another the molecules will move from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration to even out the distribution. It requires no outside energy source ...
Course Guide - Universitat de València
... components, plant cell wall and extracellular matrix of animal cells, establish fundamental differences between both type of cells: Plant cell wall allows life in non-isotonic conditions, while extracellular matrix of plant cells influences intercellular junctions, cell communication and intercellul ...
... components, plant cell wall and extracellular matrix of animal cells, establish fundamental differences between both type of cells: Plant cell wall allows life in non-isotonic conditions, while extracellular matrix of plant cells influences intercellular junctions, cell communication and intercellul ...
Introduction and the Cell
... Osmosis is the net movement of water through a semipermeable membrane down its own concentration gradient from an area of high water concentration to an area of low water concentration. In other words, water moves toward an area of higher solute concentration. The osmotic pressure of a solution is t ...
... Osmosis is the net movement of water through a semipermeable membrane down its own concentration gradient from an area of high water concentration to an area of low water concentration. In other words, water moves toward an area of higher solute concentration. The osmotic pressure of a solution is t ...
Transcription & Translation PowerPoint
... A certain gene codes for a polypeptide that is 120 amino acids long. Approximately how many nucleotides long is the mRNA that codes for this polypeptide likely to be? A. ...
... A certain gene codes for a polypeptide that is 120 amino acids long. Approximately how many nucleotides long is the mRNA that codes for this polypeptide likely to be? A. ...
Codon Practice
... 5. A certain mRNA molecule has the following sequence: 5’ G G U A U C C C G A U U 3’ A. How many codons are in this sequence? _________________ B. What amino acid sequences are in this sequence? _________________________ ...
... 5. A certain mRNA molecule has the following sequence: 5’ G G U A U C C C G A U U 3’ A. How many codons are in this sequence? _________________ B. What amino acid sequences are in this sequence? _________________________ ...
Cell-penetrating peptide

Cell-penetrating peptides (CPPs) are short peptides that facilitate cellular uptake of various molecular cargo (from nanosize particles to small chemical molecules and large fragments of DNA). The ""cargo"" is associated with the peptides either through chemical linkage via covalent bonds or through non-covalent interactions. The function of the CPPs are to deliver the cargo into cells, a process that commonly occurs through endocytosis with the cargo delivered to the endosomes of living mammalian cells.CPPs hold great potential as in vitro and in vivo delivery vectors for use in research and medicine. Current use is limited by a lack of cell specificity in CPP-mediated cargo delivery and insufficient understanding of the modes of their uptake.CPPs typically have an amino acid composition that either contains a high relative abundance of positively charged amino acids such as lysine or arginine or has sequences that contain an alternating pattern of polar/charged amino acids and non-polar, hydrophobic amino acids. These two types of structures are referred to as polycationic or amphipathic, respectively. A third class of CPPs are the hydrophobic peptides, containing only apolar residues, with low net chargeor have hydrophobic amino acid groups that are crucial for cellular uptake.The first CPP was discovered independently by two laboratories in 1988, when it was found that the trans-activating transcriptional activator (TAT) from human immunodeficiency virus 1 (HIV-1) could be efficiently taken up from the surrounding media by numerous cell types in culture. Since then, the number of known CPPs has expanded considerably and small molecule synthetic analogues with more effective protein transduction properties have been generated.