Different Types of Cells There are two main groups of cells
... meaning before nuclei). These cells have few internal structures that are distinguishable under a microscope. Cells in the monera kingdom such as bacteria and cyanobacteria (also known as blue-green algae) are prokaryotes. Prokaryotic cells differ significantly from eukaryotic cells. They don't have ...
... meaning before nuclei). These cells have few internal structures that are distinguishable under a microscope. Cells in the monera kingdom such as bacteria and cyanobacteria (also known as blue-green algae) are prokaryotes. Prokaryotic cells differ significantly from eukaryotic cells. They don't have ...
Route of exposure, mode of action and modifying factors
... • The liver contains many non-specific enzymes that give it the ability to metabolize a broad spectrum of organic molecules • Two phases: – Phase I involves the addition of reactive polar groups through oxidation, reduction, or hydrolysis; sometimes this makes a non-toxic chemical more toxic – Phase ...
... • The liver contains many non-specific enzymes that give it the ability to metabolize a broad spectrum of organic molecules • Two phases: – Phase I involves the addition of reactive polar groups through oxidation, reduction, or hydrolysis; sometimes this makes a non-toxic chemical more toxic – Phase ...
Abscopal effect seen with T-cell therapy enhancing oncolytic
... tumors and reduces the presence of immunosuppressive M2 macrophages. Oncolytic adenoviruses with human cytokines are effective in vitro. ...
... tumors and reduces the presence of immunosuppressive M2 macrophages. Oncolytic adenoviruses with human cytokines are effective in vitro. ...
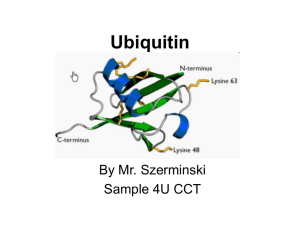
Ubiquitin
... Topics to be discussed • General info: - it is a regulatory protein that has been found in almost all tissues of eukaryotes - one of its functions: it directs protein recycling - can attach to proteins and label them for destruction. - discovery won the Nobel Prize for chemistry in 2004 ...
... Topics to be discussed • General info: - it is a regulatory protein that has been found in almost all tissues of eukaryotes - one of its functions: it directs protein recycling - can attach to proteins and label them for destruction. - discovery won the Nobel Prize for chemistry in 2004 ...
Protein Synthesis - Quakertown Community School District
... Building Blocks of Proteins • Proteins are made of subunits called amino acids • These subunits are comprised of : – Amino group – Carboxyl group – R group is different for each amino acid ...
... Building Blocks of Proteins • Proteins are made of subunits called amino acids • These subunits are comprised of : – Amino group – Carboxyl group – R group is different for each amino acid ...
The Cell Membrane
... the water (water can pass) but not the solutes (dissolved substances) such as salt and sugar. • Water moves across the membrane until an equilibrium is reached • Water concentration is equal on both sides of cell membrane. • The salts and sugars do not diffuse ...
... the water (water can pass) but not the solutes (dissolved substances) such as salt and sugar. • Water moves across the membrane until an equilibrium is reached • Water concentration is equal on both sides of cell membrane. • The salts and sugars do not diffuse ...
Cell
... Mitosis: A type of simple cell division within the body, whereby cells divide into other cells, each with the full set of chromosomes. Each of these cells receives an exact copy of the chromosomes in the original cell. During development, mitosis occurs again and again, until finally the adult organ ...
... Mitosis: A type of simple cell division within the body, whereby cells divide into other cells, each with the full set of chromosomes. Each of these cells receives an exact copy of the chromosomes in the original cell. During development, mitosis occurs again and again, until finally the adult organ ...
1/23 Notes and Classwork
... Steroids are found in animals within something called hormones. The basis of a steroid molecule is a four-ring structure: one ring with five carbons and three rings with six carbons. You may have heard of steroids in the news. Many bodybuilders and athletes have used anabolic steroids to build muscl ...
... Steroids are found in animals within something called hormones. The basis of a steroid molecule is a four-ring structure: one ring with five carbons and three rings with six carbons. You may have heard of steroids in the news. Many bodybuilders and athletes have used anabolic steroids to build muscl ...
Using the standardized (normally distributed with a mean of zero
... metrics for allelic pairs of 15-mers and 9-mers the minimum value for the pair was computed within a window ±4 from each position within the protein sequence. A least-squares mean was calculated over all permuted pairs to arrive at a number for each position in the protein sequence. Statistics for t ...
... metrics for allelic pairs of 15-mers and 9-mers the minimum value for the pair was computed within a window ±4 from each position within the protein sequence. A least-squares mean was calculated over all permuted pairs to arrive at a number for each position in the protein sequence. Statistics for t ...
Medical Chemistry and Biochemistry Exam Questions 2008/09
... 89. General principles of cell signaling. Properties of receptors. Signaling molecules, their synthesis, degradation, activation, deactivation, and role in signaling pathways. 90. G-proteins: types, significance, mechanism of function, their GTPase activity. 91. The basic cellular signaling pathways ...
... 89. General principles of cell signaling. Properties of receptors. Signaling molecules, their synthesis, degradation, activation, deactivation, and role in signaling pathways. 90. G-proteins: types, significance, mechanism of function, their GTPase activity. 91. The basic cellular signaling pathways ...
Protein Complexes – Challenges and Opportunities for
... (a) Recombinant methods like yeast-two hybrid screens or co-purification analysis of tagged proteins offer the advantage of standardized procedures and high throughput. Both are based on expression of gene construct libraries in yeast (or other cell systems), but even when applied to the proteome of ...
... (a) Recombinant methods like yeast-two hybrid screens or co-purification analysis of tagged proteins offer the advantage of standardized procedures and high throughput. Both are based on expression of gene construct libraries in yeast (or other cell systems), but even when applied to the proteome of ...
(2)membrane protein accomplish a lot of important membrane
... • In most animal cells, clathrin-coated pits and vesicles provide an efficient pathway for taking up specific macromolecules from the extracellular fluid. In this process the macromolecules bind to complementary transmembrane receptor proteins, accumulate in coated pits, and then enter the cell as ...
... • In most animal cells, clathrin-coated pits and vesicles provide an efficient pathway for taking up specific macromolecules from the extracellular fluid. In this process the macromolecules bind to complementary transmembrane receptor proteins, accumulate in coated pits, and then enter the cell as ...
travel cards B5
... •Groups of cells are called tissues. •Tissues can be grouped together and organised into organs that do a specific job. Organs work together to become systems and organisms. •Examples of cellular organisation (muscle cellmuscle tissue-heart-cardiovascular system-human ...
... •Groups of cells are called tissues. •Tissues can be grouped together and organised into organs that do a specific job. Organs work together to become systems and organisms. •Examples of cellular organisation (muscle cellmuscle tissue-heart-cardiovascular system-human ...
Chapter 5 PowerPoint
... membrane because they dissolve in lipids (alcohols) - others can not (glucose) Specific carrier proteins allow these other molecules to pass through the cell membrane easily This does not require energy (type of diffusion) only occurs when concentration is higher on one side of the membrane than the ...
... membrane because they dissolve in lipids (alcohols) - others can not (glucose) Specific carrier proteins allow these other molecules to pass through the cell membrane easily This does not require energy (type of diffusion) only occurs when concentration is higher on one side of the membrane than the ...
Document
... then the solvent will tend to diffuse across the membrane from the less concentrated to the more ...
... then the solvent will tend to diffuse across the membrane from the less concentrated to the more ...
The Chemistry of Life
... chemical in living things are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen. 3.1.2 State that a variety of other elements are needed by living organisms, including sulfur, calcium, phosphorus, iron, and sodium 3.1.3 State one role for each of the elements mentioned in 3.1.2 ...
... chemical in living things are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen. 3.1.2 State that a variety of other elements are needed by living organisms, including sulfur, calcium, phosphorus, iron, and sodium 3.1.3 State one role for each of the elements mentioned in 3.1.2 ...
Section 13.3 - CPO Science
... structure of many different molecules. Describe the importance of carbon to living organisms. Compare and contrast the structure and function of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. ...
... structure of many different molecules. Describe the importance of carbon to living organisms. Compare and contrast the structure and function of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. ...
Moving Cellular Materials
... pinches off, and the resulting vesicle enters the cytoplasm. A similar thing happens when you poke your finger into a partially inflated balloon. Your finger is surrounded by the balloon in much the same way that the protein molecule is surrounded by the cell membrane. This process of taking substan ...
... pinches off, and the resulting vesicle enters the cytoplasm. A similar thing happens when you poke your finger into a partially inflated balloon. Your finger is surrounded by the balloon in much the same way that the protein molecule is surrounded by the cell membrane. This process of taking substan ...
breakfast proteins
... Write out a template for the cereal chain using letters to correspond to the different colors of the cereal (ie. YOPPRRGYYOP). Tape this down somewhere in the corner of the room and section off this area with some string. Put some scrap paper and things to write with next to the template. To do and ...
... Write out a template for the cereal chain using letters to correspond to the different colors of the cereal (ie. YOPPRRGYYOP). Tape this down somewhere in the corner of the room and section off this area with some string. Put some scrap paper and things to write with next to the template. To do and ...
The Endosymbiotic Theory
... Mitochondrion and chloroplasts can only arise from pre-existing organelles – the DNA that codes for them is not found in the nucleus of the cell, but in naked loops of DNA within the organelles themselves. This suggests that these organelles were originally separate cells that needed to replicate th ...
... Mitochondrion and chloroplasts can only arise from pre-existing organelles – the DNA that codes for them is not found in the nucleus of the cell, but in naked loops of DNA within the organelles themselves. This suggests that these organelles were originally separate cells that needed to replicate th ...
Organic Compound Notes
... 18. Triglyceride is lipid made up of a glycerol molecule and ________(#) _____________________________. 19. The monomers that make up nucleic acids are known as __________________________________. 20. The two basic kinds of nucleic acids are _______________________ and ______________________. 21. If ...
... 18. Triglyceride is lipid made up of a glycerol molecule and ________(#) _____________________________. 19. The monomers that make up nucleic acids are known as __________________________________. 20. The two basic kinds of nucleic acids are _______________________ and ______________________. 21. If ...
unit 2 - Biochem packet_hnrs
... 18. Triglyceride is lipid made up of a glycerol molecule and ________(#) _____________________________. 19. The monomers that make up nucleic acids are known as __________________________________. 20. The two basic kinds of nucleic acids are _______________________ and ______________________. 21. If ...
... 18. Triglyceride is lipid made up of a glycerol molecule and ________(#) _____________________________. 19. The monomers that make up nucleic acids are known as __________________________________. 20. The two basic kinds of nucleic acids are _______________________ and ______________________. 21. If ...
Cell-penetrating peptide

Cell-penetrating peptides (CPPs) are short peptides that facilitate cellular uptake of various molecular cargo (from nanosize particles to small chemical molecules and large fragments of DNA). The ""cargo"" is associated with the peptides either through chemical linkage via covalent bonds or through non-covalent interactions. The function of the CPPs are to deliver the cargo into cells, a process that commonly occurs through endocytosis with the cargo delivered to the endosomes of living mammalian cells.CPPs hold great potential as in vitro and in vivo delivery vectors for use in research and medicine. Current use is limited by a lack of cell specificity in CPP-mediated cargo delivery and insufficient understanding of the modes of their uptake.CPPs typically have an amino acid composition that either contains a high relative abundance of positively charged amino acids such as lysine or arginine or has sequences that contain an alternating pattern of polar/charged amino acids and non-polar, hydrophobic amino acids. These two types of structures are referred to as polycationic or amphipathic, respectively. A third class of CPPs are the hydrophobic peptides, containing only apolar residues, with low net chargeor have hydrophobic amino acid groups that are crucial for cellular uptake.The first CPP was discovered independently by two laboratories in 1988, when it was found that the trans-activating transcriptional activator (TAT) from human immunodeficiency virus 1 (HIV-1) could be efficiently taken up from the surrounding media by numerous cell types in culture. Since then, the number of known CPPs has expanded considerably and small molecule synthetic analogues with more effective protein transduction properties have been generated.