word - My eCoach
... 5. RNA is chemically similar to DNA except that its sugars is ribose instead of deoxyribose, and the nitrogen base thymine is replaced by a structurally similar base called a. uracil. b. alanine. c. cytosine. d. codon. 6. During transcription, the genetic information on DNA for making a protein is c ...
... 5. RNA is chemically similar to DNA except that its sugars is ribose instead of deoxyribose, and the nitrogen base thymine is replaced by a structurally similar base called a. uracil. b. alanine. c. cytosine. d. codon. 6. During transcription, the genetic information on DNA for making a protein is c ...
student notes protein synthesis mutation
... THAT CODE FOR A CHARACTERISTIC, LIKE DIMPLES. REALLY ITS _______________________________I N THE DNA DETERMINE THE CHARACTERISTIC. BUT SOMETIMES PROBLEMS ARISE…. ...
... THAT CODE FOR A CHARACTERISTIC, LIKE DIMPLES. REALLY ITS _______________________________I N THE DNA DETERMINE THE CHARACTERISTIC. BUT SOMETIMES PROBLEMS ARISE…. ...
presentation source
... passed to daughter cells as a replication from the parent cell • How then, does DNA result in ‘traits’ that are exhibited in the phenotype – Answer = through transcription and translation of the genetic code to manufacture an enzyme that corresponds to a gene ...
... passed to daughter cells as a replication from the parent cell • How then, does DNA result in ‘traits’ that are exhibited in the phenotype – Answer = through transcription and translation of the genetic code to manufacture an enzyme that corresponds to a gene ...
level two biology: gene expression
... I can explain why RNA is necessary for protein synthesis by comparing the size and importance of RNA and DNA. I can show that I understand the processes of transcription and translation by stating the result of each process and why each process is necessary for protein synthesis. I can differentiate ...
... I can explain why RNA is necessary for protein synthesis by comparing the size and importance of RNA and DNA. I can show that I understand the processes of transcription and translation by stating the result of each process and why each process is necessary for protein synthesis. I can differentiate ...
Biotechnological Tools and Techniques
... • first restriction endonuclease (enzyme) isolated in 1970 • produced by bacteria • function as an “immune system” against invading viruses by cutting up the viral DNA or RNA ...
... • first restriction endonuclease (enzyme) isolated in 1970 • produced by bacteria • function as an “immune system” against invading viruses by cutting up the viral DNA or RNA ...
MUTATIONS TAKS QUESTIONS SPRING 2003 – 10: (22) The
... 10 If one nucleotide is omitted or accidentally repeated in the process of DNA duplication, which of the following is most likely to occur? F Gene deletion G* Gene mutation H Gene insertion J Gene segregation JULY 2006 – 11: 32 A deletion of a DNA base from a gene affects an organism by — F causing ...
... 10 If one nucleotide is omitted or accidentally repeated in the process of DNA duplication, which of the following is most likely to occur? F Gene deletion G* Gene mutation H Gene insertion J Gene segregation JULY 2006 – 11: 32 A deletion of a DNA base from a gene affects an organism by — F causing ...
... 9. What is mutagen? Give an example? (1) 10. How has man exploited cry protein to his benefit? (1) 11. Which type of conservation measures – in situ or ex-situ will help the larger number of species to survive? Explain. (2) 12. What is interspecific hybridization. Give an example? (2) 13. What are t ...
Higher Biology Unit 1: DNA and the Genome 5
... When a stretch of DNA does indeed behave like a molecular clock, it becomes a powerful tool for estimating the dates of lineage-splitting events. For example, imagine that a length of DNA found in two species differs by four bases (as shown below) and we know that this entire length of DNA changes a ...
... When a stretch of DNA does indeed behave like a molecular clock, it becomes a powerful tool for estimating the dates of lineage-splitting events. For example, imagine that a length of DNA found in two species differs by four bases (as shown below) and we know that this entire length of DNA changes a ...
Answers to Gene technology exam 2011-10-18
... e) Cos-sites: Sequence that give single stranded base overhang, the size of the DNA between the cos sites determines if it can be packed into phage particles. ...
... e) Cos-sites: Sequence that give single stranded base overhang, the size of the DNA between the cos sites determines if it can be packed into phage particles. ...
Gene Expression/Transcription & Translation Practice PowerPoint
... In 1917 the biologist Thomas Hunt Morgan conducted studies in which he kept some caterpillars in the dark and placed other under red, green, or blue lights. Exposure to red light produced butterflies with brightly colored wings. Exposure to green light resulted in dark-colored wings. Exposure to bl ...
... In 1917 the biologist Thomas Hunt Morgan conducted studies in which he kept some caterpillars in the dark and placed other under red, green, or blue lights. Exposure to red light produced butterflies with brightly colored wings. Exposure to green light resulted in dark-colored wings. Exposure to bl ...
Seeking an Increasingly Explicit Definition of Heredity
... Cracked genetic code- triplet mRNA codons specify each of the twenty amino acids. ...
... Cracked genetic code- triplet mRNA codons specify each of the twenty amino acids. ...
E1. A trait of pneumococci is the ability to synthesize a capsule
... E5. It does not rule out the possibility that RNA is the genetic material because RNA and DNA both contain phosphorus. One way to distinguish RNA and DNA is to provide bacteria with radiolabeled uracil in order to label RNA or provide bacteria with radiolabeled thymine to label DNA. (Note: Uracil is ...
... E5. It does not rule out the possibility that RNA is the genetic material because RNA and DNA both contain phosphorus. One way to distinguish RNA and DNA is to provide bacteria with radiolabeled uracil in order to label RNA or provide bacteria with radiolabeled thymine to label DNA. (Note: Uracil is ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis
... Deoxyribose sugar Double-stranded Thymine pairs with adenine ...
... Deoxyribose sugar Double-stranded Thymine pairs with adenine ...
Acc_Bio_Biotechnology_12
... DNA of both bacteria and yeasts. Pure chymosin can now be made. The enzyme is identical to that produced in the calf and the process itself adds no contaminants. The FDA evaluated the safety of the process and the product itself in 1990 and ruled that the enzyme preparation was safe for human consum ...
... DNA of both bacteria and yeasts. Pure chymosin can now be made. The enzyme is identical to that produced in the calf and the process itself adds no contaminants. The FDA evaluated the safety of the process and the product itself in 1990 and ruled that the enzyme preparation was safe for human consum ...
Review sheet – Chapter 10
... and builds a polypeptide by laying down the appropriate amino acid one by one; this process is called translation and occurs at a ribosome in the cytoplasm ...
... and builds a polypeptide by laying down the appropriate amino acid one by one; this process is called translation and occurs at a ribosome in the cytoplasm ...
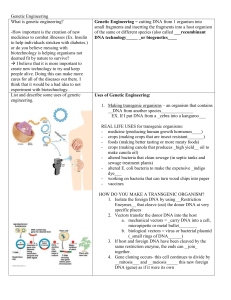
Genetic Engineering Guied Notes
... deemed fit by nature to survive? I believe that it is more important to create new technology to try and keep people alive. Doing this can make more cures for all of the diseases out there. I think that it would be a bad idea to not experiment with biotechnology. List and describe some uses of gen ...
... deemed fit by nature to survive? I believe that it is more important to create new technology to try and keep people alive. Doing this can make more cures for all of the diseases out there. I think that it would be a bad idea to not experiment with biotechnology. List and describe some uses of gen ...
Lecture, Gene Expression
... 6. The Genetic Code is used to figure out what amino acids are assembled based on the strand created from the strand ...
... 6. The Genetic Code is used to figure out what amino acids are assembled based on the strand created from the strand ...
I - Nutley Public Schools
... vi. Their historic paper describing structure pointed out "possible copying mechanism for the genetic material." ...
... vi. Their historic paper describing structure pointed out "possible copying mechanism for the genetic material." ...
Genomics on the Web Handout
... discoveries, and concepts, complete the quiz by selecting the “problem” tab at the bottom of the page. Expect to spend approximately 30 minutes to complete each chapter. ...
... discoveries, and concepts, complete the quiz by selecting the “problem” tab at the bottom of the page. Expect to spend approximately 30 minutes to complete each chapter. ...
Discovery of DNA structure
... found in the nucleus of the cell Replicates itself before the cell divides, ensuring genetic continuity Provides instructions for protein synthesis ...
... found in the nucleus of the cell Replicates itself before the cell divides, ensuring genetic continuity Provides instructions for protein synthesis ...
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... o CGA codes for o UUA codes for o UAG codes for The ribosome connects the amino acids into a protein. This protein is responsible for the appearance of a trait. ...
... o CGA codes for o UUA codes for o UAG codes for The ribosome connects the amino acids into a protein. This protein is responsible for the appearance of a trait. ...
Deoxyribozyme
_DNAzyme.png?width=300)
Deoxyribozymes, also called DNA enzymes, DNAzymes, or catalytic DNA, are DNA oligonucleotides that are capable of catalyzing specific chemical reactions, similar to the action of other biological enzymes, such as proteins or ribozymes (enzymes composed of RNA).However, in contrast to the abundance of protein enzymes in biological systems and the discovery of biological ribozymes in the 1980s,there are no known naturally occurring deoxyribozymes.Deoxyribozymes should not be confused with DNA aptamers which are oligonucleotides that selectively bind a target ligand, but do not catalyze a subsequent chemical reaction.With the exception of ribozymes, nucleic acid molecules within cells primarily serve as storage of genetic information due to its ability to form complementary base pairs, which allows for high-fidelity copying and transfer of genetic information. In contrast, nucleic acid molecules are more limited in their catalytic ability, in comparison to protein enzymes, to just three types of interactions: hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and metal-ion coordination. This is due to the limited number of functional groups of the nucleic acid monomers: while proteins are built from up to twenty different amino acids with various functional groups, nucleic acids are built from just four chemically similar nucleobases. In addition, DNA lacks the 2'-hydroxyl group found in RNA which limits the catalytic competency of deoxyribozymes even in comparison to ribozymes.In addition to the inherent inferiority of DNA catalytic activity, the apparent lack of naturally occurring deoxyribozymes may also be due to the primarily double-stranded conformation of DNA in biological systems which would limit its physical flexibility and ability to form tertiary structures, and so would drastically limit the ability of double-stranded DNA to act as a catalyst; though there are a few known instances of biological single-stranded DNA such as multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA), certain viral genomes, and the replication fork formed during DNA replication. Further structural differences between DNA and RNA may also play a role in the lack of biological deoxyribozymes, such as the additional methyl group of the DNA base thymidine compared to the RNA base uracil or the tendency of DNA to adopt the B-form helix while RNA tends to adopt the A-form helix. However, it has also been shown that DNA can form structures that RNA cannot, which suggests that, though there are differences in structures that each can form, neither is inherently more or less catalytic due to their possible structural motifs.