DNA Structure, and Function in Cells Quiz 2016 Self
... 13. Describe the 2 processes organisms use to create new cells. Why does an organism need 2 different cell division processes? ...
... 13. Describe the 2 processes organisms use to create new cells. Why does an organism need 2 different cell division processes? ...
BDOL Interactive Chalkboard - Broken Arrow Public Schools
... they provide instructions for making the protein. • More than one codon can code for the same amino acid. • However, for any one codon, there can be only one amino acid. ...
... they provide instructions for making the protein. • More than one codon can code for the same amino acid. • However, for any one codon, there can be only one amino acid. ...
experimental design
... The RNA isolation procedure is described in Jiang and Zhang (2003), no kit was used to isolate RNA. To remove any remaining DNA traces, 50µg RNA was treated with 10U of Dnase I (RNase free, TaKaRa, Code No. D2215) and 40U Ribonuclease Inhibitor (TaKaRa, Code No. D2313) in a 100µl volume. All followi ...
... The RNA isolation procedure is described in Jiang and Zhang (2003), no kit was used to isolate RNA. To remove any remaining DNA traces, 50µg RNA was treated with 10U of Dnase I (RNase free, TaKaRa, Code No. D2215) and 40U Ribonuclease Inhibitor (TaKaRa, Code No. D2313) in a 100µl volume. All followi ...
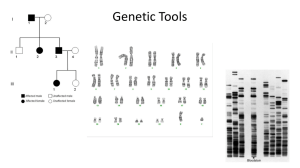
Genetic Tools
... • Mr. and Mrs. Raider are deeply worried about their child who seems to be developing at a slower rate. They are concerned for the child’s health just like any other parent and have come to you for help. ...
... • Mr. and Mrs. Raider are deeply worried about their child who seems to be developing at a slower rate. They are concerned for the child’s health just like any other parent and have come to you for help. ...
From Genes to Proteins What do genes code for?
... Retroviruses transcribe RNA into DNA through the use of an enzyme called reverse transcriptase: RNA → DNA → RNA → protein Some very primitive viruses use only RNA → proteins Prions are proteins directly replicating themselves by making conforma onal changes in other proteins, Protein → Protein (SCAR ...
... Retroviruses transcribe RNA into DNA through the use of an enzyme called reverse transcriptase: RNA → DNA → RNA → protein Some very primitive viruses use only RNA → proteins Prions are proteins directly replicating themselves by making conforma onal changes in other proteins, Protein → Protein (SCAR ...
Experiment title: Structural analysis of a chimeric bacterial α
... excursion between barrel-strands β-3 and helix α -3 (residues 104-205) forms domain B, and residues 396483 complete domain C. This gives rise to an elongated molecule, the longest axis being some 85 Å. The chimeric nature of this enzyme reveals the potential for gene shuffling to generate novel enzy ...
... excursion between barrel-strands β-3 and helix α -3 (residues 104-205) forms domain B, and residues 396483 complete domain C. This gives rise to an elongated molecule, the longest axis being some 85 Å. The chimeric nature of this enzyme reveals the potential for gene shuffling to generate novel enzy ...
No Slide Title
... All information needed for protein synthesis is located on DNA However, this information can not be used directly Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is used as an intermediate to take information from DNA to make proteins The RNA used for this transcription is called messenger RNA (mRNA) ...
... All information needed for protein synthesis is located on DNA However, this information can not be used directly Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is used as an intermediate to take information from DNA to make proteins The RNA used for this transcription is called messenger RNA (mRNA) ...
Carbon Sodium Boron Iodine Nitrogen Magnesium Cobalt
... elements within the forest ecosystem and was followed by high loss rates of nitrate, hydrogen ions, and calcium ions in stream waters for several years. (Stream chemistry data were provided by G. E. Likens with funding from the National Science Foundation and The A. W. Mellon Foundation.) ...
... elements within the forest ecosystem and was followed by high loss rates of nitrate, hydrogen ions, and calcium ions in stream waters for several years. (Stream chemistry data were provided by G. E. Likens with funding from the National Science Foundation and The A. W. Mellon Foundation.) ...
Chapter 1 Notes - Potosi School District
... 2.RNA polymerase (enzyme) binds to a region of DNA called the promoter which has the start codon AUG to code for the amino acid methionine 3.Promoters mark the beginning of a DNA chain in prokaryotes, but mark the beginning of 1 to several related genes in eukaryotes 4.The 2 DNA strands separate, bu ...
... 2.RNA polymerase (enzyme) binds to a region of DNA called the promoter which has the start codon AUG to code for the amino acid methionine 3.Promoters mark the beginning of a DNA chain in prokaryotes, but mark the beginning of 1 to several related genes in eukaryotes 4.The 2 DNA strands separate, bu ...
Gene Movement
... Gram-negative transformation (Haemophilus influenzae,Neisseriae gonorrhoeae)dsDNA binds to membraneous transformasome structure forms, which can bind sequences of up to 40 kb in length. Specific recognition sequences within the DNA are required for DNA binding and uptake in at least some Gram negati ...
... Gram-negative transformation (Haemophilus influenzae,Neisseriae gonorrhoeae)dsDNA binds to membraneous transformasome structure forms, which can bind sequences of up to 40 kb in length. Specific recognition sequences within the DNA are required for DNA binding and uptake in at least some Gram negati ...
DNA - Mrs-Lamberts-Biology
... DNA prior to cell division so the daughter cells both get a full set. The next two processes occur back to back, and this is how your genes make your body work. Each gene codes for specific protein(s) each individual cell needs to function properly and keep you alive. Many of these proteins are enz ...
... DNA prior to cell division so the daughter cells both get a full set. The next two processes occur back to back, and this is how your genes make your body work. Each gene codes for specific protein(s) each individual cell needs to function properly and keep you alive. Many of these proteins are enz ...
PTC Lab Classroom Slides
... We hope you’ve enjoyed the lab! Now you can connect phenotype to genotype in two 45- minutes classes DNA extraction ...
... We hope you’ve enjoyed the lab! Now you can connect phenotype to genotype in two 45- minutes classes DNA extraction ...
MCDB 1030
... 3. Describe the principle events that occur in the life cycle of a + strand RNA virus. i) entry into the cell; ii) replication of the genome using an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, which must copy the + strand into – strands, which are then copied to provide the + strands that will be packaged into t ...
... 3. Describe the principle events that occur in the life cycle of a + strand RNA virus. i) entry into the cell; ii) replication of the genome using an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, which must copy the + strand into – strands, which are then copied to provide the + strands that will be packaged into t ...
anti-codon
... Protein Synthesis Building protein from DNA in cells Takes code on basepai Converts it to rs ...
... Protein Synthesis Building protein from DNA in cells Takes code on basepai Converts it to rs ...
Chapter 19 Nucleic Acids
... • In prokaryotes the primary mRNA transcript is translated directly • In eukaryotes transcription occurs in the nucleus, translation in the cytoplasm • Eukaryotic mRNA is processed in the nucleus without interfering with translation • In some mRNA, pieces are removed from the middle and the ends joi ...
... • In prokaryotes the primary mRNA transcript is translated directly • In eukaryotes transcription occurs in the nucleus, translation in the cytoplasm • Eukaryotic mRNA is processed in the nucleus without interfering with translation • In some mRNA, pieces are removed from the middle and the ends joi ...
DNA, RNA, and Protein Synthesis Note Packet
... bases are covalently bonded to a sugar-phosphate unit. The paired bases meet across the helix and are joined together by ____________________ bonds. 14. ______________ always pairs with thymine. ______ hydrogen bonds form between them. ______________ always pairs with cytosine. ______ hydrogen bonds ...
... bases are covalently bonded to a sugar-phosphate unit. The paired bases meet across the helix and are joined together by ____________________ bonds. 14. ______________ always pairs with thymine. ______ hydrogen bonds form between them. ______________ always pairs with cytosine. ______ hydrogen bonds ...
Key
... phenylalanine hydroxylase contains no detectable activity for that enzyme. The mutation is best ...
... phenylalanine hydroxylase contains no detectable activity for that enzyme. The mutation is best ...
Design and Operation of Large Scale RNA production v2
... Primarily 21 nucleotides in length Double stranded ...
... Primarily 21 nucleotides in length Double stranded ...
Deoxyribozyme
_DNAzyme.png?width=300)
Deoxyribozymes, also called DNA enzymes, DNAzymes, or catalytic DNA, are DNA oligonucleotides that are capable of catalyzing specific chemical reactions, similar to the action of other biological enzymes, such as proteins or ribozymes (enzymes composed of RNA).However, in contrast to the abundance of protein enzymes in biological systems and the discovery of biological ribozymes in the 1980s,there are no known naturally occurring deoxyribozymes.Deoxyribozymes should not be confused with DNA aptamers which are oligonucleotides that selectively bind a target ligand, but do not catalyze a subsequent chemical reaction.With the exception of ribozymes, nucleic acid molecules within cells primarily serve as storage of genetic information due to its ability to form complementary base pairs, which allows for high-fidelity copying and transfer of genetic information. In contrast, nucleic acid molecules are more limited in their catalytic ability, in comparison to protein enzymes, to just three types of interactions: hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and metal-ion coordination. This is due to the limited number of functional groups of the nucleic acid monomers: while proteins are built from up to twenty different amino acids with various functional groups, nucleic acids are built from just four chemically similar nucleobases. In addition, DNA lacks the 2'-hydroxyl group found in RNA which limits the catalytic competency of deoxyribozymes even in comparison to ribozymes.In addition to the inherent inferiority of DNA catalytic activity, the apparent lack of naturally occurring deoxyribozymes may also be due to the primarily double-stranded conformation of DNA in biological systems which would limit its physical flexibility and ability to form tertiary structures, and so would drastically limit the ability of double-stranded DNA to act as a catalyst; though there are a few known instances of biological single-stranded DNA such as multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA), certain viral genomes, and the replication fork formed during DNA replication. Further structural differences between DNA and RNA may also play a role in the lack of biological deoxyribozymes, such as the additional methyl group of the DNA base thymidine compared to the RNA base uracil or the tendency of DNA to adopt the B-form helix while RNA tends to adopt the A-form helix. However, it has also been shown that DNA can form structures that RNA cannot, which suggests that, though there are differences in structures that each can form, neither is inherently more or less catalytic due to their possible structural motifs.