Document
... Genes: DNA segments that carry this information Intron: part of gene not translated into protein, spliced out of mRNA (messenger RNA – conveys genetic info from DNA to ribosome where proteins are made) Exon: mRNA translated into protein; protein consists only of exonderived sequences ...
... Genes: DNA segments that carry this information Intron: part of gene not translated into protein, spliced out of mRNA (messenger RNA – conveys genetic info from DNA to ribosome where proteins are made) Exon: mRNA translated into protein; protein consists only of exonderived sequences ...
CB098-008.22_Biochemistry
... by the U.S. Department of Labor’s Employment and Training Administration. The information contained in this product was created by a grantee organization and does not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Labor. All references to non-governmental companies or organizati ...
... by the U.S. Department of Labor’s Employment and Training Administration. The information contained in this product was created by a grantee organization and does not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Labor. All references to non-governmental companies or organizati ...
VIII. PROTEINS, continued
... o _______________________ - A change in a protein’s shape. Which results in a loss of protein’s ability to carry out ...
... o _______________________ - A change in a protein’s shape. Which results in a loss of protein’s ability to carry out ...
document
... DNA: Deoxyribonucleic acid DNA is a helical, double-stranded macromolecule with bases projecting into the interior of the molecule. DNA has the pentose, deoxyribose. Adenine hydrogen bonds to thymine, and cytosine to guanine (Chargaff’s rule). One DNA strand serves a template for a new ...
... DNA: Deoxyribonucleic acid DNA is a helical, double-stranded macromolecule with bases projecting into the interior of the molecule. DNA has the pentose, deoxyribose. Adenine hydrogen bonds to thymine, and cytosine to guanine (Chargaff’s rule). One DNA strand serves a template for a new ...
EOC Practice Test
... a. Animals use both photosynthesis and cellular respiration to produce energy for their life process b. The reactants of photosynthesis are the products of cellular respiration c. Photosynthesis is performed only by plants, and cellular respiration is performed only be animals d. The waste product o ...
... a. Animals use both photosynthesis and cellular respiration to produce energy for their life process b. The reactants of photosynthesis are the products of cellular respiration c. Photosynthesis is performed only by plants, and cellular respiration is performed only be animals d. The waste product o ...
12) Inheritance, genes and chromosomes • 13) DNA
... DNA polymerases make mistakes in replication, and DNA can be damaged in living cells. Cells have three repair mechanisms: • Proofreading (error rate 10-4 • Mismatch repair • Excision repair ...
... DNA polymerases make mistakes in replication, and DNA can be damaged in living cells. Cells have three repair mechanisms: • Proofreading (error rate 10-4 • Mismatch repair • Excision repair ...
Combining DNA Evidence for Greater Match
... analyzed in a likelihood function. Moreover, multiple STR experiments can be mathematically combined using a joint likelihood function. Statistics tells us that using more data should yield more information. We find that computing with a joint likelihood function to combine DNA evidence can infer mo ...
... analyzed in a likelihood function. Moreover, multiple STR experiments can be mathematically combined using a joint likelihood function. Statistics tells us that using more data should yield more information. We find that computing with a joint likelihood function to combine DNA evidence can infer mo ...
Lab 3 In Search of the Sickle Cell GeneSp08
... In lab today, we will be working with DNA from two hypothetical parents. These parents would like to test their DNA, and their child’s DNA, for the Sickle Cell gene. There are a variety of ways such a test could be conducted, including through the use of a Southern Blot. To conduct a Southern Blot, ...
... In lab today, we will be working with DNA from two hypothetical parents. These parents would like to test their DNA, and their child’s DNA, for the Sickle Cell gene. There are a variety of ways such a test could be conducted, including through the use of a Southern Blot. To conduct a Southern Blot, ...
Causes of Microevolution - Effingham County Schools
... Modes of Selection • Directional Selection – shifts the frequency curve for variations in some phenotypic character in one direction or the other by favoring what are initially relatively rare individuals that deviate from the average for that character • Diversifying Selection – occurs when enviro ...
... Modes of Selection • Directional Selection – shifts the frequency curve for variations in some phenotypic character in one direction or the other by favoring what are initially relatively rare individuals that deviate from the average for that character • Diversifying Selection – occurs when enviro ...
THE DNA DIET - Stellenbosch University
... but his girlfriend didn't lose even half as much weight? The answer could be in their genes — maybe he drops kilos eating sirloin and nuts but her DNA mix is better suited to pasta with pesto. The pioneers of a new diet in South Africa claim the days of "trial and error" dieting are over. But is the ...
... but his girlfriend didn't lose even half as much weight? The answer could be in their genes — maybe he drops kilos eating sirloin and nuts but her DNA mix is better suited to pasta with pesto. The pioneers of a new diet in South Africa claim the days of "trial and error" dieting are over. But is the ...
REVIEW UNIT 4 & 5: HEREDITY & MOLECULAR GENETICS SAMPLE QUESTIONS
... a. Discuss the organization of the genetic material in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. b. Contrast the following activities in prokaryotes and eukaryotes: ...
... a. Discuss the organization of the genetic material in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. b. Contrast the following activities in prokaryotes and eukaryotes: ...
Dangerous Ideas and Forbidden Knowledge, Spring 2005 Lab 3
... In lab today, we will be working with DNA from two hypothetical parents. These parents would like to test their DNA, and their child’s DNA, for the Sickle Cell gene. There are a variety of ways such a test could be conducted, including through the use of a Southern Blot. To conduct a Southern Blot, ...
... In lab today, we will be working with DNA from two hypothetical parents. These parents would like to test their DNA, and their child’s DNA, for the Sickle Cell gene. There are a variety of ways such a test could be conducted, including through the use of a Southern Blot. To conduct a Southern Blot, ...
Carbon Compounds 2-3 Foldable Instructions
... Proteins (C,H,O,N) sometimes (C,H,O,N,S) Proteins are macromolecules that contain nitrogen, carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Proteins are large molecules (polymers) made up of monomers called amino acids. Biuret Solution is an indicator solution for proteins. It turns blue-violet in the presence ...
... Proteins (C,H,O,N) sometimes (C,H,O,N,S) Proteins are macromolecules that contain nitrogen, carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Proteins are large molecules (polymers) made up of monomers called amino acids. Biuret Solution is an indicator solution for proteins. It turns blue-violet in the presence ...
Overview of Eukaryotic Gene Prediction
... extract sequence features such as {G,C} content, hexamer frequencies, etc... ...
... extract sequence features such as {G,C} content, hexamer frequencies, etc... ...
PDF
... The homeodomain is a DNA binding domain about 60 amino acids in length that occurs in many developmental regulatory proteins. Based on their degree of relatedness, homeodomain sequences have been grouped into 10 different families plus some unclassified sequences (1). Using a set of degenerate oligo ...
... The homeodomain is a DNA binding domain about 60 amino acids in length that occurs in many developmental regulatory proteins. Based on their degree of relatedness, homeodomain sequences have been grouped into 10 different families plus some unclassified sequences (1). Using a set of degenerate oligo ...
2014 Training Handout
... Notice that many of the amino acids have more than one codon A three base code on the DNA produces the mRNA codon The three base code on the t RNA is termed an anticodon because it will bond to a m-RNA codon during translation or protein synthesis ...
... Notice that many of the amino acids have more than one codon A three base code on the DNA produces the mRNA codon The three base code on the t RNA is termed an anticodon because it will bond to a m-RNA codon during translation or protein synthesis ...
7. According to Dr. Malcolm (guy in black leather jacket), “Dinosaurs
... from the mother, and one from the father. The chromosome starts as half of the familiar X. As the cell grows, it replicates the DNA to make the other half of the X, which is identical. When the cell divides, each daughter cell receives half of each chromosome (called a chromatid). The two copies of ...
... from the mother, and one from the father. The chromosome starts as half of the familiar X. As the cell grows, it replicates the DNA to make the other half of the X, which is identical. When the cell divides, each daughter cell receives half of each chromosome (called a chromatid). The two copies of ...
CHAPTER 18 OBJECTIVES-BACTERIAL GENOME The Genetics of
... 5. Describe techniques that allow identification of recombinant cells that have taken up a gene of interest. 6. Define and distinguish between genomic libraries using plasmids, phages, and cDNA. 7. Describe two techniques to introduce recombinant DNA into eukaryotic cells. 8. Describe the polymerase ...
... 5. Describe techniques that allow identification of recombinant cells that have taken up a gene of interest. 6. Define and distinguish between genomic libraries using plasmids, phages, and cDNA. 7. Describe two techniques to introduce recombinant DNA into eukaryotic cells. 8. Describe the polymerase ...
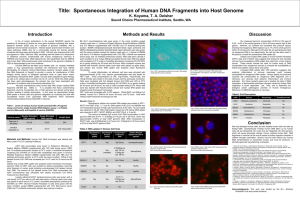
Title: Spontaneous Integration of Human DNA Fragments into Host
... spectrum disorder (ASD) may be a disease of genomic instability, with a significant environmental component. Altered double strand break formation and repair pathways (DSB) may be a commonality among the diverse genetic mutations that have been documented in ASD. US birth year change points in AD ar ...
... spectrum disorder (ASD) may be a disease of genomic instability, with a significant environmental component. Altered double strand break formation and repair pathways (DSB) may be a commonality among the diverse genetic mutations that have been documented in ASD. US birth year change points in AD ar ...
Direct measurement of electrical transport through DNA molecules
... states7,8, which could, for example, be associated with the base pairs. The hopping process could be either unidirectional or involve one-dimensional diffusion. It can be argued that the back-and-forth diffusive hopping8 is less likely in our case due to the high electric ®elds used, which will tilt ...
... states7,8, which could, for example, be associated with the base pairs. The hopping process could be either unidirectional or involve one-dimensional diffusion. It can be argued that the back-and-forth diffusive hopping8 is less likely in our case due to the high electric ®elds used, which will tilt ...
Deoxyribozyme
_DNAzyme.png?width=300)
Deoxyribozymes, also called DNA enzymes, DNAzymes, or catalytic DNA, are DNA oligonucleotides that are capable of catalyzing specific chemical reactions, similar to the action of other biological enzymes, such as proteins or ribozymes (enzymes composed of RNA).However, in contrast to the abundance of protein enzymes in biological systems and the discovery of biological ribozymes in the 1980s,there are no known naturally occurring deoxyribozymes.Deoxyribozymes should not be confused with DNA aptamers which are oligonucleotides that selectively bind a target ligand, but do not catalyze a subsequent chemical reaction.With the exception of ribozymes, nucleic acid molecules within cells primarily serve as storage of genetic information due to its ability to form complementary base pairs, which allows for high-fidelity copying and transfer of genetic information. In contrast, nucleic acid molecules are more limited in their catalytic ability, in comparison to protein enzymes, to just three types of interactions: hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and metal-ion coordination. This is due to the limited number of functional groups of the nucleic acid monomers: while proteins are built from up to twenty different amino acids with various functional groups, nucleic acids are built from just four chemically similar nucleobases. In addition, DNA lacks the 2'-hydroxyl group found in RNA which limits the catalytic competency of deoxyribozymes even in comparison to ribozymes.In addition to the inherent inferiority of DNA catalytic activity, the apparent lack of naturally occurring deoxyribozymes may also be due to the primarily double-stranded conformation of DNA in biological systems which would limit its physical flexibility and ability to form tertiary structures, and so would drastically limit the ability of double-stranded DNA to act as a catalyst; though there are a few known instances of biological single-stranded DNA such as multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA), certain viral genomes, and the replication fork formed during DNA replication. Further structural differences between DNA and RNA may also play a role in the lack of biological deoxyribozymes, such as the additional methyl group of the DNA base thymidine compared to the RNA base uracil or the tendency of DNA to adopt the B-form helix while RNA tends to adopt the A-form helix. However, it has also been shown that DNA can form structures that RNA cannot, which suggests that, though there are differences in structures that each can form, neither is inherently more or less catalytic due to their possible structural motifs.