WEEK 11
... WEEK 11 This week's lecturers dealt with biotechnology (i.e. modern molecular methods). You should now be able to articulate on the following: 1) Describe truncation selection. 2) Explain the difference between genetic engineering and standard breeding programs 3) Explain how the process of recombin ...
... WEEK 11 This week's lecturers dealt with biotechnology (i.e. modern molecular methods). You should now be able to articulate on the following: 1) Describe truncation selection. 2) Explain the difference between genetic engineering and standard breeding programs 3) Explain how the process of recombin ...
T-17 Chapter 2B notes Section 2.3 Carbon Based Molecules To this
... Enzymes are involved in almost every reaction in your body. Enzymes are a specialized protein made up of long chains of amino acids. Enzymes function is affected by temperature and pH. Enzymes work in a certain pH and temperature range and will not work properly if conditions change. This is one rea ...
... Enzymes are involved in almost every reaction in your body. Enzymes are a specialized protein made up of long chains of amino acids. Enzymes function is affected by temperature and pH. Enzymes work in a certain pH and temperature range and will not work properly if conditions change. This is one rea ...
Efficient whole-genome DNA methylation analysis of the Human
... Aberrant DNA methylation is characteristic of many cancers and differences in methylation have been observed in a wide variety of genomic contexts; for example, both within “classic” promoter-associated CpG islands and also in distal, non-CpG island regions [1, 2]. Establishing a method to broadly a ...
... Aberrant DNA methylation is characteristic of many cancers and differences in methylation have been observed in a wide variety of genomic contexts; for example, both within “classic” promoter-associated CpG islands and also in distal, non-CpG island regions [1, 2]. Establishing a method to broadly a ...
Enduring understanding 1.A: Change in the genetic makeup of a
... mathematical methods and conceptual understandings to investigate the cause(s) and effect(s) of this change. [See SP 1.5, 2.2] LO 1.2 The student is able to evaluate evidence provided by data to qualitatively and quantitatively investigate the role of natural selection in evolution. [See SP 2.2, 5.3 ...
... mathematical methods and conceptual understandings to investigate the cause(s) and effect(s) of this change. [See SP 1.5, 2.2] LO 1.2 The student is able to evaluate evidence provided by data to qualitatively and quantitatively investigate the role of natural selection in evolution. [See SP 2.2, 5.3 ...
Natural Selection Worksheet
... 3. Natural selection is the process by which certain _______________________________ make it easier 4. for some individuals to ___________________ and ____________________ , changing the 5. _____________________________________of ______________________ over time. 6. Charles Darwin’s _______ book was ...
... 3. Natural selection is the process by which certain _______________________________ make it easier 4. for some individuals to ___________________ and ____________________ , changing the 5. _____________________________________of ______________________ over time. 6. Charles Darwin’s _______ book was ...
Required Lab - Arcadia Unified School District
... cells. • Describe cells enclosed within semi-permeable membranes that regulate their interaction with their surroundings (1.a) P Investigate how enzymes are proteins that catalyze biochemical reactions by lowering the activation energy (1.b) P Assess the impact of varying temperature, ionic conditio ...
... cells. • Describe cells enclosed within semi-permeable membranes that regulate their interaction with their surroundings (1.a) P Investigate how enzymes are proteins that catalyze biochemical reactions by lowering the activation energy (1.b) P Assess the impact of varying temperature, ionic conditio ...
Nerve activates contraction
... 2. Restriction enzymes are used to make recombinant DNA • Gene cloning and genetic engineering were made possible by the discovery of restriction enzymes that cut DNA molecules at specific locations. • In nature, bacteria use restriction enzymes to cut foreign DNA, such as from phages or other bact ...
... 2. Restriction enzymes are used to make recombinant DNA • Gene cloning and genetic engineering were made possible by the discovery of restriction enzymes that cut DNA molecules at specific locations. • In nature, bacteria use restriction enzymes to cut foreign DNA, such as from phages or other bact ...
Nerve activates contraction
... 2. Restriction enzymes are used to make recombinant DNA • Gene cloning and genetic engineering were made possible by the discovery of restriction enzymes that cut DNA molecules at specific locations. • In nature, bacteria use restriction enzymes to cut foreign DNA, such as from phages or other bact ...
... 2. Restriction enzymes are used to make recombinant DNA • Gene cloning and genetic engineering were made possible by the discovery of restriction enzymes that cut DNA molecules at specific locations. • In nature, bacteria use restriction enzymes to cut foreign DNA, such as from phages or other bact ...
Section A: DNA Cloning CHAPTER 20 DNA TECHNOLOGY AND
... • A more limited kind of gene library can be developed from complementary DNA. • During the process of producing cDNA, all mRNAs are converted to cDNA strands. • This cDNA library represents that part of a cell’s genome that was transcribed in the starting cells. • This is an advantage if a researc ...
... • A more limited kind of gene library can be developed from complementary DNA. • During the process of producing cDNA, all mRNAs are converted to cDNA strands. • This cDNA library represents that part of a cell’s genome that was transcribed in the starting cells. • This is an advantage if a researc ...
Overview of New Structures and Strategies for DNA
... (red) going in opposite directions through the DX tile and are used to encode input and output information. Panel-b gives the truth table for XOR and a representation of the computational tile types. The two helical domains are drawn as rectangles, flanked by sticky ends shown as geometrical shapes. ...
... (red) going in opposite directions through the DX tile and are used to encode input and output information. Panel-b gives the truth table for XOR and a representation of the computational tile types. The two helical domains are drawn as rectangles, flanked by sticky ends shown as geometrical shapes. ...
Chem 400 Biochemistry I
... •Biochemistry is essential to all of the life sciences (biomedical and plant sciences) All advanced degrees require that biochemistry is one of the first courses •This class will be taught not - as an advanced organic but as an encompassing science that should help tie several of your classes togeth ...
... •Biochemistry is essential to all of the life sciences (biomedical and plant sciences) All advanced degrees require that biochemistry is one of the first courses •This class will be taught not - as an advanced organic but as an encompassing science that should help tie several of your classes togeth ...
Nucleic Acids
... 1) Name the monomer of nucleic acids. 2) Draw & Label a nucleotide. 3) How are the four nitrogen bases of DNA abbreviated? RNA? 4) What does the phosphate molecule of a nucleotide bond with? 5) What do you call a section of DNA that codes for a specific protein? 6) If the DNA nitrogen bases were TAC ...
... 1) Name the monomer of nucleic acids. 2) Draw & Label a nucleotide. 3) How are the four nitrogen bases of DNA abbreviated? RNA? 4) What does the phosphate molecule of a nucleotide bond with? 5) What do you call a section of DNA that codes for a specific protein? 6) If the DNA nitrogen bases were TAC ...
Modeling Genetic Engineering Lab
... An understanding of the basis of inheritance has led to a new form of applied genetics called genetic engineering. Genetic engineering is the use of genetics for practical purposes. For example, it can be used to identify genes for specific traits or transfer genes for a specific trait from one orga ...
... An understanding of the basis of inheritance has led to a new form of applied genetics called genetic engineering. Genetic engineering is the use of genetics for practical purposes. For example, it can be used to identify genes for specific traits or transfer genes for a specific trait from one orga ...
biology - OoCities
... responsible for polymerization reactions were clay minerals and RNA. Polymers are chains of similar building blcoks or monomers, synthesized by condensation reactions (H and OH are removed from polymers and H20 is produced). Early polymerization reactions must have occurred without the help of enzym ...
... responsible for polymerization reactions were clay minerals and RNA. Polymers are chains of similar building blcoks or monomers, synthesized by condensation reactions (H and OH are removed from polymers and H20 is produced). Early polymerization reactions must have occurred without the help of enzym ...
Study Questions-II
... 1. In the 1940's, scientists knew that chromosomes consisted of DNA and protein. Given the great amount, and the diversity, of heritable information known to be passed from parent to offspring, most researchers thought that proteins must be the genetic material. Why do you think they thought that? ( ...
... 1. In the 1940's, scientists knew that chromosomes consisted of DNA and protein. Given the great amount, and the diversity, of heritable information known to be passed from parent to offspring, most researchers thought that proteins must be the genetic material. Why do you think they thought that? ( ...
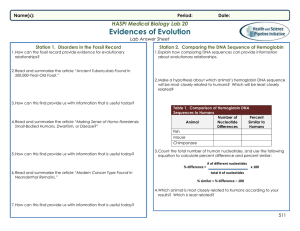
Evidence for Evolution Student Answer Sheet
... 1. Explain how comparing DNA sequences can provide information about evolutionary relationships. ...
... 1. Explain how comparing DNA sequences can provide information about evolutionary relationships. ...
Building Monomers of Macromolecules
... 14. Glycerol and other organic compounds with an –ol ending are called ___________________. 15. Triglycerides are the monomers for what type of macromolecule? ...
... 14. Glycerol and other organic compounds with an –ol ending are called ___________________. 15. Triglycerides are the monomers for what type of macromolecule? ...
Building Monomers of Macromolecules
... 14. Glycerol and other organic compounds with an –ol ending are called ___________________. 15. Triglycerides are the monomers for what type of macromolecule? ...
... 14. Glycerol and other organic compounds with an –ol ending are called ___________________. 15. Triglycerides are the monomers for what type of macromolecule? ...
Genetics Project
... Collects and passes out group materials and work Communicates with the teacher Assigns a ‘Daily Participation Grade’ for each member of the group Collects and grades homework for the group when necessary ...
... Collects and passes out group materials and work Communicates with the teacher Assigns a ‘Daily Participation Grade’ for each member of the group Collects and grades homework for the group when necessary ...
Correct response
... a. The genetic sequence is found on the pyrimidine bases, so there must be a pyrimidine in each step of the DNA ladder b. The number of hydrogen bonds between the bases must “match” in order for the helix to be double stranded. c. The phosphate bonds required to hold each single strand together must ...
... a. The genetic sequence is found on the pyrimidine bases, so there must be a pyrimidine in each step of the DNA ladder b. The number of hydrogen bonds between the bases must “match” in order for the helix to be double stranded. c. The phosphate bonds required to hold each single strand together must ...
Organic Compounds PowerPoint PDF
... All amino acids have the same Amino group and carboxyl groups, but each amino acid has its own unique R- group. Only 20 amino acids can combine in different arrangements to form all of the many different kinds of proteins in our bodies! Shape is very important; if a protein is not the right shape, i ...
... All amino acids have the same Amino group and carboxyl groups, but each amino acid has its own unique R- group. Only 20 amino acids can combine in different arrangements to form all of the many different kinds of proteins in our bodies! Shape is very important; if a protein is not the right shape, i ...
Deoxyribozyme
_DNAzyme.png?width=300)
Deoxyribozymes, also called DNA enzymes, DNAzymes, or catalytic DNA, are DNA oligonucleotides that are capable of catalyzing specific chemical reactions, similar to the action of other biological enzymes, such as proteins or ribozymes (enzymes composed of RNA).However, in contrast to the abundance of protein enzymes in biological systems and the discovery of biological ribozymes in the 1980s,there are no known naturally occurring deoxyribozymes.Deoxyribozymes should not be confused with DNA aptamers which are oligonucleotides that selectively bind a target ligand, but do not catalyze a subsequent chemical reaction.With the exception of ribozymes, nucleic acid molecules within cells primarily serve as storage of genetic information due to its ability to form complementary base pairs, which allows for high-fidelity copying and transfer of genetic information. In contrast, nucleic acid molecules are more limited in their catalytic ability, in comparison to protein enzymes, to just three types of interactions: hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and metal-ion coordination. This is due to the limited number of functional groups of the nucleic acid monomers: while proteins are built from up to twenty different amino acids with various functional groups, nucleic acids are built from just four chemically similar nucleobases. In addition, DNA lacks the 2'-hydroxyl group found in RNA which limits the catalytic competency of deoxyribozymes even in comparison to ribozymes.In addition to the inherent inferiority of DNA catalytic activity, the apparent lack of naturally occurring deoxyribozymes may also be due to the primarily double-stranded conformation of DNA in biological systems which would limit its physical flexibility and ability to form tertiary structures, and so would drastically limit the ability of double-stranded DNA to act as a catalyst; though there are a few known instances of biological single-stranded DNA such as multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA), certain viral genomes, and the replication fork formed during DNA replication. Further structural differences between DNA and RNA may also play a role in the lack of biological deoxyribozymes, such as the additional methyl group of the DNA base thymidine compared to the RNA base uracil or the tendency of DNA to adopt the B-form helix while RNA tends to adopt the A-form helix. However, it has also been shown that DNA can form structures that RNA cannot, which suggests that, though there are differences in structures that each can form, neither is inherently more or less catalytic due to their possible structural motifs.