30. genetic code
... and coworkers in 1961. During their experiment, when they added or deleted single, or double base pairs in a particular region of DNA of T4 bacteriophages of E. coli, they found that such bacteriophages ceased to perform their normal functions. However, bacteriophages with addition or deletion of th ...
... and coworkers in 1961. During their experiment, when they added or deleted single, or double base pairs in a particular region of DNA of T4 bacteriophages of E. coli, they found that such bacteriophages ceased to perform their normal functions. However, bacteriophages with addition or deletion of th ...
Vitamins and Coenzymes - KSU - Home
... (1) Essential ions (mostly metal ions) (2) Coenzymes (organic compounds) Apoenzyme + Cofactor ...
... (1) Essential ions (mostly metal ions) (2) Coenzymes (organic compounds) Apoenzyme + Cofactor ...
Coenzyme B 12-Dependent Ribonucleotide Reductase: Evidence
... coli ribonucleoside diphosphate reductase. Despite the differences between these two reductases in primary sequence, quaternary structure, and cofactor requirements, their mechanisms are strikingly similar. The mutagenesis studies reported herein further suggest that the complex role of the five cys ...
... coli ribonucleoside diphosphate reductase. Despite the differences between these two reductases in primary sequence, quaternary structure, and cofactor requirements, their mechanisms are strikingly similar. The mutagenesis studies reported herein further suggest that the complex role of the five cys ...
to Sample Chapter
... v. Awarded Nobel prize. i. Took interest in both proteins and nucleic acid at Cambridge in UK ii. Shared Nobel prize for medicine and physiology for cracking the genetic code. i. Most noted for one of two co-discoveries of the structure of DNA molecule. ii. Awarded Nobel prize i. Two times awarded N ...
... v. Awarded Nobel prize. i. Took interest in both proteins and nucleic acid at Cambridge in UK ii. Shared Nobel prize for medicine and physiology for cracking the genetic code. i. Most noted for one of two co-discoveries of the structure of DNA molecule. ii. Awarded Nobel prize i. Two times awarded N ...
Molecular Analysis of the Coprinus cinereus Mating Type A Factor
... We initially transformed with poolsof DNA composed of 96 clones from microtiter plates and once A was located in plate 203, used the “elimination” scheme of METZENBERG and KANG(1987) to locate the A clone. Because plate 203 had 2 clones of A , an incorrect well (A2) was indicated by the results of t ...
... We initially transformed with poolsof DNA composed of 96 clones from microtiter plates and once A was located in plate 203, used the “elimination” scheme of METZENBERG and KANG(1987) to locate the A clone. Because plate 203 had 2 clones of A , an incorrect well (A2) was indicated by the results of t ...
Evolutionary aspects of recombination in RNA viruses
... RNA viruses deserve their reputation as Nature’s swiftest evolvers. Their high rates of mutation and replication (Holland et al., 1982) allow them to move through sequence space at a pace that often makes their DNA-based hosts ’ evolution look glacial by comparison. Over the last two decades it has ...
... RNA viruses deserve their reputation as Nature’s swiftest evolvers. Their high rates of mutation and replication (Holland et al., 1982) allow them to move through sequence space at a pace that often makes their DNA-based hosts ’ evolution look glacial by comparison. Over the last two decades it has ...
Practical and Efficient Synthesis of -Aminophosphonic Acids
... of this synthesis is the introduction of the phosphonate group in the N-acyliminium ion intermediates, obtained from activation of the quinoline and isoquinoline heterocycles or from the appropriate δ-lactam with benzyl chloroformate. Finally, the hydrolysis of phosphonate moiety with simultaneous c ...
... of this synthesis is the introduction of the phosphonate group in the N-acyliminium ion intermediates, obtained from activation of the quinoline and isoquinoline heterocycles or from the appropriate δ-lactam with benzyl chloroformate. Finally, the hydrolysis of phosphonate moiety with simultaneous c ...
A-level Biology Previous essay titles and mark schemes
... Making Use of Bacteria 3.5.8 Use of bacterial enzymes e.g. restriction endonuclease, DNA polymerase for PCR 3.5.8 Use of bacterial plasmids e.g. in vivo gene cloning, geneticallymodified crops, gene therapy 3.5.8 Use of bacteria to produce useful ...
... Making Use of Bacteria 3.5.8 Use of bacterial enzymes e.g. restriction endonuclease, DNA polymerase for PCR 3.5.8 Use of bacterial plasmids e.g. in vivo gene cloning, geneticallymodified crops, gene therapy 3.5.8 Use of bacteria to produce useful ...
AAlast+nuc
... Most amino acid degradations begin with transaminations to make glutamate; the resulting alpha-keto acids are further metabolized ...
... Most amino acid degradations begin with transaminations to make glutamate; the resulting alpha-keto acids are further metabolized ...
One-Pot Asymmetric Synthesis of β-Cyanohydroxymethyl r
... of L-proline.3a Because of the aldehyde functionality present in the product, the excellent diastereo- and enantioselectivities of the reaction, and the mild reaction conditions provided by L-proline catalysis,4 the products should be useful for the further transformations such as nucleophilic react ...
... of L-proline.3a Because of the aldehyde functionality present in the product, the excellent diastereo- and enantioselectivities of the reaction, and the mild reaction conditions provided by L-proline catalysis,4 the products should be useful for the further transformations such as nucleophilic react ...
SQA CfE Higher Human Biology Unit 1: Human Cells
... After fertilisation, the zygote undergoes repeated mitotic divisions to form first a solid ball of cells and then a hollow ball with a fluid-filled interior. Early in this process, the cells are unspecialised and are capable of developing into any of the body's cell types. Later, the cells lose this ...
... After fertilisation, the zygote undergoes repeated mitotic divisions to form first a solid ball of cells and then a hollow ball with a fluid-filled interior. Early in this process, the cells are unspecialised and are capable of developing into any of the body's cell types. Later, the cells lose this ...
tRNA-derived short RNAs bind to Saccharomyces cerevisiae
... are highly stable, and therefore their rapid turnover would not be beneficial for the cell. Nevertheless, if tRNA is unable to accurately and efficiently play its role in protein synthesis by correctly charging its cognate amino acid or to perform other additional functions, its presence may be harm ...
... are highly stable, and therefore their rapid turnover would not be beneficial for the cell. Nevertheless, if tRNA is unable to accurately and efficiently play its role in protein synthesis by correctly charging its cognate amino acid or to perform other additional functions, its presence may be harm ...
Associated with Interstitial Lung Disease Asparaginyl
... IPP from HeLa cell extracts was performed as previously described (5, 9). A total of 10 ml of patient sera was mixed with 2 mg of protein A-Sepharose CL-4B (Pharmacia Biotech AB, Uppsala, Sweden) in 500 ml of IPP buffer (10 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0, 500 mM NaCl, 0.1% Nonidet P-40) and incubated with end- ...
... IPP from HeLa cell extracts was performed as previously described (5, 9). A total of 10 ml of patient sera was mixed with 2 mg of protein A-Sepharose CL-4B (Pharmacia Biotech AB, Uppsala, Sweden) in 500 ml of IPP buffer (10 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0, 500 mM NaCl, 0.1% Nonidet P-40) and incubated with end- ...
Enzyme kinetics and its relevance to enzyme assay
... simpler to use and require less costly equipment, but their reliability is suspect. In two-point assay systems measurements are only taken before and after a fixed incubation period, and consequently there is no certainty that the rate is constant during the whole of the reaction period, ie, there i ...
... simpler to use and require less costly equipment, but their reliability is suspect. In two-point assay systems measurements are only taken before and after a fixed incubation period, and consequently there is no certainty that the rate is constant during the whole of the reaction period, ie, there i ...
TOTAL POLYPHENOLIC CONTENT AND FREE RADICAL QUENCHING POTENTIAL OF DIOSCOREA ALATA
... and can be effectively utilized as source of natural antioxidants. DA is an important staple food as well as medicinal plant but its scientific authentication and mechanism of action has not been investigated. Methods: We investigated ethanolic and water extracts of DA for its polyphenolic content a ...
... and can be effectively utilized as source of natural antioxidants. DA is an important staple food as well as medicinal plant but its scientific authentication and mechanism of action has not been investigated. Methods: We investigated ethanolic and water extracts of DA for its polyphenolic content a ...
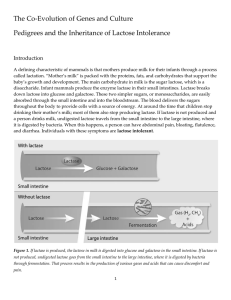
The Co-Evolution of Genes and Culture Pedigrees and the
... lactose tolerant. They can also be referred to as being lactase persistent, meaning that lactase production persists beyond childhood. (People who no longer produce lactase as adults are called lactase nonpersistent.) Genetic studies suggest that lactose tolerance arose among human populations in th ...
... lactose tolerant. They can also be referred to as being lactase persistent, meaning that lactase production persists beyond childhood. (People who no longer produce lactase as adults are called lactase nonpersistent.) Genetic studies suggest that lactose tolerance arose among human populations in th ...
A standard nomenclature for von Willebrand factor gene mutations
... For intronic changes, where nt close to the intron/exon boundary are numbered, it is simple to use the cDNA numbering with a + or - sign to designate distance into the intron. For alterations deeper into the intron, the full VWF genomic DNA sequence should be used once it is readily available, until ...
... For intronic changes, where nt close to the intron/exon boundary are numbered, it is simple to use the cDNA numbering with a + or - sign to designate distance into the intron. For alterations deeper into the intron, the full VWF genomic DNA sequence should be used once it is readily available, until ...
Microbial Ecology: Where are we now?
... ecology and epidemiology. Typing systems are evaluated in terms of reliability, reproducibility, discriminatory power, as well as data interpretation. The method of choice also depends upon ease of use, time taken and cost involved (Foxman et al. 2005). Perhaps the most important application of iden ...
... ecology and epidemiology. Typing systems are evaluated in terms of reliability, reproducibility, discriminatory power, as well as data interpretation. The method of choice also depends upon ease of use, time taken and cost involved (Foxman et al. 2005). Perhaps the most important application of iden ...
An improved protocol for pulsed-field gel electrophoresis typing of
... has very potent endonucleases that may degrade the extracted DNA inside the agarose plug during the extended process (Spigaglia et al., 2001). Some strains may produce fewer nucleases, which could be removed or degraded during nucleic acid extraction. In our proposed protocol, we shortened incubatio ...
... has very potent endonucleases that may degrade the extracted DNA inside the agarose plug during the extended process (Spigaglia et al., 2001). Some strains may produce fewer nucleases, which could be removed or degraded during nucleic acid extraction. In our proposed protocol, we shortened incubatio ...
Deoxyribozyme
_DNAzyme.png?width=300)
Deoxyribozymes, also called DNA enzymes, DNAzymes, or catalytic DNA, are DNA oligonucleotides that are capable of catalyzing specific chemical reactions, similar to the action of other biological enzymes, such as proteins or ribozymes (enzymes composed of RNA).However, in contrast to the abundance of protein enzymes in biological systems and the discovery of biological ribozymes in the 1980s,there are no known naturally occurring deoxyribozymes.Deoxyribozymes should not be confused with DNA aptamers which are oligonucleotides that selectively bind a target ligand, but do not catalyze a subsequent chemical reaction.With the exception of ribozymes, nucleic acid molecules within cells primarily serve as storage of genetic information due to its ability to form complementary base pairs, which allows for high-fidelity copying and transfer of genetic information. In contrast, nucleic acid molecules are more limited in their catalytic ability, in comparison to protein enzymes, to just three types of interactions: hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and metal-ion coordination. This is due to the limited number of functional groups of the nucleic acid monomers: while proteins are built from up to twenty different amino acids with various functional groups, nucleic acids are built from just four chemically similar nucleobases. In addition, DNA lacks the 2'-hydroxyl group found in RNA which limits the catalytic competency of deoxyribozymes even in comparison to ribozymes.In addition to the inherent inferiority of DNA catalytic activity, the apparent lack of naturally occurring deoxyribozymes may also be due to the primarily double-stranded conformation of DNA in biological systems which would limit its physical flexibility and ability to form tertiary structures, and so would drastically limit the ability of double-stranded DNA to act as a catalyst; though there are a few known instances of biological single-stranded DNA such as multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA), certain viral genomes, and the replication fork formed during DNA replication. Further structural differences between DNA and RNA may also play a role in the lack of biological deoxyribozymes, such as the additional methyl group of the DNA base thymidine compared to the RNA base uracil or the tendency of DNA to adopt the B-form helix while RNA tends to adopt the A-form helix. However, it has also been shown that DNA can form structures that RNA cannot, which suggests that, though there are differences in structures that each can form, neither is inherently more or less catalytic due to their possible structural motifs.