MIDTERM EXAM – JANUARY, 2003
... 23. What is the total number of neutrons in an atom with an atomic number of 16 and a mass number of 35? 24. The first person to devise something similar to the modern periodic table was 25. The ______________________ uncertainty principle states that it is impossible to simultaneously know both the ...
... 23. What is the total number of neutrons in an atom with an atomic number of 16 and a mass number of 35? 24. The first person to devise something similar to the modern periodic table was 25. The ______________________ uncertainty principle states that it is impossible to simultaneously know both the ...
Multi-electron atoms
... What affects total energy of outermost electron? 3s 1. The effective charge (force) it feels towards center 2p of atom. 1s 2s 2. It’s distance from the nucleus. What effective charge does 3s electron feel pulling it towards the nucleus? Close to 1 proton… 10 electrons closer in shield (cancel) a lot ...
... What affects total energy of outermost electron? 3s 1. The effective charge (force) it feels towards center 2p of atom. 1s 2s 2. It’s distance from the nucleus. What effective charge does 3s electron feel pulling it towards the nucleus? Close to 1 proton… 10 electrons closer in shield (cancel) a lot ...
Atomic Physics
... The structure of atoms and that of the periodic table can be explained with this principle and the further assumption that atomic electrons tend to occupy the lowest available energy states. To see how this works, let us consider the next simplest atom after hydrogen, i.e., helium. The helium atom ...
... The structure of atoms and that of the periodic table can be explained with this principle and the further assumption that atomic electrons tend to occupy the lowest available energy states. To see how this works, let us consider the next simplest atom after hydrogen, i.e., helium. The helium atom ...
Chapter 7. Atomic Physics
... The structure of atoms and that of the periodic table can be explained with this principle and the further assumption that atomic electrons tend to occupy the lowest available energy states. To see how this works, let us consider the next simplest atom after hydrogen, i.e., helium. The helium atom ...
... The structure of atoms and that of the periodic table can be explained with this principle and the further assumption that atomic electrons tend to occupy the lowest available energy states. To see how this works, let us consider the next simplest atom after hydrogen, i.e., helium. The helium atom ...
Unit B review - mvhs
... IE and EA “increase” (although EA gets more neg) as you move right across a period, but radius decreases B Group I(A) elements have 1 valence e- (compared to 7), lower EA, larger radii, and lower IE D 2nd IE is removing an e- from a filled shell in Na and K, but since the e- is being removed from a ...
... IE and EA “increase” (although EA gets more neg) as you move right across a period, but radius decreases B Group I(A) elements have 1 valence e- (compared to 7), lower EA, larger radii, and lower IE D 2nd IE is removing an e- from a filled shell in Na and K, but since the e- is being removed from a ...
3 section 4.2
... atomic orbitals and the properties of electrons in those orbitals Magnetic quantum # (ml) – orientation of the orbital around the nucleus Spin quantum # – indicate the two ...
... atomic orbitals and the properties of electrons in those orbitals Magnetic quantum # (ml) – orientation of the orbital around the nucleus Spin quantum # – indicate the two ...
The Atom and Its Properties
... “neon core” + 3s1 [Ne] 3s1 (uses noble gas notation) Note that we have begun a new period. ...
... “neon core” + 3s1 [Ne] 3s1 (uses noble gas notation) Note that we have begun a new period. ...
Bio_130_files/Chemistry Review
... • A substance that is composed of only one type of atom is called an element. – Elements are the simplest form of matter with unique chemical properties. They are charted on the periodic table based on some of their chemical characteristics. • There are 24 major elements that have various roles in t ...
... • A substance that is composed of only one type of atom is called an element. – Elements are the simplest form of matter with unique chemical properties. They are charted on the periodic table based on some of their chemical characteristics. • There are 24 major elements that have various roles in t ...
QUANTUM NUMBERS
... these diagrams indicate which orbital energy levels are occupied by electrons for an atom or ion In fig.2 on p. 187, as atoms become larger & the main energy levels come closer, some sublevels may overlap Generally the sublevels for a particular value of n, increase in energy in the order of s ...
... these diagrams indicate which orbital energy levels are occupied by electrons for an atom or ion In fig.2 on p. 187, as atoms become larger & the main energy levels come closer, some sublevels may overlap Generally the sublevels for a particular value of n, increase in energy in the order of s ...
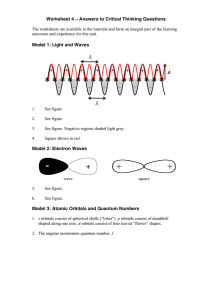
Answers to Critical Thinking Questions 4
... a. The Aufbau principle: Orbitals are filled with electrons in order of energy with the lowest energy orbital being filled first. b. Pauli Exclusion Principle: no two electrons may have the same set of quantum numbers. No orbital can accommodate more than 2 electrons. c. Hund’s Rule: in a set of orb ...
... a. The Aufbau principle: Orbitals are filled with electrons in order of energy with the lowest energy orbital being filled first. b. Pauli Exclusion Principle: no two electrons may have the same set of quantum numbers. No orbital can accommodate more than 2 electrons. c. Hund’s Rule: in a set of orb ...
Technisch-Administrativer Leiter - Max-Born
... chirp encoded property of the electron recollisions. The initial experimental confirmation of this technique in H2 and CH4 are presented and discussed. New observations of transient two-centre interference in the H2 molecule are obtained via the same method. In this case the two-centre destructive i ...
... chirp encoded property of the electron recollisions. The initial experimental confirmation of this technique in H2 and CH4 are presented and discussed. New observations of transient two-centre interference in the H2 molecule are obtained via the same method. In this case the two-centre destructive i ...
Combining and Choosing Analytical Techniques
... One of the most common and useful analytical tools used in combination with other techniques is mass spectrometry. Mass Spec can be used for: ...
... One of the most common and useful analytical tools used in combination with other techniques is mass spectrometry. Mass Spec can be used for: ...
Worksheets for Chapter 7
... Which quantum number indicates the electron’s energy level? Which quantum number indicates the electron’s sub-energy level? Which quantum number indicates the electron’s orbital within the sub-energy level? Which quantum number indicates the electron’s spin? What is the lowest energy level that has ...
... Which quantum number indicates the electron’s energy level? Which quantum number indicates the electron’s sub-energy level? Which quantum number indicates the electron’s orbital within the sub-energy level? Which quantum number indicates the electron’s spin? What is the lowest energy level that has ...
Physics 124 : Particles and Waves
... 2. Atoms emit and absorb a discrete spectrum of light, only photons that match the interval between stationary states can be emitted or absorbed; 3. Emission spectra can be produced by collisions; 4. Absorption wavelengths are a subset of the emission wavelengths; ...
... 2. Atoms emit and absorb a discrete spectrum of light, only photons that match the interval between stationary states can be emitted or absorbed; 3. Emission spectra can be produced by collisions; 4. Absorption wavelengths are a subset of the emission wavelengths; ...
Ch05ElectronConfig - Journigan-wiki
... space; the direction in which it points. Degenerate orbitals: those orbitals with the same size (n) and shape (l) which have the same energy. e.g., the three 2p orbitals the five 3d orbitals ...
... space; the direction in which it points. Degenerate orbitals: those orbitals with the same size (n) and shape (l) which have the same energy. e.g., the three 2p orbitals the five 3d orbitals ...
EMR and the Bohr Model of the Atom
... • stated that EMR could be viewed as a stream of particles “photons” • photon- a quantum of light • energy of these photons could be calculated by Planck’s equation • stated that the photons strike the electrons therefore ejecting them from the metal ...
... • stated that EMR could be viewed as a stream of particles “photons” • photon- a quantum of light • energy of these photons could be calculated by Planck’s equation • stated that the photons strike the electrons therefore ejecting them from the metal ...
Auger electron spectroscopy
.jpg?width=300)
Auger electron spectroscopy (AES; pronounced [oʒe] in French) is a common analytical technique used specifically in the study of surfaces and, more generally, in the area of materials science. Underlying the spectroscopic technique is the Auger effect, as it has come to be called, which is based on the analysis of energetic electrons emitted from an excited atom after a series of internal relaxation events. The Auger effect was discovered independently by both Lise Meitner and Pierre Auger in the 1920s. Though the discovery was made by Meitner and initially reported in the journal Zeitschrift für Physik in 1922, Auger is credited with the discovery in most of the scientific community. Until the early 1950s Auger transitions were considered nuisance effects by spectroscopists, not containing much relevant material information, but studied so as to explain anomalies in x-ray spectroscopy data. Since 1953 however, AES has become a practical and straightforward characterization technique for probing chemical and compositional surface environments and has found applications in metallurgy, gas-phase chemistry, and throughout the microelectronics industry.