Pairwise sequence alignments
... • Substitution matrices do not take into account long range interactions between residues. • They assume that identical residues are equal (whereas in reallife a residue at the active site has other evolutionary constraints than the same residue outside of the active site) • They assume evolution ra ...
... • Substitution matrices do not take into account long range interactions between residues. • They assume that identical residues are equal (whereas in reallife a residue at the active site has other evolutionary constraints than the same residue outside of the active site) • They assume evolution ra ...
Vitaminler - mustafaaltinisik.org.uk
... 1860- Louis Pasteur demonstrated that microscopic organisms can cause diseases 1880- Christian Eijkman vitamin-deficiency conditions in animals on an experimental basis 1905- Julius Friedenwald and John Ruhräh Beri-Beri is probably of microbic origin ...
... 1860- Louis Pasteur demonstrated that microscopic organisms can cause diseases 1880- Christian Eijkman vitamin-deficiency conditions in animals on an experimental basis 1905- Julius Friedenwald and John Ruhräh Beri-Beri is probably of microbic origin ...
Improved RP-HPLC and anion-exchange chromatography methods
... and between mannose and xylose can be achieved with the CarboPac PA 1 columns. The co-elution of mannose and xylose on the CarboPac PA 10 (Jahnel et al., 1998; Guignard et al., 2005; DeRuiter et al., 1992; Borch and Kirchman, 1997) is unfavorable as well. Currie and Perry (2006) could fully resolve ...
... and between mannose and xylose can be achieved with the CarboPac PA 1 columns. The co-elution of mannose and xylose on the CarboPac PA 10 (Jahnel et al., 1998; Guignard et al., 2005; DeRuiter et al., 1992; Borch and Kirchman, 1997) is unfavorable as well. Currie and Perry (2006) could fully resolve ...
Dosyayı İndir
... Within the cell, the protein will not be found in this linear state Rather, it will adapt a compact 3-D structure ...
... Within the cell, the protein will not be found in this linear state Rather, it will adapt a compact 3-D structure ...
Summary - University of Amsterdam
... -oxidation, the degradation of purines,, polyamines, L-pipecoic acid and D-amino acids, and the biosynthesis of etherphospholipids andd bile acids. The peroxisomal localization of these functions raises the question of how the transportt across the peroxisomal membrane is accomplished. Soon after th ...
... -oxidation, the degradation of purines,, polyamines, L-pipecoic acid and D-amino acids, and the biosynthesis of etherphospholipids andd bile acids. The peroxisomal localization of these functions raises the question of how the transportt across the peroxisomal membrane is accomplished. Soon after th ...
Unit 1 (ch 3)
... 3.8 Lipids include fats, which are mostly energystorage molecules • These compounds are composed largely of carbon and hydrogen – They are not true polymers ...
... 3.8 Lipids include fats, which are mostly energystorage molecules • These compounds are composed largely of carbon and hydrogen – They are not true polymers ...
Hydrocarbons and Fuels - Deans Community High School
... called alkaloids which are produced by plants. The name alkaloid means “alkali-like”, where alkali is a base and hence refers to these basic properties. ...
... called alkaloids which are produced by plants. The name alkaloid means “alkali-like”, where alkali is a base and hence refers to these basic properties. ...
Carbohydrate metabolism
... •Epinephrine stimulates α1 adrenergic receptors in liver → activation of phospholipase-C which hydrolyses phosphatidyl inositol into 1,2 diacylglycerol and inositol triphosphate → release Ca++ from its intracellular stores into the cytoplasm raising the intracytoplasmic concentration of Ca++ which r ...
... •Epinephrine stimulates α1 adrenergic receptors in liver → activation of phospholipase-C which hydrolyses phosphatidyl inositol into 1,2 diacylglycerol and inositol triphosphate → release Ca++ from its intracellular stores into the cytoplasm raising the intracytoplasmic concentration of Ca++ which r ...
Liver glycogen constitutes a reserve of glucose for the
... by gluconeogenesis, which is the synthesis of glucose from non-carbohydrate precursors: lactate, propionate, glycerol, pyruvate, gluconeogenic amino acids. The contribution of gluconeogensis to meeting glucose requirements clearly depends on the amount of carbohydrates absorbed from the intestine, w ...
... by gluconeogenesis, which is the synthesis of glucose from non-carbohydrate precursors: lactate, propionate, glycerol, pyruvate, gluconeogenic amino acids. The contribution of gluconeogensis to meeting glucose requirements clearly depends on the amount of carbohydrates absorbed from the intestine, w ...
Amino acid analysis in biofluids using LC
... limited samples volumes, (d) inherently selective to enable validation of analyte signals in every sample. This doctoral thesis project achieved development of a new LC-MS/MS method for AA determination meeting all of these requirements. The presented protocol combines derivatization and ion-pairing ...
... limited samples volumes, (d) inherently selective to enable validation of analyte signals in every sample. This doctoral thesis project achieved development of a new LC-MS/MS method for AA determination meeting all of these requirements. The presented protocol combines derivatization and ion-pairing ...
Structure and function of the eukaryotic ADP
... reaction converting glucose and ADP to glucose-6-phosphate and AMP. The enzyme is well studied in extremophilic archaea, where ADPGK is part of a set of glycolytic enzymes that use ADP instead of ATP for the phosphorylation of various sugars. However, ADPGK has also been found in the genomes of meso ...
... reaction converting glucose and ADP to glucose-6-phosphate and AMP. The enzyme is well studied in extremophilic archaea, where ADPGK is part of a set of glycolytic enzymes that use ADP instead of ATP for the phosphorylation of various sugars. However, ADPGK has also been found in the genomes of meso ...
Rapid Reversion from Monomer to Dimer
... novo synthesis following destruction of the monomer. Rather, regeneration occurs by reversion from the monomer to the dimer. However, regeneration of dimeric UVR8 in darkness following UV-B exposure occurs much more rapidly in vivo than in vitro with illuminated plant extracts or purified UVR8, indic ...
... novo synthesis following destruction of the monomer. Rather, regeneration occurs by reversion from the monomer to the dimer. However, regeneration of dimeric UVR8 in darkness following UV-B exposure occurs much more rapidly in vivo than in vitro with illuminated plant extracts or purified UVR8, indic ...
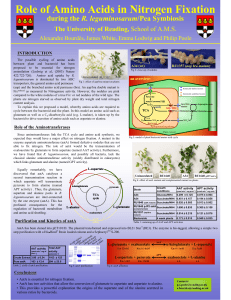
Amino Acid Degradation
... Glucogenic amino acids are broken down into one of the following metabolites: pyruvate, αketoglutarate, succinyl CoA, fumarate or oxaloacetate. Ketogenic amino acids are broken down into acetoacetate or acetyl-CoA. Larger amino acids, tryptophan, phenylalanine, tyrosine, isoleucine and threonine are ...
... Glucogenic amino acids are broken down into one of the following metabolites: pyruvate, αketoglutarate, succinyl CoA, fumarate or oxaloacetate. Ketogenic amino acids are broken down into acetoacetate or acetyl-CoA. Larger amino acids, tryptophan, phenylalanine, tyrosine, isoleucine and threonine are ...
PDF - International Journal of Medical Sciences
... were polymorphisms existing in two important antigens, MPT64 (4) and PstS1 (5) in clinical M. tuberculosis strains isolated from China. This may be the reason for changes in the antigens produced, which may in turn cause alteration of related functions, thereby allowing immune evasion. Some other pr ...
... were polymorphisms existing in two important antigens, MPT64 (4) and PstS1 (5) in clinical M. tuberculosis strains isolated from China. This may be the reason for changes in the antigens produced, which may in turn cause alteration of related functions, thereby allowing immune evasion. Some other pr ...
Microsoft Word
... preserved in apo eIF4E while the loops exhibited mobility on the ns - ps time scale that became abrogated upon the cap binding. The structural differences in the regions of loops S1-S2, S3-S4, S5-S6, and S7-S8 (Fig. 2A), resulted in the formation of the positively charged pocket to anchor the cap ph ...
... preserved in apo eIF4E while the loops exhibited mobility on the ns - ps time scale that became abrogated upon the cap binding. The structural differences in the regions of loops S1-S2, S3-S4, S5-S6, and S7-S8 (Fig. 2A), resulted in the formation of the positively charged pocket to anchor the cap ph ...
7 Fig. 1. "Double-sieve" (two- step subtrate selection - SPring-8
... in IleRS and ValRS [1]. In IleRS, amino acids larger than the cognate L-isoleucine are strictly excluded by the amino acid activation site which serves as the "first, coarse sieve", and smaller ones, such as L-valine, are strictly eliminated at the hydrolytic editing site by the "second, fine sieve. ...
... in IleRS and ValRS [1]. In IleRS, amino acids larger than the cognate L-isoleucine are strictly excluded by the amino acid activation site which serves as the "first, coarse sieve", and smaller ones, such as L-valine, are strictly eliminated at the hydrolytic editing site by the "second, fine sieve. ...
Chapter 4 Calsequestrin - Department of Molecular Physiology and
... which have Kd values for Ca2+ binding of about 1-5 µM (Greaser et al., 1972b; Kretsinger. 1976). The contest for Ca2+ is, therefore, unequal and Ca 2+ finds itself in the lumen of the sarcoplasmic reticulum There it encounters another of the many Ca 2+-binding proteins of muscle, the calcium sequest ...
... which have Kd values for Ca2+ binding of about 1-5 µM (Greaser et al., 1972b; Kretsinger. 1976). The contest for Ca2+ is, therefore, unequal and Ca 2+ finds itself in the lumen of the sarcoplasmic reticulum There it encounters another of the many Ca 2+-binding proteins of muscle, the calcium sequest ...
The 20 amino acids
... In proline, the side chain is connected to the backbone at two places: the C and the N. Proline does not have a backbone proton*, and thus is not good for helices and strands. Due to the extra covalent bond, proline is already ‘pre-bend’, and thus good for turns. And turns tend to be at the surface ...
... In proline, the side chain is connected to the backbone at two places: the C and the N. Proline does not have a backbone proton*, and thus is not good for helices and strands. Due to the extra covalent bond, proline is already ‘pre-bend’, and thus good for turns. And turns tend to be at the surface ...
Ideal Amino Acid Profile For Piglets
... Recent advances and update of the amino acids profile for piglets The increasing availability of crystalline amino acids (AA), as L-Tryptophan and L-Valine, has definitely changed the piglet feed structure and the way to deal with the nitrogen nutrition issue for these animals. Recently, the availab ...
... Recent advances and update of the amino acids profile for piglets The increasing availability of crystalline amino acids (AA), as L-Tryptophan and L-Valine, has definitely changed the piglet feed structure and the way to deal with the nitrogen nutrition issue for these animals. Recently, the availab ...
File
... Metabolism: These are the sequences of the biochemical reaction that degrade, synthesize, or interconvert small molecules inside a cell. This is for the understanding both normal functioning and metabolic basis of human diseases, molecular basis of drug action, drug interaction and many genetic dise ...
... Metabolism: These are the sequences of the biochemical reaction that degrade, synthesize, or interconvert small molecules inside a cell. This is for the understanding both normal functioning and metabolic basis of human diseases, molecular basis of drug action, drug interaction and many genetic dise ...
Unit: Enzymes I
... UNIT: Enzymes I (Colorimetric/Turbidimetric/End-point) (continued) Enzymes are present in all body cells. Enzymes catalyze all essential reactions: oxidation, reduction, hydrolysis, esterification, synthesis, and molecular interconversions necessary for vital activities. Enzymes are also found in l ...
... UNIT: Enzymes I (Colorimetric/Turbidimetric/End-point) (continued) Enzymes are present in all body cells. Enzymes catalyze all essential reactions: oxidation, reduction, hydrolysis, esterification, synthesis, and molecular interconversions necessary for vital activities. Enzymes are also found in l ...
ppt
... Figure was assumed from textbook: Devlin, T. M. (editor): Textbook of Biochemistry with Clinical Correlations, 4th ed. Wiley-Liss, Inc., New York, 1997. ...
... Figure was assumed from textbook: Devlin, T. M. (editor): Textbook of Biochemistry with Clinical Correlations, 4th ed. Wiley-Liss, Inc., New York, 1997. ...
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Low pH or high temperatures can also cause proteolysis non-enzymatically.Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or abnormal proteins in cells. Consequently, dis-regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases, and is used in some venoms to damage their prey.Proteolysis is important as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, as well as industrially, for example in food processing and stain removal.