Industrial Biotechnology
... • Carrier-mediated transportation is selective, and is the rate-limiting step in the metabolism of available carbon and energy sources. • Increasing rate of accumulation of metabolizable carbon source can increase the extent of catabolite repression of enzyme synthesis. • The rate of metabolizable ...
... • Carrier-mediated transportation is selective, and is the rate-limiting step in the metabolism of available carbon and energy sources. • Increasing rate of accumulation of metabolizable carbon source can increase the extent of catabolite repression of enzyme synthesis. • The rate of metabolizable ...
5-MGD Session 3, Lec 5, 2014
... *Coenzymes or cofactors that are tightly or covalently linked to the enzyme protein are known as prosthetic groups. 2. Enzymes are highly specific Interact with one or only a few substrates and catalyse one type of reaction. ...
... *Coenzymes or cofactors that are tightly or covalently linked to the enzyme protein are known as prosthetic groups. 2. Enzymes are highly specific Interact with one or only a few substrates and catalyse one type of reaction. ...
Enzymes - WordPress.com
... Uses of inhibitors: drugs The antibiotics penicillin and vancomycin inhibit enzymes involved in the production of bacterial cell walls. Methotrexate is used in the treatment of cancer and some autoimmune diseases. It inhibits the enzyme dihydrofolate reductase, which is involved with the metabolism ...
... Uses of inhibitors: drugs The antibiotics penicillin and vancomycin inhibit enzymes involved in the production of bacterial cell walls. Methotrexate is used in the treatment of cancer and some autoimmune diseases. It inhibits the enzyme dihydrofolate reductase, which is involved with the metabolism ...
MASE1 and MASE2: Two Novel Integral Membrane Sensory Domains
... al., 2003]. An important feature of all those domains is their propensity to associate with more than one type of signal output domains (histidine kinases, adenylate cyclases, chemotaxis transducers), which made possible their recognition as conserved domains. In addition, these domains are often fo ...
... al., 2003]. An important feature of all those domains is their propensity to associate with more than one type of signal output domains (histidine kinases, adenylate cyclases, chemotaxis transducers), which made possible their recognition as conserved domains. In addition, these domains are often fo ...
effects of insulin and anchorage on hepatocytic protein metabolism
... the hormone may exert its effect indirectly by acting upon the more basal amino acid control mechanism. Glucagon, which stimulates protein degradation, similarly displays its effect only in the presence of intermediate amino acid concentrations. The insulin inhibition is not affected by the aminotra ...
... the hormone may exert its effect indirectly by acting upon the more basal amino acid control mechanism. Glucagon, which stimulates protein degradation, similarly displays its effect only in the presence of intermediate amino acid concentrations. The insulin inhibition is not affected by the aminotra ...
Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
... ancient lines of bacteria or from the most complex forms of life, are constructed from the same ubiquitous set of 20 amino acids, covalently linked in characteristic linear sequences. Because each of these amino acids has a side chain with distinctive chemical properties, this group of 20 precursor ...
... ancient lines of bacteria or from the most complex forms of life, are constructed from the same ubiquitous set of 20 amino acids, covalently linked in characteristic linear sequences. Because each of these amino acids has a side chain with distinctive chemical properties, this group of 20 precursor ...
2.3.3 Protein and amino acid metabolism
... universal fuels, for other tissues. This enables the liver to accommodate dietary amino acid disposal within the bounds of its oxygen consumption. In an adult in nitrogen balance, the daily dietary amino acid intake must be oxidized in a 24-h period. If the liver were too efficient in the clearance ...
... universal fuels, for other tissues. This enables the liver to accommodate dietary amino acid disposal within the bounds of its oxygen consumption. In an adult in nitrogen balance, the daily dietary amino acid intake must be oxidized in a 24-h period. If the liver were too efficient in the clearance ...
Guard Cells Possess a Calcium-Dependent
... (slow) and R-type (rapid) plasma membrane anion channels, which allow Cl2 and malate efflux during stomatal closure, are also activated by elevated cytosolic Ca21 concentrations (Schroeder and Hagiwara, 1989; Hedrich et al., 1990). Consistent with these electrophysiological data, exogenous applicati ...
... (slow) and R-type (rapid) plasma membrane anion channels, which allow Cl2 and malate efflux during stomatal closure, are also activated by elevated cytosolic Ca21 concentrations (Schroeder and Hagiwara, 1989; Hedrich et al., 1990). Consistent with these electrophysiological data, exogenous applicati ...
S4 Text
... [3] Keener J, Nomura M. Regulation of ribosome synthesis. In: Neidhardt FC, III RC, Ingraham JL, Lin ECC, Low KB, Magasanik B, et al., editors. Escherichia coli and Salmonella: Cellular and Molecular Biology. 2nd ed. Washington, DC: ASM Press; 1996. p. 1417–31. ...
... [3] Keener J, Nomura M. Regulation of ribosome synthesis. In: Neidhardt FC, III RC, Ingraham JL, Lin ECC, Low KB, Magasanik B, et al., editors. Escherichia coli and Salmonella: Cellular and Molecular Biology. 2nd ed. Washington, DC: ASM Press; 1996. p. 1417–31. ...
Gilbert Ling Lecture 21
... atom of the NH+ group of the third amino acid down the chain. In this way, the protein chains assumes what is known as the alpha-helix structure. Both the polar NH+ and CO- groups also have affinity for water molecules. The O end of the H2O water molecule can adsorb onto the protein's NH+ site; the ...
... atom of the NH+ group of the third amino acid down the chain. In this way, the protein chains assumes what is known as the alpha-helix structure. Both the polar NH+ and CO- groups also have affinity for water molecules. The O end of the H2O water molecule can adsorb onto the protein's NH+ site; the ...
A presentation of Dr. Gilbert Ling`s Association
... atom of the NH+ group of the third amino acid down the chain. In this way, the protein chains assumes what is known as the alpha-helix structure. Both the polar NH+ and CO- groups also have affinity for water molecules. The O end of the H2O water molecule can adsorb onto the protein's NH+ site; the ...
... atom of the NH+ group of the third amino acid down the chain. In this way, the protein chains assumes what is known as the alpha-helix structure. Both the polar NH+ and CO- groups also have affinity for water molecules. The O end of the H2O water molecule can adsorb onto the protein's NH+ site; the ...
Molecular Weight and the Metal Amino Acid Chelate
... transport carrier systems. Indeed, there have been a considerable number of other studies that have substantiated this. Active transport systems for tetrapeptides and larger peptides do not exist. (Thus, there is probably no transport system for chelates that are greater than 800 daltons in size. Th ...
... transport carrier systems. Indeed, there have been a considerable number of other studies that have substantiated this. Active transport systems for tetrapeptides and larger peptides do not exist. (Thus, there is probably no transport system for chelates that are greater than 800 daltons in size. Th ...
Combinatorial mutagenesis to restrict amino acid usage in an
... occurring amino acids. Does a protein need the full set of 20 amino acids to encode a specific protein function? Only a few studies have addressed this question experimentally. De novo protein-designing experiments have demonstrated that entire helical bundle architectures can be constructed from a ...
... occurring amino acids. Does a protein need the full set of 20 amino acids to encode a specific protein function? Only a few studies have addressed this question experimentally. De novo protein-designing experiments have demonstrated that entire helical bundle architectures can be constructed from a ...
milk-spoilage-biochemical-activities-of-microbes
... Micrococcus spp.: – these are very notorious and may even cause the proteolysis of freshly drawn milk as some of them inhabit the cow’s udder Streptococcus faecalis and Streptococcus liquifasciens: – very active proteolytic bacteria that may cause proteolysis of pasteurized milk Spores of some strai ...
... Micrococcus spp.: – these are very notorious and may even cause the proteolysis of freshly drawn milk as some of them inhabit the cow’s udder Streptococcus faecalis and Streptococcus liquifasciens: – very active proteolytic bacteria that may cause proteolysis of pasteurized milk Spores of some strai ...
“Nice” plotting of proteins
... Is polynomial interpolation good for plotting protein curves? After the lengthy “introduction” to polynomials and interpolation it is about the time to ask: “Is the polynomial fit any good for protein chains”? Can we use polynomial fits to get a much smoother and better views of protein structures? ...
... Is polynomial interpolation good for plotting protein curves? After the lengthy “introduction” to polynomials and interpolation it is about the time to ask: “Is the polynomial fit any good for protein chains”? Can we use polynomial fits to get a much smoother and better views of protein structures? ...
Amino acids [qualitative tests]
... Amino acids tyrosine and tryptophan contain activated benzene rings [aromatic nucleus] which are easily nitrated to yellow colored compounds. The aromatic ring of phenyl alanine dose not react with nitric acid despite it contains a benzene ring, but it is not activated, therefore it will not react ...
... Amino acids tyrosine and tryptophan contain activated benzene rings [aromatic nucleus] which are easily nitrated to yellow colored compounds. The aromatic ring of phenyl alanine dose not react with nitric acid despite it contains a benzene ring, but it is not activated, therefore it will not react ...
Chapter 22 Biosynthesis of amino acids, nucleotides and related
... cleave the amide bond, forming a covalent glutamylenzyme intermediate with the NH3 produced remain in the active site and react with the second substrate to form an aminated product. ...
... cleave the amide bond, forming a covalent glutamylenzyme intermediate with the NH3 produced remain in the active site and react with the second substrate to form an aminated product. ...
Quiz 7 Name: 1. After ATP fuels the Na+/K+ pump at the cell
... A) Glycolysis continues to produce ATP irrespective of what happens to NADH. B) Glycolysis stops unless NADH is used for something else. 6. During intense exercise, as muscles go into anaerobiosis (O2-deprived energy creation), the body will increase its consumption of A) fats. B) proteins. C) carbo ...
... A) Glycolysis continues to produce ATP irrespective of what happens to NADH. B) Glycolysis stops unless NADH is used for something else. 6. During intense exercise, as muscles go into anaerobiosis (O2-deprived energy creation), the body will increase its consumption of A) fats. B) proteins. C) carbo ...
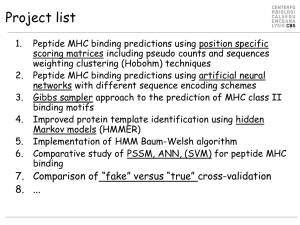
Gibbs sampler
... Peptide MHC binding predictions using artificial neural networks with different sequence encoding schemes Gibbs sampler approach to the prediction of MHC class II binding motifs Improved protein template identification using hidden Markov models (HMMER) Implementation of HMM Baum-Welsh algorithm Com ...
... Peptide MHC binding predictions using artificial neural networks with different sequence encoding schemes Gibbs sampler approach to the prediction of MHC class II binding motifs Improved protein template identification using hidden Markov models (HMMER) Implementation of HMM Baum-Welsh algorithm Com ...
IV RNA Synthesis: Transcription
... RNA polymerase is a large protein and makes contact with many bases of DNA simultaneously. Proteins such as RNA polymerase can interact specifically with DNA because portions of the bases are exposed in the major groove. However, in order to initiate RNA synthesis correctly, RNA polymerase must first ...
... RNA polymerase is a large protein and makes contact with many bases of DNA simultaneously. Proteins such as RNA polymerase can interact specifically with DNA because portions of the bases are exposed in the major groove. However, in order to initiate RNA synthesis correctly, RNA polymerase must first ...
Polymer Lesson - Penn Arts and Sciences
... Sickle cell anemia is caused by a genetic change in hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is a protein that is made up of chains of amino acids. Its function is to pick up oxygen in our lungs and deliver it to other cells. It performs this function well unless it is inherited in another form called hemoglobin S. H ...
... Sickle cell anemia is caused by a genetic change in hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is a protein that is made up of chains of amino acids. Its function is to pick up oxygen in our lungs and deliver it to other cells. It performs this function well unless it is inherited in another form called hemoglobin S. H ...
The Structure of Cell Walls of Phycomycetes
... Control acid hydrolyses of laminarin, laminaribiose, cellulose and cellobiose indicate that gentiobiose does not appear to any signihcant extent on our chromatograms as a reversion product. Proteolysis of non-dialysable acid fractions. Both Phytophthora heveae and Pythium butleri yielded similar ami ...
... Control acid hydrolyses of laminarin, laminaribiose, cellulose and cellobiose indicate that gentiobiose does not appear to any signihcant extent on our chromatograms as a reversion product. Proteolysis of non-dialysable acid fractions. Both Phytophthora heveae and Pythium butleri yielded similar ami ...
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Low pH or high temperatures can also cause proteolysis non-enzymatically.Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or abnormal proteins in cells. Consequently, dis-regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases, and is used in some venoms to damage their prey.Proteolysis is important as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, as well as industrially, for example in food processing and stain removal.















![Amino acids [qualitative tests]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008282328_1-c8bb4ef27caebe478c13494a7af59cc2-300x300.png)