INVESTIGATION OF THE REPLACEMENT OF CYSTEINE
... DOTA0‐[D‐Pen2, Tyr3, D‐Pen7]‐octreotate, 11b – Isolated fraction from preparative HPLC purification ...................................................................... 179 4.18 Radio‐TLC of radiolabelling experiments. (i)Radio‐TLC of 111InCl3; (ii and iii)Radio‐TLC of 111In(III) radiolabell ...
... DOTA0‐[D‐Pen2, Tyr3, D‐Pen7]‐octreotate, 11b – Isolated fraction from preparative HPLC purification ...................................................................... 179 4.18 Radio‐TLC of radiolabelling experiments. (i)Radio‐TLC of 111InCl3; (ii and iii)Radio‐TLC of 111In(III) radiolabell ...
Cholesterol
... LYSOLECITHIN + CHOLESTEROL ESTER • LCAT is activated by apo-A1 and deficiency in LCAT means that HDL can’t take ...
... LYSOLECITHIN + CHOLESTEROL ESTER • LCAT is activated by apo-A1 and deficiency in LCAT means that HDL can’t take ...
Chapter 9 Slides
... the other by flippase proteins Some flippases operate passively and do not require an energy source Other flippases appear to operate actively and require the energy of hydrolysis of ATP ...
... the other by flippase proteins Some flippases operate passively and do not require an energy source Other flippases appear to operate actively and require the energy of hydrolysis of ATP ...
Mammalian CSAD and GADL1 have distinct biochemical properties
... biosynthesis of taurine. In the present study, we compared the catalytic properties, inhibitor sensitivity and expression profiles of GADL1 and CSAD in brain tissue. In mouse and human brain we observed distinct patterns of expression of the PLP-dependent decarboxylases CSAD, GADL1 and glutamic acid ...
... biosynthesis of taurine. In the present study, we compared the catalytic properties, inhibitor sensitivity and expression profiles of GADL1 and CSAD in brain tissue. In mouse and human brain we observed distinct patterns of expression of the PLP-dependent decarboxylases CSAD, GADL1 and glutamic acid ...
Genetic code as a harmonic system
... another); only then does the copying of (–NH2) group with 3 atoms follow and finally, the copying of (–COOH) group with 4 atoms, which represents the highest degree of oxydation (and substitution) in the main aliphatic chain. All three copyings are related to functional groups with a single covalent ...
... another); only then does the copying of (–NH2) group with 3 atoms follow and finally, the copying of (–COOH) group with 4 atoms, which represents the highest degree of oxydation (and substitution) in the main aliphatic chain. All three copyings are related to functional groups with a single covalent ...
Module 3 Metabolism of carbohydrates, lipids
... D. All of the above E. None of the above 17. ATP is a cosubstrate of the enzyme PFK-1. In most species ATP is also an inhibitor of PFK-1 at higher concentrations. This seems to violate Le Chatelier's Principle. Which statement below would provide a suitable explanation? A. PFK-1 must be phosphorylat ...
... D. All of the above E. None of the above 17. ATP is a cosubstrate of the enzyme PFK-1. In most species ATP is also an inhibitor of PFK-1 at higher concentrations. This seems to violate Le Chatelier's Principle. Which statement below would provide a suitable explanation? A. PFK-1 must be phosphorylat ...
Multiple Functions of the New Cytokine
... The TSLP forms can be produced by a number of cell types, including epithelial and dendritic cells (DCs). lfTSLP can activate mast cells, DCs, and T cells through binding to the lfTSLP receptor (TSLPR) and has a pro-inflammatory function. In contrast, sfTSLP inhibits cytokine secretion of DCs, but t ...
... The TSLP forms can be produced by a number of cell types, including epithelial and dendritic cells (DCs). lfTSLP can activate mast cells, DCs, and T cells through binding to the lfTSLP receptor (TSLPR) and has a pro-inflammatory function. In contrast, sfTSLP inhibits cytokine secretion of DCs, but t ...
Some Structural and Kinetic Aspects of L
... that binding of the effector to the one site of enzyme subunit affects the substrate (PEP) binding in another PK subunit. Thus the binding of FBP to the C domain influences the binding of PEP to A domain of PK subunit. Also M2, R and L isoenzymes exhibit a sigmoidal kinetics toward the substrate PE ...
... that binding of the effector to the one site of enzyme subunit affects the substrate (PEP) binding in another PK subunit. Thus the binding of FBP to the C domain influences the binding of PEP to A domain of PK subunit. Also M2, R and L isoenzymes exhibit a sigmoidal kinetics toward the substrate PE ...
Staphylococcus haemolyticus lipase
... explained from two postulations: that the lipase L62 was secreted as a complex with some compound, which complex has been already reported from several lipases [17] and that this `lipase complex' has much lower lipolytic activity in comparison with the puri¢ed enzyme. This lipase complex was evidenc ...
... explained from two postulations: that the lipase L62 was secreted as a complex with some compound, which complex has been already reported from several lipases [17] and that this `lipase complex' has much lower lipolytic activity in comparison with the puri¢ed enzyme. This lipase complex was evidenc ...
Molecular cloning of Per a 1 and definition of the cross
... reported, but unidentified, sequences from B germanica and P americana. These sequences encoded proteins with multiple molecular sizes containing approximately 100 amino acid repeats. The Per a 1 sequence also showed 31% identity to a mosquito precursor protein, ANG12, which may be involved in diges ...
... reported, but unidentified, sequences from B germanica and P americana. These sequences encoded proteins with multiple molecular sizes containing approximately 100 amino acid repeats. The Per a 1 sequence also showed 31% identity to a mosquito precursor protein, ANG12, which may be involved in diges ...
Free aromatic amino acids in egg yolk show antioxidant properties
... acids, unlike the isoflavonoids, in egg yolk is very low under natural conditions. However, it is not known if other phenolic compounds are present in egg yolk. This study was designed to investigate the possibility of deposition of phenolic acids in egg yolk and the total antioxidant capacity of yol ...
... acids, unlike the isoflavonoids, in egg yolk is very low under natural conditions. However, it is not known if other phenolic compounds are present in egg yolk. This study was designed to investigate the possibility of deposition of phenolic acids in egg yolk and the total antioxidant capacity of yol ...
METABOLIC CUES AND REGULATORY PROTEINS
... Maris Fonseca, Ari Molofsky, J-D Sauer, Natalie Whitfield and Brian Yagi. Each has provided me with thoughtful suggestions regarding my thesis project and has made the Swanson lab a fun and exciting place to work. Thanks to Dr. Carmen Buchrieser and Dr. Matthieu Jules who enabled me to conduct resea ...
... Maris Fonseca, Ari Molofsky, J-D Sauer, Natalie Whitfield and Brian Yagi. Each has provided me with thoughtful suggestions regarding my thesis project and has made the Swanson lab a fun and exciting place to work. Thanks to Dr. Carmen Buchrieser and Dr. Matthieu Jules who enabled me to conduct resea ...
THE SARCOTUBULAR SYSTEM OF FROG
... p r e p a r a t i o n was the result of a fragmentation of mitochondria, or due to the presence a m o n g the myofibrils of " g r a n u l a r " structures endowed with a completely different physiological function (19). T h e present investigation was u n d e r t a k e n to identify, by means of a c ...
... p r e p a r a t i o n was the result of a fragmentation of mitochondria, or due to the presence a m o n g the myofibrils of " g r a n u l a r " structures endowed with a completely different physiological function (19). T h e present investigation was u n d e r t a k e n to identify, by means of a c ...
Full-Text PDF
... to embed this bacteria within the biofilm matrix. SRB has been reported to exist in biofilm matrices that are electroactive [32] or are determined to impart localized biocorrosion [2,33,34]. The biofilm matrix not only serves to adhere SRB onto surfaces but also hinders penetration of biocides. This ...
... to embed this bacteria within the biofilm matrix. SRB has been reported to exist in biofilm matrices that are electroactive [32] or are determined to impart localized biocorrosion [2,33,34]. The biofilm matrix not only serves to adhere SRB onto surfaces but also hinders penetration of biocides. This ...
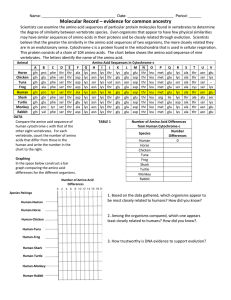
Molecular Record – evidence for common ancestry
... Molecular Record – evidence for common ancestry Scientists can examine the amino acid sequences of particular protein molecules found in vertebrates to determine the degree of similarity between vertebrate species. Even organisms that appear to have few physical similarities may have similar sequenc ...
... Molecular Record – evidence for common ancestry Scientists can examine the amino acid sequences of particular protein molecules found in vertebrates to determine the degree of similarity between vertebrate species. Even organisms that appear to have few physical similarities may have similar sequenc ...
Enzymes responsible for chlorate reduction by Pseudomonas sp
... Pseudomonas sp. PDA is a relatively novel chloraterespiring bacterium due to its ability to completely degrade chlorate in the presence of dissolved oxygen [7]. While other chlorate respiring bacteria are known to constitutively express chlorite dismutase, no other bacterium is known to constitutive ...
... Pseudomonas sp. PDA is a relatively novel chloraterespiring bacterium due to its ability to completely degrade chlorate in the presence of dissolved oxygen [7]. While other chlorate respiring bacteria are known to constitutively express chlorite dismutase, no other bacterium is known to constitutive ...
CH Zinc Fingers As DNA Binding Domains
... Louis. *The number is f o r proteins containing two C2C2 fingers. finger proteins can be divided into four classes (Fig. 2), (A) single C2H2, (B) triple C2H2, (C) multiple-adjacent C2H2, and (D) separated-paired C2H2 zinc finger proteins. ^^ This classification is usefiil to predict how the zinc fin ...
... Louis. *The number is f o r proteins containing two C2C2 fingers. finger proteins can be divided into four classes (Fig. 2), (A) single C2H2, (B) triple C2H2, (C) multiple-adjacent C2H2, and (D) separated-paired C2H2 zinc finger proteins. ^^ This classification is usefiil to predict how the zinc fin ...
Read more about this
... SGOT (serum glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase) – an enzyme found in the liver, muscles (including the heart), and red blood cells. It is released into the blood when cells that contain it are damaged. Other names for this enzyme are aspartate aminotranskinase, aspartate transaminase, and AST. GGT (g ...
... SGOT (serum glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase) – an enzyme found in the liver, muscles (including the heart), and red blood cells. It is released into the blood when cells that contain it are damaged. Other names for this enzyme are aspartate aminotranskinase, aspartate transaminase, and AST. GGT (g ...
Regulation of the Escherichia coli Tryptophan Operon by Early
... 10-' M 2-mercaptoethanol. Nucleic acids were not removed before crude extracts were placed on the column. At the end of the fractionation, a small amount of 10-2 M K2HPO4, pH 7.0, containing 1.0 M KCl was washed through the column to insure that all DAHP synthetase activity had been eluted. Recovery ...
... 10-' M 2-mercaptoethanol. Nucleic acids were not removed before crude extracts were placed on the column. At the end of the fractionation, a small amount of 10-2 M K2HPO4, pH 7.0, containing 1.0 M KCl was washed through the column to insure that all DAHP synthetase activity had been eluted. Recovery ...
DECALEPIS HAMILTONII ACETAMINOPHEN-INDUCED HEPATIC INJURY IN RATS Research Article
... several degenerative diseases, such as coronary artery diseases, stroke, rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes and cancer4. It is well known that, free radicals are the reactive species derived from them cause damage through mechanisms of covalent binding and lipid peroxidation with subsequent tissue injur ...
... several degenerative diseases, such as coronary artery diseases, stroke, rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes and cancer4. It is well known that, free radicals are the reactive species derived from them cause damage through mechanisms of covalent binding and lipid peroxidation with subsequent tissue injur ...
Molecular networks in skeletal muscle plasticity
... is dominant, while during endurance exercise, mechanical stress is low but metabolic disturbances can be severe and protracted. In any kind of muscle activity, neuronal activation and associated Ca2+ and other ion transients, as well as load- and duration-specific hormonal adjustments occur. These s ...
... is dominant, while during endurance exercise, mechanical stress is low but metabolic disturbances can be severe and protracted. In any kind of muscle activity, neuronal activation and associated Ca2+ and other ion transients, as well as load- and duration-specific hormonal adjustments occur. These s ...
Enzymologychapter13 - Panama College of Cell Science
... specificity. Intimate interaction between an enzyme and its substrates occurs through molecular recognition based on structural complementarity; such mutual recognition is the basis of specificity. The specific site on the enzyme where substrate binds and catalysis occurs is called the active site. ...
... specificity. Intimate interaction between an enzyme and its substrates occurs through molecular recognition based on structural complementarity; such mutual recognition is the basis of specificity. The specific site on the enzyme where substrate binds and catalysis occurs is called the active site. ...
The Ostrich (Struthio camelus) egg
... lysozyme activity was recovered in a peak which was dialyzed (1 h) against distilled water, concentrated in a desiccator and finally desalted on a Sephadex G-25 column (140 cm x 3.4 cm) with 0.1 M acetic acid as eluent. The biologically active fractions were concentrated in a desiccator. ...
... lysozyme activity was recovered in a peak which was dialyzed (1 h) against distilled water, concentrated in a desiccator and finally desalted on a Sephadex G-25 column (140 cm x 3.4 cm) with 0.1 M acetic acid as eluent. The biologically active fractions were concentrated in a desiccator. ...
Sex-based individual variation of snake venom proteome among
... proteome variation among the venoms of this litter as well as the sex-based differences observed by both SDS-PAGE and 2D-PAGE we decided to compare the individual venom samples by measuring their proteolytic activities on protein and peptide substrates. At first we determined the plasma coagulant ac ...
... proteome variation among the venoms of this litter as well as the sex-based differences observed by both SDS-PAGE and 2D-PAGE we decided to compare the individual venom samples by measuring their proteolytic activities on protein and peptide substrates. At first we determined the plasma coagulant ac ...
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Low pH or high temperatures can also cause proteolysis non-enzymatically.Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or abnormal proteins in cells. Consequently, dis-regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases, and is used in some venoms to damage their prey.Proteolysis is important as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, as well as industrially, for example in food processing and stain removal.