Perspective: emerging evidence for signaling roles of mitochondrial
... There are two phases of insulin secretion. The first phase starts within seconds of an increased level of a fuel secretagogue making contact with the -cell and has been called the triggering phase. In this phase, a sharp peak of insulin is released, probably from insulin granules stored immediately ...
... There are two phases of insulin secretion. The first phase starts within seconds of an increased level of a fuel secretagogue making contact with the -cell and has been called the triggering phase. In this phase, a sharp peak of insulin is released, probably from insulin granules stored immediately ...
A modular approach to sphingolipid analogs mediated by aziridines: Synthesis
... and cholesterol form platforms or rafts that float in the liquid phase.3 Furthermore, these lipid rafts are important in signal transduction processes and some key components of signal transduction are located on rafts.4 ...
... and cholesterol form platforms or rafts that float in the liquid phase.3 Furthermore, these lipid rafts are important in signal transduction processes and some key components of signal transduction are located on rafts.4 ...
Regulation of Arabidopsis 14-3
... kinases (Camoni, Harper & Palmgren 1998; Moorhead et al. 1999) and SnRK1-related protein kinases (Ikeda et al. 2000) that phosphorylate 14-3-3 targets like nitrate reductase. 14-3-3 gene family members are differentially regulated during a range of stress responses (Roberts & Bowles 1999; Roberts, S ...
... kinases (Camoni, Harper & Palmgren 1998; Moorhead et al. 1999) and SnRK1-related protein kinases (Ikeda et al. 2000) that phosphorylate 14-3-3 targets like nitrate reductase. 14-3-3 gene family members are differentially regulated during a range of stress responses (Roberts & Bowles 1999; Roberts, S ...
Mutant selection and phenotypic and genetic characterization of
... Clostridium thermocellum is a candidate microorganism for CBP since it can rapidly hydrolyze cellulosic material, with the aid of a complexed cellulase system termed the cellulosome, and ferment the hydrolysis products to ethanol and organic acids. Genetic tools have been recently developed and succ ...
... Clostridium thermocellum is a candidate microorganism for CBP since it can rapidly hydrolyze cellulosic material, with the aid of a complexed cellulase system termed the cellulosome, and ferment the hydrolysis products to ethanol and organic acids. Genetic tools have been recently developed and succ ...
Treatment of patients with non-Hodgkin lymphoma and lactic acidosis
... anaerobically, which leads to an overproduction of lactate. Type A is more common then Type B (see below), which is most related with haematological malignancies like leukaemia and lymphomas3. Several patients with lactic acidosis also have been diagnosed with hypoglycaemia, which is due to a high r ...
... anaerobically, which leads to an overproduction of lactate. Type A is more common then Type B (see below), which is most related with haematological malignancies like leukaemia and lymphomas3. Several patients with lactic acidosis also have been diagnosed with hypoglycaemia, which is due to a high r ...
Chromatin Condensing Functions of the Linker Histone C
... experiments were performed in 0.25 mM MgCl2, which induces only partial folding, and 0.45 mM MgCl2, which induces nearly complete folding of saturated chromatin fibers that contain stoichiometric amounts of bound linker histone. We purposely did not work at higher MgCl2 concentrations to avoid induc ...
... experiments were performed in 0.25 mM MgCl2, which induces only partial folding, and 0.45 mM MgCl2, which induces nearly complete folding of saturated chromatin fibers that contain stoichiometric amounts of bound linker histone. We purposely did not work at higher MgCl2 concentrations to avoid induc ...
Structure of a Pheromone Receptor-Associated MHC Molecule with
... Rich Olson1, Kathryn E. Huey-Tubman1,2, Catherine Dulac3, Pamela J. Bjorkman1,2* 1 Division of Biology, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, California, United States of America, 2 Howard Hughes Medical Institute, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, California, United States of Am ...
... Rich Olson1, Kathryn E. Huey-Tubman1,2, Catherine Dulac3, Pamela J. Bjorkman1,2* 1 Division of Biology, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, California, United States of America, 2 Howard Hughes Medical Institute, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, California, United States of Am ...
Hücrelerin Yapısı - mustafaaltinisik.org.uk
... the other by flippase proteins Some flippases operate passively and do not require an energy source Other flippases appear to operate actively and require the energy of hydrolysis of ATP ...
... the other by flippase proteins Some flippases operate passively and do not require an energy source Other flippases appear to operate actively and require the energy of hydrolysis of ATP ...
Enzymes
... 2. Enzymes are Stereospecific. If a molecule exists as a pair of enantiomers, the enzyme will use only one of the pair as substrate and produce only one of the pair as the product. For example, the enzymes that are involved in amino acid metabolism and/or protein synthesis will only utilize the L-am ...
... 2. Enzymes are Stereospecific. If a molecule exists as a pair of enantiomers, the enzyme will use only one of the pair as substrate and produce only one of the pair as the product. For example, the enzymes that are involved in amino acid metabolism and/or protein synthesis will only utilize the L-am ...
The C-terminal domain of the Rhizobium leguminosarum
... legume plants. NodC proteins have two hydrophobic domains, one of about 21 residues at the N-terminus and a longer one, which could consist of two or three transmembrane spans, near the C-terminus. These two hydrophobic domains flank a large hydrophilic region that shows extensive homology with othe ...
... legume plants. NodC proteins have two hydrophobic domains, one of about 21 residues at the N-terminus and a longer one, which could consist of two or three transmembrane spans, near the C-terminus. These two hydrophobic domains flank a large hydrophilic region that shows extensive homology with othe ...
Determination of amino acid enantiomers in human urine and blood
... In four out of six urine samples of 24 h urines, highest absolute amounts among D-AAs were determined for D-Ser, in one sample D-Ser and D-Ala were about equal, and in one sample D-Ala was about twice the amount of D-Ser. Quantities of D-Ser ranged from 64 to 199 mmol/ day, of D-Ala from 24 to 138 m ...
... In four out of six urine samples of 24 h urines, highest absolute amounts among D-AAs were determined for D-Ser, in one sample D-Ser and D-Ala were about equal, and in one sample D-Ala was about twice the amount of D-Ser. Quantities of D-Ser ranged from 64 to 199 mmol/ day, of D-Ala from 24 to 138 m ...
Untitled - Heart and Metabolism
... ven subtle variations in the efficiency of energy generation or utilization may have a profound impact on cellular energy levels. Different cardiac pathologies can alter cardiac efficiency, both as a result of a decrease efficiency of producing ATP or alterations in the efficiency of using ATP to pr ...
... ven subtle variations in the efficiency of energy generation or utilization may have a profound impact on cellular energy levels. Different cardiac pathologies can alter cardiac efficiency, both as a result of a decrease efficiency of producing ATP or alterations in the efficiency of using ATP to pr ...
12659942_three sites - University of Canterbury
... Tyr binding mode in site 3 In contrast to Tyr binding in site 2, specific interactions with the phenolic hydroxyl of Tyr are established when Tyr binds in site 3: the main-chain carbonyl of Pro16 and a water molecule, which in turn interacts with the backbone amide N–H of Leu261, are located 2.7 and ...
... Tyr binding mode in site 3 In contrast to Tyr binding in site 2, specific interactions with the phenolic hydroxyl of Tyr are established when Tyr binds in site 3: the main-chain carbonyl of Pro16 and a water molecule, which in turn interacts with the backbone amide N–H of Leu261, are located 2.7 and ...
FATTY ACID METABOLISM
... 1. Synthesis takes place in the cytosol, in contrast with degradation, which takes place primarily in the mitochondrial matrix. 2. Intermediates in fatty acid synthesis are covalently linked to the sulfhydryl groups of an acyl carrier protein (ACP), whereas intermediates in fatty acid breakdown are ...
... 1. Synthesis takes place in the cytosol, in contrast with degradation, which takes place primarily in the mitochondrial matrix. 2. Intermediates in fatty acid synthesis are covalently linked to the sulfhydryl groups of an acyl carrier protein (ACP), whereas intermediates in fatty acid breakdown are ...
Physiological and Chemical Properties of a
... according to amino acid analysis, consistent with values of 43,000 f.7000 from ultracentrifugation and exclusion chromatography. The enzyme was very unstable at both 4" and 15' and was easily damaged physically: it lost 75 % of activity on freezing and thawing and was progressively destroyed if 02, ...
... according to amino acid analysis, consistent with values of 43,000 f.7000 from ultracentrifugation and exclusion chromatography. The enzyme was very unstable at both 4" and 15' and was easily damaged physically: it lost 75 % of activity on freezing and thawing and was progressively destroyed if 02, ...
M.Sc. (Semester - III) BIOCHEMISTRY BCH
... a) Discuss in detail effect of substrate concentration on enzyme catalyzed reaction. b) Explain the various conditions under which the enzyme-substrate complex is stabilized to determine the mechanism of enzyme catalysis by X-ray crystallography. c) How activity of an enzyme is regulated by irrevers ...
... a) Discuss in detail effect of substrate concentration on enzyme catalyzed reaction. b) Explain the various conditions under which the enzyme-substrate complex is stabilized to determine the mechanism of enzyme catalysis by X-ray crystallography. c) How activity of an enzyme is regulated by irrevers ...
Vitamins
... They differ only in the nature of the functional group attached to the ring. Pyridoxine occurs primarily in plants, whereas pyridoxal and pyridoxamine are found in foods obtained from animals. All three compounds can serve as precursors of the biologically active coenzyme, pyridoxal phosphate. Pyrid ...
... They differ only in the nature of the functional group attached to the ring. Pyridoxine occurs primarily in plants, whereas pyridoxal and pyridoxamine are found in foods obtained from animals. All three compounds can serve as precursors of the biologically active coenzyme, pyridoxal phosphate. Pyrid ...
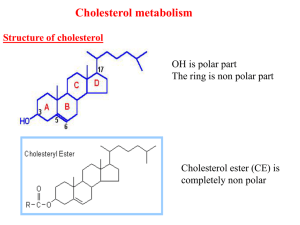
Lec4 Cholesterol met..
... 2- Drug inhibition: Statins such as atorvastatin (by Pfizer), lovastatin and simvastatin are drugs with a side chain structurally similar to HMG-CoA so competitively inhibit HMG-CoA reductase. They are used to decrease cholesterol levels in patients with hypercholesterolemia. 3- Diet: its activity a ...
... 2- Drug inhibition: Statins such as atorvastatin (by Pfizer), lovastatin and simvastatin are drugs with a side chain structurally similar to HMG-CoA so competitively inhibit HMG-CoA reductase. They are used to decrease cholesterol levels in patients with hypercholesterolemia. 3- Diet: its activity a ...
Lipids- Structure and Metabolism
... 5. Lipids, in the form of lipoproteins, are the important cellular constituents and occur in cell membrane, mitochondria and cytoplasm. Lipoproteins are also essential for the transport of lipids in blood. 6. Lipids are the source of fat soluble vitamins (vitamins A, D, E and K) and of essential fat ...
... 5. Lipids, in the form of lipoproteins, are the important cellular constituents and occur in cell membrane, mitochondria and cytoplasm. Lipoproteins are also essential for the transport of lipids in blood. 6. Lipids are the source of fat soluble vitamins (vitamins A, D, E and K) and of essential fat ...
medical chemistry and biochemistry
... 3. Explain osmosis, osmotic pressure, solution freezing point depression and boiling point elevation, and compare electrolytes to nonelectrolytes. 4. Determine whether the solution is isotonic, hypertonic or hypotonic. 5. Derive units of measurement and conclude which units are used in which formula ...
... 3. Explain osmosis, osmotic pressure, solution freezing point depression and boiling point elevation, and compare electrolytes to nonelectrolytes. 4. Determine whether the solution is isotonic, hypertonic or hypotonic. 5. Derive units of measurement and conclude which units are used in which formula ...
Milk production and energy metabolism in ruminants fed 2
... The capacity of the lactatlng mammary gland to produce milk Is determined by the degree of development of the mammary gland prepartum and by the ability of the animal to supply the necessary substrates for milk synthesis. This review will deal primarily with the topic of substrate supply and some ba ...
... The capacity of the lactatlng mammary gland to produce milk Is determined by the degree of development of the mammary gland prepartum and by the ability of the animal to supply the necessary substrates for milk synthesis. This review will deal primarily with the topic of substrate supply and some ba ...
Rabbit genome editing with zinc finger nucleases
... selected parameter is chosen from (a) rate of elimination of the agent or its metabolite(s); (b) circulatory levels of the agent or its metabolite(s); (c) bioavailability of the agent or its metabolite(s); (d) rate of metabolism of the agent or its metabolite(s); (e) rate of clearance of the agent o ...
... selected parameter is chosen from (a) rate of elimination of the agent or its metabolite(s); (b) circulatory levels of the agent or its metabolite(s); (c) bioavailability of the agent or its metabolite(s); (d) rate of metabolism of the agent or its metabolite(s); (e) rate of clearance of the agent o ...
Design and Evaluation of Hydrophobic Ion
... or introducing functional groups that can be easily substituted or conjugated to the particle matrix. For example, substituting acyl groups on poly(glycerol adipate) backbone (PGA) with various amounts of pendant C18 chain by which the dexamethasone phosphate loaded nanoparticles were yielded [7]. T ...
... or introducing functional groups that can be easily substituted or conjugated to the particle matrix. For example, substituting acyl groups on poly(glycerol adipate) backbone (PGA) with various amounts of pendant C18 chain by which the dexamethasone phosphate loaded nanoparticles were yielded [7]. T ...
Chapter 10: Anorexia Nervosa and Bulimia Nervosa
... Theory was to prevent oxidation of RBC membranes that might occur at altitude ...
... Theory was to prevent oxidation of RBC membranes that might occur at altitude ...
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Low pH or high temperatures can also cause proteolysis non-enzymatically.Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or abnormal proteins in cells. Consequently, dis-regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases, and is used in some venoms to damage their prey.Proteolysis is important as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, as well as industrially, for example in food processing and stain removal.