Reasons for the Fall of the Roman Empire
... who passed his values to his family, but also filled the cities with unemployed people. At one time, the emperor was importing grain to feed more than 100,000 people in Rome alone. These people were not only a burden but also had little to do but cause trouble and contribute to an ever increasing cr ...
... who passed his values to his family, but also filled the cities with unemployed people. At one time, the emperor was importing grain to feed more than 100,000 people in Rome alone. These people were not only a burden but also had little to do but cause trouble and contribute to an ever increasing cr ...
Rome & Han China - Miami Beach Senior High School
... The late centuries BCE and the early centuries CE see the rise of larger, more centralized empires ...
... The late centuries BCE and the early centuries CE see the rise of larger, more centralized empires ...
Today`s powerpoint slides - Manhasset Public Schools
... information about PM 2.5 a secret from their citizens. They are running away from the problems the country is facing because they are scared of being questioned by the rest of the world. ...
... information about PM 2.5 a secret from their citizens. They are running away from the problems the country is facing because they are scared of being questioned by the rest of the world. ...
The Pax Romana (31 B.C.
... The central scene lavishly depicted on the side of a silver cup shows Augustus seated in majesty. In his right hand he holds an orb that represents his position as master of the world. The scroll in his left hand symbolizes his authority as lawgiver. On his right is a group of divinities who support ...
... The central scene lavishly depicted on the side of a silver cup shows Augustus seated in majesty. In his right hand he holds an orb that represents his position as master of the world. The scroll in his left hand symbolizes his authority as lawgiver. On his right is a group of divinities who support ...
Year 4 Summer Term 1 The Roman Empire.
... What did the British do to defend themselves and how successful were they? What changes did the Romans bring? Why did the Romans leave Britain? ...
... What did the British do to defend themselves and how successful were they? What changes did the Romans bring? Why did the Romans leave Britain? ...
The development of the Roman alphabet.
... four hundred years. This republic was ruled by a senate, and people called Senators were elected to do different jobs in the senate. However, not everyone was allowed to vote in these elections. Women and slaves were not allowed to vote and neither were poor people. Those Roman people who were not s ...
... four hundred years. This republic was ruled by a senate, and people called Senators were elected to do different jobs in the senate. However, not everyone was allowed to vote in these elections. Women and slaves were not allowed to vote and neither were poor people. Those Roman people who were not s ...
Honors Ancient Rome Test Study Guide
... The Roman Army from 14-180 A.D. improvements and growth (146) Trade and Commerce and how it is characterized in the early Empire (149) Marcus Aurelius influences in philosophy (145) The use of a particular substance that enhanced Roman architecture (150) The Colosseum (what emperor what responsible ...
... The Roman Army from 14-180 A.D. improvements and growth (146) Trade and Commerce and how it is characterized in the early Empire (149) Marcus Aurelius influences in philosophy (145) The use of a particular substance that enhanced Roman architecture (150) The Colosseum (what emperor what responsible ...
Ancient Rome Timeline Activity File
... Label every 1 inch 200 years starting with 800 BC (note: these dates are B.C., so numbers go backwards). IMPORTANT: You must have an accurate scale (i.e. 1 inches = 200 years). Write the scale on the paper. Step #5 Put each of the dates below on your timeline where they appropriately fit. Make sure ...
... Label every 1 inch 200 years starting with 800 BC (note: these dates are B.C., so numbers go backwards). IMPORTANT: You must have an accurate scale (i.e. 1 inches = 200 years). Write the scale on the paper. Step #5 Put each of the dates below on your timeline where they appropriately fit. Make sure ...
Comparing/Contrasting Rome to Han China
... Territorial size of both was approx. 2.5 million at their peak Territorial size of Rome was ultimately restricted by deserts (N. Africa/Middle East) and European mountains (Alps) Han’s territorial size was limited by the Tibetan Plateau, western deserts (Gobi, Taklimakan), mountains (Himalayas ...
... Territorial size of both was approx. 2.5 million at their peak Territorial size of Rome was ultimately restricted by deserts (N. Africa/Middle East) and European mountains (Alps) Han’s territorial size was limited by the Tibetan Plateau, western deserts (Gobi, Taklimakan), mountains (Himalayas ...
Key Terms and People Section Summary
... began to follow Greek culture instead of Roman culture. The cultural ties to Rome were slowly lost. Constantinople was a major trade route among Europeans, Africans, and Asians. Because of this, the people of Constantinople were exposed to new ideas from other cultures. They blended those ideas with ...
... began to follow Greek culture instead of Roman culture. The cultural ties to Rome were slowly lost. Constantinople was a major trade route among Europeans, Africans, and Asians. Because of this, the people of Constantinople were exposed to new ideas from other cultures. They blended those ideas with ...
APWH MITERM TEST 1. All Mesoamerican societies used calendars
... d. Buddhism. e. Zoroastrianism. 15. The first ruler to unite all of China was a. Liu Bang. b. Prince Wu. c. Qin Shihuangdi. d. Wang Mang. e. Prince Yu. 16. Although only fragments remain, some of our best information about early Indian history comes from the Indika, written by a. Socrates. b. Megast ...
... d. Buddhism. e. Zoroastrianism. 15. The first ruler to unite all of China was a. Liu Bang. b. Prince Wu. c. Qin Shihuangdi. d. Wang Mang. e. Prince Yu. 16. Although only fragments remain, some of our best information about early Indian history comes from the Indika, written by a. Socrates. b. Megast ...
Ten Theories on the Fall of Rome
... One of Rome’s most serious problems was choosing new emperors. The Romans had never created an effective system to determine how the new emperors were to be selected. For this reason, the choice of a new emperor was always be open to debate between the old emperor, the regular army and the emperor’s ...
... One of Rome’s most serious problems was choosing new emperors. The Romans had never created an effective system to determine how the new emperors were to be selected. For this reason, the choice of a new emperor was always be open to debate between the old emperor, the regular army and the emperor’s ...
Chapter 6- Ancient Rome and the Rise of Christianity
... Consul- government official who supervised the business of government and the army. Patrician- landholding elite. Plebeians- farmers, merchants, and traders who made up the bulk of Roman Society. Aqueduct- bridge-like stone structure that bought water from the hills to the cities.* ...
... Consul- government official who supervised the business of government and the army. Patrician- landholding elite. Plebeians- farmers, merchants, and traders who made up the bulk of Roman Society. Aqueduct- bridge-like stone structure that bought water from the hills to the cities.* ...
8000 bce- 600 ce PP Review
... The Persian Wars: Overview The threat of the powerful Persian empire united the Greek city-states. Around 500B.C. Greeks were attacked by the ...
... The Persian Wars: Overview The threat of the powerful Persian empire united the Greek city-states. Around 500B.C. Greeks were attacked by the ...
Glossary and Terms
... Citizen - A Roman citizen had certain rights and privileges including the right to vote. Only freeborn men were fully Roman citizens. Cohort - A cohort was a division of the Roman army. It was made up of five or six centuries or 480 men. There were 10 cohorts in a Roman legion. Consul - The highest ...
... Citizen - A Roman citizen had certain rights and privileges including the right to vote. Only freeborn men were fully Roman citizens. Cohort - A cohort was a division of the Roman army. It was made up of five or six centuries or 480 men. There were 10 cohorts in a Roman legion. Consul - The highest ...
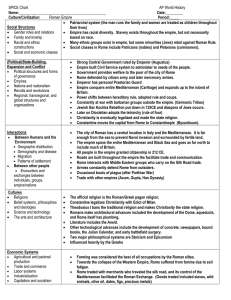
Rome SPICE Chart
... Empire built Civil Service system to administer to needs of the people. Government provides welfare to the poor of the city of Rome Rome defended by citizen army and later mercenary armies. Emperor has personal Praetorian Guard Empire conquers entire Mediterranean (Carthage) and expands up to the is ...
... Empire built Civil Service system to administer to needs of the people. Government provides welfare to the poor of the city of Rome Rome defended by citizen army and later mercenary armies. Emperor has personal Praetorian Guard Empire conquers entire Mediterranean (Carthage) and expands up to the is ...
The Roman Empire - Suffolk Archaeology
... The Roman Empire was a mul ‐cultural society with La n spoken in the West and Greek in the East. Roman rule fostered a sense of Romanisa on by building public monuments and communal spaces such as forums, amphitheatres, racetracks and baths. A rectangular plaza, the forum was for centuries the cent ...
... The Roman Empire was a mul ‐cultural society with La n spoken in the West and Greek in the East. Roman rule fostered a sense of Romanisa on by building public monuments and communal spaces such as forums, amphitheatres, racetracks and baths. A rectangular plaza, the forum was for centuries the cent ...
SOL Rome Review
... •Geographically Rome is on a peninsula in the center of which body of water? ...
... •Geographically Rome is on a peninsula in the center of which body of water? ...
Slide 1
... and the Hellenistic Kingdoms. Hellenistic Kingdoms = Alexander the Great’s kingdom: Macedonia (northern Greece) + spread East all the way to Indian border + Egypt Leaders during this time: Julius Caesar, Augustus Caesar, & Marcus Aurelius ...
... and the Hellenistic Kingdoms. Hellenistic Kingdoms = Alexander the Great’s kingdom: Macedonia (northern Greece) + spread East all the way to Indian border + Egypt Leaders during this time: Julius Caesar, Augustus Caesar, & Marcus Aurelius ...
The Early Byzantine Period: The `First Golden Age
... At the Eastern Empire's greatest expanse during the sixth century, the emperor Justinian (483-565) controlled most of the lands surrounding the Mediterranean Sea. He was an ambitious builder, his greatest monument being the magnificent domed church of Hagia Sophia (Holy Wisdom), which was constructe ...
... At the Eastern Empire's greatest expanse during the sixth century, the emperor Justinian (483-565) controlled most of the lands surrounding the Mediterranean Sea. He was an ambitious builder, his greatest monument being the magnificent domed church of Hagia Sophia (Holy Wisdom), which was constructe ...
well - OpenStudy
... about the Ivies being elitist; they should go look at ancient China. You one of those ego bruised people complaining about how they never got into an Ivy? Yeah well try not being able to go AT ALL, to any college or university. ...
... about the Ivies being elitist; they should go look at ancient China. You one of those ego bruised people complaining about how they never got into an Ivy? Yeah well try not being able to go AT ALL, to any college or university. ...
d. Harsha
... a. the Song emperors outlawed the printing of paper money by anyone. b. the Song emperors transferred the printing of paper money from governmental to private control. c. the Chinese economy collapsed because of inflation caused by the printing of paper money. d. the Tang emperors established the fi ...
... a. the Song emperors outlawed the printing of paper money by anyone. b. the Song emperors transferred the printing of paper money from governmental to private control. c. the Chinese economy collapsed because of inflation caused by the printing of paper money. d. the Tang emperors established the fi ...
1. Do reading #1 and answer the following questions: * Who were
... * How did the office of dictator contribute to the balance and stability of the Roman Republic? * What were the requirements for Roman citizenship? What "rights" did Roman citizens have? * How "democratic" was the government of the early Roman Republic? 2. What was the purpose of the Twelve Tables ...
... * How did the office of dictator contribute to the balance and stability of the Roman Republic? * What were the requirements for Roman citizenship? What "rights" did Roman citizens have? * How "democratic" was the government of the early Roman Republic? 2. What was the purpose of the Twelve Tables ...
Sino-Roman relations

Sino-Roman relations were essentially indirect throughout the existence of both empires. The Roman Empire and the ancient Han dynasty progressively inched closer in the course of the Roman expansion into the Ancient Near East and simultaneous Chinese military incursions into Central Asia. However, powerful intermediate empires such as the Parthians and Kushans kept the two Eurasian flanking powers permanently apart and mutual awareness remained low and knowledge fuzzy.Only a few attempts at direct contact are known from records: In 97 BCE, the Chinese general Ban Chao unsuccessfully tried to send an envoy to Rome. Several alleged Roman emissaries to China were recorded by ancient Chinese historians. The first one on record, supposedly from either the Roman emperor Antoninus Pius or the later emperor Marcus Aurelius, arrived in 166 CE.The indirect exchange of goods on the land (the so-called silk road) and sea routes included Chinese silk and Roman glassware and high-quality cloth.In classical sources, the problem of identifying references to ancient China is exacerbated by the interpretation of the Latin term ""Seres,"" whose meaning fluctuated and could refer to a number of Asian people in a wide arc from India over Central Asia to China. In Chinese records, the Roman Empire came to be known as ""Da Qin"", Great Qin, apparently thought to be a sort of counter-China at the other end of the world. According to Edwin G. Pulleyblank, the ""point that needs to be stressed is that the Chinese conception of Da Qin was confused from the outset with ancient mythological notions about the far west"".