Unit 1: Biology Review
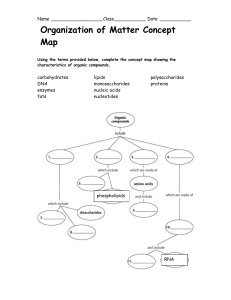
... and reproduction. Phospholipids are extremely important, as they form the membranes around your cells. Phospholipids have a hydrophyllic (water loving, polar) head, and a hydrophobic (nonpolar, water fearing) tail/s. Proteins serve a variety of functions in your body including structure and reaction ...
... and reproduction. Phospholipids are extremely important, as they form the membranes around your cells. Phospholipids have a hydrophyllic (water loving, polar) head, and a hydrophobic (nonpolar, water fearing) tail/s. Proteins serve a variety of functions in your body including structure and reaction ...
Study guide for research assistants
... proteins; with this assignment we will try to flesh out your understanding of this process (and thus your understanding of the work being done by some others in the Van Voorhis group and collaborating groups). Abstract Note that the words “protein” and “target” are sometimes used interchangeably. In ...
... proteins; with this assignment we will try to flesh out your understanding of this process (and thus your understanding of the work being done by some others in the Van Voorhis group and collaborating groups). Abstract Note that the words “protein” and “target” are sometimes used interchangeably. In ...
Polymers vs. monomers wkst. and concept map
... ________________________________________ 20. Your best friend tells you that they are deathly allergic to certain amino acids in food. Your mom has prepared dinner already, so you need to tell her not to serve what macromolecule to them? ...
... ________________________________________ 20. Your best friend tells you that they are deathly allergic to certain amino acids in food. Your mom has prepared dinner already, so you need to tell her not to serve what macromolecule to them? ...
Theme 1 - NUI Galway
... To make the problem more readily tractable we propose to study a dimer system. The test molecule is Azurin, a structurally well-characterised -sheet protein, which can Figure 2. FITC-Azurin uptake in invade mammalian cells.2 The crystal structure of Azurin breast cancer cell line MCF-7. reveals a d ...
... To make the problem more readily tractable we propose to study a dimer system. The test molecule is Azurin, a structurally well-characterised -sheet protein, which can Figure 2. FITC-Azurin uptake in invade mammalian cells.2 The crystal structure of Azurin breast cancer cell line MCF-7. reveals a d ...
how does it end up in the correct place?
... What happens to the protein? Folding Sorting What happens to the mRNA, the ribosomes & the tRNA? Reuse Polysomes ...
... What happens to the protein? Folding Sorting What happens to the mRNA, the ribosomes & the tRNA? Reuse Polysomes ...
Pressure - People Server at UNCW
... Ligand binding: Charged/polar regions of active site and ligand have a hydration shell of densely packed water. Protein-ligand binding forces water into a less dense bulk phase (increased system V). Protein conformational change: (1) Packing of amino acids in protein may change protein density. (2) ...
... Ligand binding: Charged/polar regions of active site and ligand have a hydration shell of densely packed water. Protein-ligand binding forces water into a less dense bulk phase (increased system V). Protein conformational change: (1) Packing of amino acids in protein may change protein density. (2) ...
Biochemistry WebQuest
... A) forms a chain of amino acids B) forms a spiral (helix) C) folds on itself (bends) D) More than one chain joins together E) all of these Enzymes Go to http://science.howstuffworks.com/cell2.htm Read the text and answer the following questions 1. What is the purpose of enzymes? 2. What type of orga ...
... A) forms a chain of amino acids B) forms a spiral (helix) C) folds on itself (bends) D) More than one chain joins together E) all of these Enzymes Go to http://science.howstuffworks.com/cell2.htm Read the text and answer the following questions 1. What is the purpose of enzymes? 2. What type of orga ...
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY SEMINAR Professor Jeff Kelly Biological and Chemical Approaches to Adapt
... Biological and Chemical Approaches to Adapt Proteostasis to Ameliorate Protein Aggregation Diseases The cellular protein homeostasis, or proteostasis network, regulates proteome function by controlling ribosomal protein synthesis, chaperone and enzyme mediated protein folding, protein trafficking, p ...
... Biological and Chemical Approaches to Adapt Proteostasis to Ameliorate Protein Aggregation Diseases The cellular protein homeostasis, or proteostasis network, regulates proteome function by controlling ribosomal protein synthesis, chaperone and enzyme mediated protein folding, protein trafficking, p ...
DNA to Protein Name____________ Period______ DNA Location
... 1. DNA is contained in the nucleus of eukaryotes (plants/animals) 2. DNA mRNA The DNA message gets copied into mRNA. This is called transcription. 3. The mRNA leaves nucleus and sticks to ribosomes. (The ribosomes can be floating in cytoplasm (free) or stuck to rough endoplasmic reticulum.) 4. Ribo ...
... 1. DNA is contained in the nucleus of eukaryotes (plants/animals) 2. DNA mRNA The DNA message gets copied into mRNA. This is called transcription. 3. The mRNA leaves nucleus and sticks to ribosomes. (The ribosomes can be floating in cytoplasm (free) or stuck to rough endoplasmic reticulum.) 4. Ribo ...
Chapter 2 Study Guide
... 16. What two reactions (processes) take place during metabolism? What is the difference between the two? ...
... 16. What two reactions (processes) take place during metabolism? What is the difference between the two? ...
Hints on Column Chromatography
... 1. Protect N-terminus of valine 2. Protect C-terminus of alanine 3. Couple valine and alanine 4. Deprotect to get dipeptide ...
... 1. Protect N-terminus of valine 2. Protect C-terminus of alanine 3. Couple valine and alanine 4. Deprotect to get dipeptide ...
I. Biology (35 points total) The following questions cover some of the
... primary structure: The chemical structure of the polypeptide chain or chains in a given protein i.e., the number and sequence of amino acid residues linked together by peptide bonds. Since the peptide bonds are directional (one amino acid’s –NH2 is connected to the other amino acid’s –COOH), this ...
... primary structure: The chemical structure of the polypeptide chain or chains in a given protein i.e., the number and sequence of amino acid residues linked together by peptide bonds. Since the peptide bonds are directional (one amino acid’s –NH2 is connected to the other amino acid’s –COOH), this ...
Style D 36 by 54 - Bourns College of Engineering
... Genetic incorporation of unnatural amino acids site-specifically into proteins provides a way to manipulate the structures of proteins, monitor protein function and create proteins with novel properties. In previous studies, by creating orthogonal tRNA- synthetase pairs with specificity to unnatural ...
... Genetic incorporation of unnatural amino acids site-specifically into proteins provides a way to manipulate the structures of proteins, monitor protein function and create proteins with novel properties. In previous studies, by creating orthogonal tRNA- synthetase pairs with specificity to unnatural ...
From Genes to Proteins
... • When a tRNA’s anticodon matches up with the codon of mRNA, it drops off its’ amino acid. • Each amino acid forms a peptide bond with the previous amino acid which results in the production of a protein. ...
... • When a tRNA’s anticodon matches up with the codon of mRNA, it drops off its’ amino acid. • Each amino acid forms a peptide bond with the previous amino acid which results in the production of a protein. ...
From DNA to Protein
... Why do we need to store the genetic code in the polymer DNA? After a cell divides, the offspring cells should have the same ability to produce the right proteins as the parent cell. A skin cell should be able to produce skin proteins, a hair follicle cell hair proteins. The linear polymer DNA with a ...
... Why do we need to store the genetic code in the polymer DNA? After a cell divides, the offspring cells should have the same ability to produce the right proteins as the parent cell. A skin cell should be able to produce skin proteins, a hair follicle cell hair proteins. The linear polymer DNA with a ...
BIO C211 - BITS Pilani
... Biochemistry is the language of biology. Therefore, this course is introduced at the cellular and molecular level and focuses upon biomacromolecules, biosynthesis of macromolecules, energy yielding and energy requiring processes, genetic information etc. This would help going for higher level activi ...
... Biochemistry is the language of biology. Therefore, this course is introduced at the cellular and molecular level and focuses upon biomacromolecules, biosynthesis of macromolecules, energy yielding and energy requiring processes, genetic information etc. This would help going for higher level activi ...
LS1a Fall 09
... c. Use the terms shown below to describe the path that a plasma membrane protein would take from translation to reach its destination. Terms may be used multiple times or not at all. Lysosome Plasma Membrane Vesicles Golgi Apparatus ...
... c. Use the terms shown below to describe the path that a plasma membrane protein would take from translation to reach its destination. Terms may be used multiple times or not at all. Lysosome Plasma Membrane Vesicles Golgi Apparatus ...
midterm 2 asnwer scheme
... Primary structure of protein is its unique sequence of amino acids forming its polypeptide chain Every polypeptides has a specific amino acid sequence the primary structure of a protein is starting from the amino-terminal (N) end to the carboxyl-terminal (C) end secondary structure These coi ...
... Primary structure of protein is its unique sequence of amino acids forming its polypeptide chain Every polypeptides has a specific amino acid sequence the primary structure of a protein is starting from the amino-terminal (N) end to the carboxyl-terminal (C) end secondary structure These coi ...
Gene Ontology (GO)
... Saccharomyces Genome Database (SGD) - database for the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae Mouse Genome Database (MGD) & Gene Expression Database (GXD) - databases for the mouse Mus musculus The Arabidopsis Information Resource (TAIR) - database for the brassica family plant Arabidopsis thaliana ...
... Saccharomyces Genome Database (SGD) - database for the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae Mouse Genome Database (MGD) & Gene Expression Database (GXD) - databases for the mouse Mus musculus The Arabidopsis Information Resource (TAIR) - database for the brassica family plant Arabidopsis thaliana ...
Protein structure prediction

Protein structure prediction is the prediction of the three-dimensional structure of a protein from its amino acid sequence — that is, the prediction of its folding and its secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure from its primary structure. Structure prediction is fundamentally different from the inverse problem of protein design. Protein structure prediction is one of the most important goals pursued by bioinformatics and theoretical chemistry; it is highly important in medicine (for example, in drug design) and biotechnology (for example, in the design of novel enzymes). Every two years, the performance of current methods is assessed in the CASP experiment (Critical Assessment of Techniques for Protein Structure Prediction). A continuous evaluation of protein structure prediction web servers is performed by the community project CAMEO3D.