All About Proteins Proteins are highly folded polymers constructed
... and be able to draw the general structure of an amino acid shown at left. The R groups are important because they may make an amino acid nonpolar, or polar, and some of the polar ones may become charged in water or act as acids or bases. These properties will play a role in helping the finished prot ...
... and be able to draw the general structure of an amino acid shown at left. The R groups are important because they may make an amino acid nonpolar, or polar, and some of the polar ones may become charged in water or act as acids or bases. These properties will play a role in helping the finished prot ...
Chapter 15 Review Questions
... uniform width and to orient the bases correctly for bonding; bases bond together by hydrogen bonding (2 bonds between A and T, 3 bonds between C and G) ...
... uniform width and to orient the bases correctly for bonding; bases bond together by hydrogen bonding (2 bonds between A and T, 3 bonds between C and G) ...
Macromolecules - Teacher Pages
... Carbon compounds can vary greatly in size. Some contain just one or two C atoms, others can have 10 or even 1000 C atoms. Macromolecules form when many smaller molecules bond together. ...
... Carbon compounds can vary greatly in size. Some contain just one or two C atoms, others can have 10 or even 1000 C atoms. Macromolecules form when many smaller molecules bond together. ...
Lipids and proteins Lipids:
... The order of solubility of the above compound is as follows: Ether > Acetone > CCl4 > Alcohol & no solubility for oil in water. ...
... The order of solubility of the above compound is as follows: Ether > Acetone > CCl4 > Alcohol & no solubility for oil in water. ...
Chapter 4 - WordPress.com
... • Glucose is the primary source of energy. • Glucose can be stored as glycogen, and converted to and stored as fat. • Glucose can be catabolized anaerobically and aerobically. Anaerobically, glucose is incompletely broken down (glycolysis) into lactic acid and small amounts of ATP. Aerobically, gluc ...
... • Glucose is the primary source of energy. • Glucose can be stored as glycogen, and converted to and stored as fat. • Glucose can be catabolized anaerobically and aerobically. Anaerobically, glucose is incompletely broken down (glycolysis) into lactic acid and small amounts of ATP. Aerobically, gluc ...
Translation/Protein Synthesis
... Translation/Protein Synthesis Steps 1. Once the mRNA sequence leave the nucleus it attaches to the ribosome 2. The ribosome (which is partly made up of an rRNA molecule) travels down the mRNA sequence until it finds a start spot called a start codon AUG: the ONLY start codon 3. The start codon is ...
... Translation/Protein Synthesis Steps 1. Once the mRNA sequence leave the nucleus it attaches to the ribosome 2. The ribosome (which is partly made up of an rRNA molecule) travels down the mRNA sequence until it finds a start spot called a start codon AUG: the ONLY start codon 3. The start codon is ...
The stuff of life?
... functional groups that form hydrogen bonds with water. Why is a water-insoluble molecule good for: storing energy, or building cell membranes, or ...
... functional groups that form hydrogen bonds with water. Why is a water-insoluble molecule good for: storing energy, or building cell membranes, or ...
RNA
... Tertiary structure: the overall shape of a single protein molecule; most commonly the formation of a hydrophobic core, but also through salt bridges, hydrogen bonds, disulfide bonds. The tertiary structure is ...
... Tertiary structure: the overall shape of a single protein molecule; most commonly the formation of a hydrophobic core, but also through salt bridges, hydrogen bonds, disulfide bonds. The tertiary structure is ...
Slides - gserianne.com
... • Breakdown of proteins regulates the amount of a given protein that exists at any time. • Each protein has unique lifetime, but the lifetimes of different proteins varies tremendously. • Proteins with short life-spans, that are misfolded, or that become oxidized must be destroyed and recycled by th ...
... • Breakdown of proteins regulates the amount of a given protein that exists at any time. • Each protein has unique lifetime, but the lifetimes of different proteins varies tremendously. • Proteins with short life-spans, that are misfolded, or that become oxidized must be destroyed and recycled by th ...
Chapter 5 Guided Notes
... ○ Although these three interactions are relatively ______________________________, their cumulative effect helps _________________________________________________________________________. ○ Strong covalent bonds called _____________________________________________ that form between the sulfhydryl gr ...
... ○ Although these three interactions are relatively ______________________________, their cumulative effect helps _________________________________________________________________________. ○ Strong covalent bonds called _____________________________________________ that form between the sulfhydryl gr ...
Final Exam: Multiple Choice Portion Biochem Block Spring 2016
... B) it has a large value of viscosity C) it has a higher density as a liquid than as a solid D) it has very strong intermolecular forces E) it has a high boiling point of 100 oC F) not applicable; all of these statements are true for water 17. (3 pts) For a favorable reaction, it is always true that: ...
... B) it has a large value of viscosity C) it has a higher density as a liquid than as a solid D) it has very strong intermolecular forces E) it has a high boiling point of 100 oC F) not applicable; all of these statements are true for water 17. (3 pts) For a favorable reaction, it is always true that: ...
Biopolymers
... That extra phosphate group turns out to be very important, and many people think that phosphorus has several unique properties that make it an optimal (and maybe the only) choice for the third monomer of nucleic acids. ...
... That extra phosphate group turns out to be very important, and many people think that phosphorus has several unique properties that make it an optimal (and maybe the only) choice for the third monomer of nucleic acids. ...
Organic Molecules
... – 2nd electron level not full – Only has 4 electrons in 2nd level – Will bond up to four times • Monomer: Small carbon molecules – Ex: Amino acid • Polymer: chain of linked monomers – Ex: Protein ...
... – 2nd electron level not full – Only has 4 electrons in 2nd level – Will bond up to four times • Monomer: Small carbon molecules – Ex: Amino acid • Polymer: chain of linked monomers – Ex: Protein ...
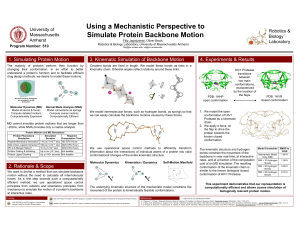
Using a Mechanistic Perspective to Simulate Protein Backbone Motion
... changing their conformation. In an effort to better understand a protein’s function and to facilitate efficient drug design methods, we desire to model these motions. ...
... changing their conformation. In an effort to better understand a protein’s function and to facilitate efficient drug design methods, we desire to model these motions. ...
Name: Proteins Activity Amino Acids, Building Blocks of Proteins
... 7. Cut out the four amino acids. Attempt to join the amino acids. 8. Can the amino acid models easily join to form a protein molecule? 9. Join the molecules by removing as many –OH groups and –H groups as needed from the amino acids. All four amino acid molecules can be joined in this manner to form ...
... 7. Cut out the four amino acids. Attempt to join the amino acids. 8. Can the amino acid models easily join to form a protein molecule? 9. Join the molecules by removing as many –OH groups and –H groups as needed from the amino acids. All four amino acid molecules can be joined in this manner to form ...
here - BioGeometry
... fanfare last month – researchers now face an even more daunting task of figuring out how the 30,000 or so genes give rise to the biological protein machinery that makes humans uniquely humans. A central problem in this field, called “proteomics,” is how to mathematically describe the intricate foldi ...
... fanfare last month – researchers now face an even more daunting task of figuring out how the 30,000 or so genes give rise to the biological protein machinery that makes humans uniquely humans. A central problem in this field, called “proteomics,” is how to mathematically describe the intricate foldi ...
View InSportRecovery Magazine Advertisement
... Amino acids are the building blocks of protein and, in fact, the building blocks of life itself. They are essential to optimal metabolic function and critical to growing and maintaining both muscle mass and lean body mass; therefore, the key to MAXIMUM human performance. The essential amino acids in ...
... Amino acids are the building blocks of protein and, in fact, the building blocks of life itself. They are essential to optimal metabolic function and critical to growing and maintaining both muscle mass and lean body mass; therefore, the key to MAXIMUM human performance. The essential amino acids in ...
Chemistry on living things
... A. Organic compounds made from C, H, and O B. They also contain nitrogen, and sometimes sulfur and phosphorus C. The buildings blocks of proteins are called amino acids. I. There are about 20 different amino acids II. These amino acids combine in many different ways to produce thousands of proteins ...
... A. Organic compounds made from C, H, and O B. They also contain nitrogen, and sometimes sulfur and phosphorus C. The buildings blocks of proteins are called amino acids. I. There are about 20 different amino acids II. These amino acids combine in many different ways to produce thousands of proteins ...
Illustrating Protein Synthesis
... Illustrating Protein Synthesis The Central dogma states that DNA is transcribed into RNA and RNA is then translated into Proteins. For this assignment, you (and 1 partner if you would like) will illustrate this process being sure to include the components below. This illustration must show the proce ...
... Illustrating Protein Synthesis The Central dogma states that DNA is transcribed into RNA and RNA is then translated into Proteins. For this assignment, you (and 1 partner if you would like) will illustrate this process being sure to include the components below. This illustration must show the proce ...
Protein structure prediction

Protein structure prediction is the prediction of the three-dimensional structure of a protein from its amino acid sequence — that is, the prediction of its folding and its secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure from its primary structure. Structure prediction is fundamentally different from the inverse problem of protein design. Protein structure prediction is one of the most important goals pursued by bioinformatics and theoretical chemistry; it is highly important in medicine (for example, in drug design) and biotechnology (for example, in the design of novel enzymes). Every two years, the performance of current methods is assessed in the CASP experiment (Critical Assessment of Techniques for Protein Structure Prediction). A continuous evaluation of protein structure prediction web servers is performed by the community project CAMEO3D.