Macromolecules For Identification
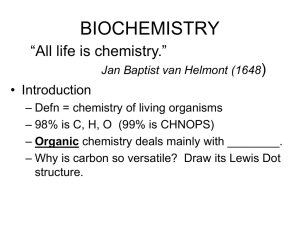
... • The building blocks of proteins are amino acids. There are 20 different amino acids that combine to form polypeptides (proteins). • The different amino acids are similar in structure. • The different amino acids have different side chain, but are otherwise identical. • Proteins have many important ...
... • The building blocks of proteins are amino acids. There are 20 different amino acids that combine to form polypeptides (proteins). • The different amino acids are similar in structure. • The different amino acids have different side chain, but are otherwise identical. • Proteins have many important ...
Chapter 3 Everyday Chemistry of Life Chemistry is crucial Biology
... o They are important for a wide variety of functions in the body including hormones, structure, enzymes, communication, and transport o All of the huge variety of proteins are composed of the same 20 amino acids o They can denature, changing in shape, causing loss of function Amino acids o All amino ...
... o They are important for a wide variety of functions in the body including hormones, structure, enzymes, communication, and transport o All of the huge variety of proteins are composed of the same 20 amino acids o They can denature, changing in shape, causing loss of function Amino acids o All amino ...
Document
... restricted in the absence of an experimental structure of the receptor protein/enzyme. When we analyze, it occurred to us that most of these ‘important target receptors’ whose structures are not available belong to the class of ‘membrane proteins’. ...
... restricted in the absence of an experimental structure of the receptor protein/enzyme. When we analyze, it occurred to us that most of these ‘important target receptors’ whose structures are not available belong to the class of ‘membrane proteins’. ...
MTC15 - toddgreen
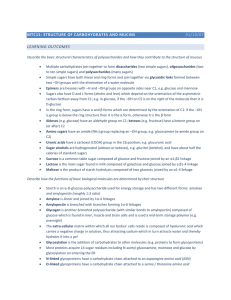
... Amylose is linear and joined by 1α-4 linkages Amylopectin is branched with branches forming 1α-6 linkages Glycogen is another branched polysaccharide (with similar bonds to amylopectin) composed of glucose which is found in liver, muscle and brain cells and is used a mid-term storage polymer (e.g. o ...
... Amylose is linear and joined by 1α-4 linkages Amylopectin is branched with branches forming 1α-6 linkages Glycogen is another branched polysaccharide (with similar bonds to amylopectin) composed of glucose which is found in liver, muscle and brain cells and is used a mid-term storage polymer (e.g. o ...
Madhavi_11072005
... – Measure how far away from “truth” the prediction is (what threshold would have classified the segment correctly as TM or non TM) – Characteristics of the segments misclassified ...
... – Measure how far away from “truth” the prediction is (what threshold would have classified the segment correctly as TM or non TM) – Characteristics of the segments misclassified ...
هيتايحلأءايميكلأ د دادعأ . باهولأدبع ناميأ
... and formed from elimination of amine group from amino acid such as , urea, creatinin, uric acid , ammonia, etc--Transportation of ammonia: 1. The final de amination and production of ammonia is taking place in liver. 2. Glutamic acid the major transport form of ammonia from the tissues to the liver. ...
... and formed from elimination of amine group from amino acid such as , urea, creatinin, uric acid , ammonia, etc--Transportation of ammonia: 1. The final de amination and production of ammonia is taking place in liver. 2. Glutamic acid the major transport form of ammonia from the tissues to the liver. ...
Chapter 4: Amino Acids General Features of Amino Acids
... Peptide bond formation is a condensation reaction leading to the polymerization of amino acids into peptides and proteins. (Peptide: hormones, neurotransmitters, several antibiotics and antitumor agents) The presence of the carbonyl group in a peptide bond allows electron resonance stabilization to ...
... Peptide bond formation is a condensation reaction leading to the polymerization of amino acids into peptides and proteins. (Peptide: hormones, neurotransmitters, several antibiotics and antitumor agents) The presence of the carbonyl group in a peptide bond allows electron resonance stabilization to ...
What is Health SCIENCE? - petlakhealthscience20
... • CORRECT AS CLASS – SELF-ASSESS – SUBMIT MARK ...
... • CORRECT AS CLASS – SELF-ASSESS – SUBMIT MARK ...
doc - DePaul University
... conducted by Desjarlais and Handle [6] [19] [20]. Their approach focused on the repacking of the hydrophobic core and results suggested that the core amino acids are likely responsible for the overall stability of the protein while the non-core amino acids play a significant role in determining the ...
... conducted by Desjarlais and Handle [6] [19] [20]. Their approach focused on the repacking of the hydrophobic core and results suggested that the core amino acids are likely responsible for the overall stability of the protein while the non-core amino acids play a significant role in determining the ...
the code of translation
... 5. The first tRNA leaves, and the ribosome moves along the mRNA to the next codon. 6. The next tRNA brings in the next amino acid, and a peptide bond is formed between this amino acid and the growing amino acid chain. 7. The process continues with the ribosome moving along the mRNA molecule and the ...
... 5. The first tRNA leaves, and the ribosome moves along the mRNA to the next codon. 6. The next tRNA brings in the next amino acid, and a peptide bond is formed between this amino acid and the growing amino acid chain. 7. The process continues with the ribosome moving along the mRNA molecule and the ...
fat-soluble
... NADH produced by glycolysis in skeletal muscle fibers leads to production of two ATP molecules in mitochondria, but NADH produced by glycolysis in cardiac muscle cells leads to production of three ATP molecules. Why? ...
... NADH produced by glycolysis in skeletal muscle fibers leads to production of two ATP molecules in mitochondria, but NADH produced by glycolysis in cardiac muscle cells leads to production of three ATP molecules. Why? ...
Chapter 25 - FacultyWeb
... NADH produced by glycolysis in skeletal muscle fibers leads to production of two ATP molecules in mitochondria, but NADH produced by glycolysis in cardiac muscle cells leads to production of three ATP molecules. Why? ...
... NADH produced by glycolysis in skeletal muscle fibers leads to production of two ATP molecules in mitochondria, but NADH produced by glycolysis in cardiac muscle cells leads to production of three ATP molecules. Why? ...
What is a Genome? - Mainlab Bioinformatics
... Protein structure • Properties of amino acids determine the structure of the protein ...
... Protein structure • Properties of amino acids determine the structure of the protein ...
Chapter 11: DNA and Genes
... ribosomes for protein manufacturing. In the nucleus, enzymes make an RNA copy of a portion of a DNA strand by this process. Forms a single-stranded RNA molecule rather than a double-stranded DNA molecule. Page 296, Figure 11.6 has a diagram and step-bystep information for this process. http://www.dn ...
... ribosomes for protein manufacturing. In the nucleus, enzymes make an RNA copy of a portion of a DNA strand by this process. Forms a single-stranded RNA molecule rather than a double-stranded DNA molecule. Page 296, Figure 11.6 has a diagram and step-bystep information for this process. http://www.dn ...
Kids Building Bricks - Johnston County Schools
... • tRNA brings aa’s to the ribosome • Each tRNA attaches to only one type of amino acid, but how does it know which one is needed? • Each tRNA has a sequence of 3 nucleotides (anticodon) • tRNA anticodon pairs w/ the mRNA codon ...
... • tRNA brings aa’s to the ribosome • Each tRNA attaches to only one type of amino acid, but how does it know which one is needed? • Each tRNA has a sequence of 3 nucleotides (anticodon) • tRNA anticodon pairs w/ the mRNA codon ...
Protein structure prediction

Protein structure prediction is the prediction of the three-dimensional structure of a protein from its amino acid sequence — that is, the prediction of its folding and its secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure from its primary structure. Structure prediction is fundamentally different from the inverse problem of protein design. Protein structure prediction is one of the most important goals pursued by bioinformatics and theoretical chemistry; it is highly important in medicine (for example, in drug design) and biotechnology (for example, in the design of novel enzymes). Every two years, the performance of current methods is assessed in the CASP experiment (Critical Assessment of Techniques for Protein Structure Prediction). A continuous evaluation of protein structure prediction web servers is performed by the community project CAMEO3D.