6.13 Study Guide 1 - answers - buaron-history
... 10. Why were slaves important in to the Roman Empire? (p. 522) The day to day running of the Roman Empire depended on them. 11. What did the Roman Census tell us? (p. 522) At the time of Augustus, 1 million people lived in Rome. ...
... 10. Why were slaves important in to the Roman Empire? (p. 522) The day to day running of the Roman Empire depended on them. 11. What did the Roman Census tell us? (p. 522) At the time of Augustus, 1 million people lived in Rome. ...
ss8_earlymid_quiz
... 1. The Roman Empire soon became too large, so what did the Romans do to insure the continuation of the Empire? a. The army was made bigger b. the Empire was spilt into two c. Pax Romana was enforced d. More roads were built 2. The Roman’s considered their neighbours to be Barbarians, largely because ...
... 1. The Roman Empire soon became too large, so what did the Romans do to insure the continuation of the Empire? a. The army was made bigger b. the Empire was spilt into two c. Pax Romana was enforced d. More roads were built 2. The Roman’s considered their neighbours to be Barbarians, largely because ...
Fall of the Roman Empire
... who ruled the eastern half. The real reason it fell was because of greed. ...
... who ruled the eastern half. The real reason it fell was because of greed. ...
The Lasting Contributions of Rome
... have been influenced by Roman law. • Principles of the Roman Republic, such as equal justice under the law, are still important. ...
... have been influenced by Roman law. • Principles of the Roman Republic, such as equal justice under the law, are still important. ...
File - According to Phillips
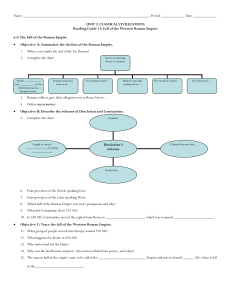
... Objective C: Trace the fall of the Western Roman Empire. 11. What group of people moved into Europe around 370 AD? 12. What happened in Rome in 410 AD? 13. Who united and led the Huns? 14. Who was the last Roman emperor, who removed him from power, and when? 15. The eastern half of the empire came t ...
... Objective C: Trace the fall of the Western Roman Empire. 11. What group of people moved into Europe around 370 AD? 12. What happened in Rome in 410 AD? 13. Who united and led the Huns? 14. Who was the last Roman emperor, who removed him from power, and when? 15. The eastern half of the empire came t ...
Flashcards for Rome Test
... An item/good that a country has a surplus of and is able to ship out to make a profit ...
... An item/good that a country has a surplus of and is able to ship out to make a profit ...
Beginning of the Empire—after Caesar`s death, civil war broke out
... Pax Romana—(27 B.C.-180 A.D.)GOLDEN AGE! A period of peace and prosperity during which Romans developed many styles of art, architecture, literature and drama which made long lasting contributions to Western ...
... Pax Romana—(27 B.C.-180 A.D.)GOLDEN AGE! A period of peace and prosperity during which Romans developed many styles of art, architecture, literature and drama which made long lasting contributions to Western ...
homework due. Republic to Empire
... • 12/6 Focus – The fall of Rome didn’t happen over night. Rome was hit with many years of corruption, invasions and bad rulers. All these factors slowly caused the Roman empire to collapse ...
... • 12/6 Focus – The fall of Rome didn’t happen over night. Rome was hit with many years of corruption, invasions and bad rulers. All these factors slowly caused the Roman empire to collapse ...
The Byzantine Empire – Introduction (HA) In this chapter, you will
... Later, control of the huge original empire was divided between two emperors— one based in Rome and one based in Constantinople. After the fall of Rome, ...
... Later, control of the huge original empire was divided between two emperors— one based in Rome and one based in Constantinople. After the fall of Rome, ...
The basic unit of the ancient roman army, made up of 5,000 soldiers
... 19. What did the government try to do to bring more money into the government after the Pax Romana but was a failure because it hurt the economy? ...
... 19. What did the government try to do to bring more money into the government after the Pax Romana but was a failure because it hurt the economy? ...
Country Life PowerPoint
... would grow grain and use animals such as cows, pigs, goats, sheep, and bees for other foods and supplies ...
... would grow grain and use animals such as cows, pigs, goats, sheep, and bees for other foods and supplies ...
Ancient Rome-The Roman Empire Notes
... people could meet for business or fun. It was there that merchants sold goods and food and that public notices were posted. The _________________________________ was an arena where Romans watched battles between _____________________________________. People found it entertaining to watch the gladiat ...
... people could meet for business or fun. It was there that merchants sold goods and food and that public notices were posted. The _________________________________ was an arena where Romans watched battles between _____________________________________. People found it entertaining to watch the gladiat ...
Student Made PowerPoint on Byzantium
... •Initial Byzantine Economics involved strict government involvement in the exports and imports of the Empire •Regulated interest rates and had a monopoly on coining currency •Often intervened to prevent economic failures and to redistribute surplus through public works and burucratic salaries •Const ...
... •Initial Byzantine Economics involved strict government involvement in the exports and imports of the Empire •Regulated interest rates and had a monopoly on coining currency •Often intervened to prevent economic failures and to redistribute surplus through public works and burucratic salaries •Const ...
The Fall of the Roman Empire: There are 3 main reasons for the
... By 400AD Rome was not as strong as it had been before, historians are unsure why. Here are some suggestions: o The Climate changed = less food grown = declining population. o Lead poisoning from water pipes o Loss of business in the city: Emperor Constantine moved a lot of important business to Cons ...
... By 400AD Rome was not as strong as it had been before, historians are unsure why. Here are some suggestions: o The Climate changed = less food grown = declining population. o Lead poisoning from water pipes o Loss of business in the city: Emperor Constantine moved a lot of important business to Cons ...
Contributions of the Romans
... Romance Languages (from Rome) such as French, Spanish, Portuguese, Italian, and Romanian are all based on Latin. There are Latin roots in many of the words and phrases we use today. ...
... Romance Languages (from Rome) such as French, Spanish, Portuguese, Italian, and Romanian are all based on Latin. There are Latin roots in many of the words and phrases we use today. ...
Daqin

Daqin (Chinese: 大秦; pinyin: Dàqín; Wade–Giles: Ta4-ch'in2; alternative transliterations include Tachin, Tai-Ch'in) is the ancient Chinese name for the Roman Empire or, depending on context, the Near East, especially Syria. It literally means ""Great Qin"", Qin (Chinese: 秦; pinyin: Qín; Wade–Giles: Ch'in2) being the name of the founding dynasty of the Chinese Empire. Historian John Foster defined it as ""...the Roman Empire, or rather that part of it which alone was known to the Chinese, Syria.""