Chapter 18 Section 1 The Conquest of an Empire
... The Roman Army (Input) • Military service was expected of Rome’s male citizens • At first military campaigns were short • A campaign is a military operation with a specific goal, such as capture a city • Unpaid citizen-soldiers left their farms to fight for a few weeks and then returned home ...
... The Roman Army (Input) • Military service was expected of Rome’s male citizens • At first military campaigns were short • A campaign is a military operation with a specific goal, such as capture a city • Unpaid citizen-soldiers left their farms to fight for a few weeks and then returned home ...
Rome-RDG
... We think of bathing as a very private activity conducted in the home, but bathing in Rome was a communal activity, conducted for the most part in public facilities that in some ways resembled modern spas or health clubs. Roman baths were a central part of Roman social life, as well as a way for the ...
... We think of bathing as a very private activity conducted in the home, but bathing in Rome was a communal activity, conducted for the most part in public facilities that in some ways resembled modern spas or health clubs. Roman baths were a central part of Roman social life, as well as a way for the ...
PowerPoint Presentation - The Rise and Fall of the Roman Empire
... Pax Romana • Rome lived in peace for 200 years. • It was called the Pax Romana, the Peace of Rome. Unfortunately for Rome, the peace would not last. ...
... Pax Romana • Rome lived in peace for 200 years. • It was called the Pax Romana, the Peace of Rome. Unfortunately for Rome, the peace would not last. ...
Ancient Greece - Calaveras Unified School District
... 3. Pottery was another source of art - telling myths and legends. C. Sparta defeated Athens in Peloponnesian War of 27 years starting in 431 BC. 1. After having its navy destroyed and the city depleted by plagues, it surrenders. 2. Athens is shaken by defeat. a. Democracy begins to fail. b. Art begi ...
... 3. Pottery was another source of art - telling myths and legends. C. Sparta defeated Athens in Peloponnesian War of 27 years starting in 431 BC. 1. After having its navy destroyed and the city depleted by plagues, it surrenders. 2. Athens is shaken by defeat. a. Democracy begins to fail. b. Art begi ...
File - Mr Boayue`s Social Studies And Science site
... The golden age of Greece saw advances in government, art, and philosophy. • The period between 500 and 300 BC in Greece was a golden age, a period marked by great achievements. • The golden age began after the Greeks banded together to defeat the powerful Persian Empire. • Athens, the city-state tha ...
... The golden age of Greece saw advances in government, art, and philosophy. • The period between 500 and 300 BC in Greece was a golden age, a period marked by great achievements. • The golden age began after the Greeks banded together to defeat the powerful Persian Empire. • Athens, the city-state tha ...
Document
... The golden age of Greece saw advances in government, art, and philosophy. • The period between 500 and 300 BC in Greece was a golden age, a period marked by great achievements. • The golden age began after the Greeks banded together to defeat the powerful Persian Empire. • Athens, the city-state tha ...
... The golden age of Greece saw advances in government, art, and philosophy. • The period between 500 and 300 BC in Greece was a golden age, a period marked by great achievements. • The golden age began after the Greeks banded together to defeat the powerful Persian Empire. • Athens, the city-state tha ...
Rome: Republic and Empire - room203-Rome
... Much of the themes emphasize war and conquest The arts mostly had a practical side Toward the end of the era, wealth mattered more than duty that had marked Rome’s earlier years The insecurity of the latter years also opened the populace to new ideologies: mystical cults, revivals of older b ...
... Much of the themes emphasize war and conquest The arts mostly had a practical side Toward the end of the era, wealth mattered more than duty that had marked Rome’s earlier years The insecurity of the latter years also opened the populace to new ideologies: mystical cults, revivals of older b ...
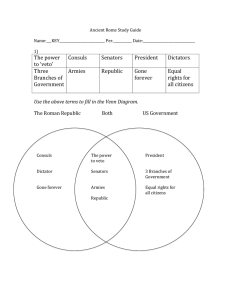
Rome Study Guide Answer Key
... __TAXES____________________. The Romans were more interested in using their knowledge to ____BUILD__________________ things better than anyone else. Roman ___LAW___________________ is passed down through other cultures because it promoted fairness. ...
... __TAXES____________________. The Romans were more interested in using their knowledge to ____BUILD__________________ things better than anyone else. Roman ___LAW___________________ is passed down through other cultures because it promoted fairness. ...
The city of Rome was founded on a group of hills about fourteen
... the Apennine Mountains. This mountain range ran north and south through nearly the entire length of the peninsula. Rome was not right on the sea, but the Romans had easy access to the sea. This helped them develop trade with merchants from Greece and Carthage. The earliest Romans were shepherds and ...
... the Apennine Mountains. This mountain range ran north and south through nearly the entire length of the peninsula. Rome was not right on the sea, but the Romans had easy access to the sea. This helped them develop trade with merchants from Greece and Carthage. The earliest Romans were shepherds and ...
An Army Like No Other:The Roman Army
... Auxiliaries were men from conquered territories who received similar training like Romans Majority served as archers or as horse archers Granted citizenship after 25 years and were paid lower wages than Roman troops Stationed in along frontiers away from home countries ...
... Auxiliaries were men from conquered territories who received similar training like Romans Majority served as archers or as horse archers Granted citizenship after 25 years and were paid lower wages than Roman troops Stationed in along frontiers away from home countries ...
chapter_9_the_glory_of_ancient_rome_1
... flowed freely to all parts of the empire. • Merchants made their living from tourists who visited the city. ...
... flowed freely to all parts of the empire. • Merchants made their living from tourists who visited the city. ...
Ancient Rome
... way to northern Italy, crossed the Alps (on elephants) and surprised the Romans. • He was on the verge of destroying Rome when Roman soldiers landed in Carthage. He had to return home to defend his city. • Fifty years later, in 149 B.C.E., the Third Punic War was instigated by Rome. ...
... way to northern Italy, crossed the Alps (on elephants) and surprised the Romans. • He was on the verge of destroying Rome when Roman soldiers landed in Carthage. He had to return home to defend his city. • Fifty years later, in 149 B.C.E., the Third Punic War was instigated by Rome. ...
Y2 Q3A Roman Art Tutor Guide
... Arch of Titus (detail on inside of arch) “Spoils of Jerusalem”, 82 AD The realism of Roman art was not confined to imperial art. It is evident in the trompe l’oeil frescoes of Roman villas uncovered in Pompeii and even in funeral portraits made in honor of beloved relatives. Many portraits painted o ...
... Arch of Titus (detail on inside of arch) “Spoils of Jerusalem”, 82 AD The realism of Roman art was not confined to imperial art. It is evident in the trompe l’oeil frescoes of Roman villas uncovered in Pompeii and even in funeral portraits made in honor of beloved relatives. Many portraits painted o ...
File - Harrer History
... After fighting several northern tribes (Celtics, Gauls) and seeing Rome destroyed in 387 B.C.E., The Republic recovered and began to conquer other city-states, controlling the entire Italian Peninsula by 321 B.C.E. How did Roman did rule of conquered people similar and differ from the Persians? ...
... After fighting several northern tribes (Celtics, Gauls) and seeing Rome destroyed in 387 B.C.E., The Republic recovered and began to conquer other city-states, controlling the entire Italian Peninsula by 321 B.C.E. How did Roman did rule of conquered people similar and differ from the Persians? ...
World History Study Guide Ch 7 The Roman World File
... 3. What was the Conflict of the Orders, and how did it change the early Roman Republic? 4. How were the roles of citizens and noncitizens under Roman rule different? 5. How was Rome helped by its location? 6. How did the Romans organize the government of the republic? ...
... 3. What was the Conflict of the Orders, and how did it change the early Roman Republic? 4. How were the roles of citizens and noncitizens under Roman rule different? 5. How was Rome helped by its location? 6. How did the Romans organize the government of the republic? ...
Ancient Roman Inventions Ancient Roman inventions abound and
... although the variety of uses and production techniques of ancient Roman glass greatly evolved thanks to the market economy and open trade across the Roman empire. A particularly interesting example of this is mould blown glass which appears to have been introduced to Rome and "took off" during the r ...
... although the variety of uses and production techniques of ancient Roman glass greatly evolved thanks to the market economy and open trade across the Roman empire. A particularly interesting example of this is mould blown glass which appears to have been introduced to Rome and "took off" during the r ...
Rome-Republic_to_Empire
... The first 200 years of the Roman Empire were a time of general peace and prosperity. Characteristics of the Pax Romana were a stable government and an organized military. There were no major wars or rebellions in the empire. The empire’s trade increased, the population grew, and there was an improve ...
... The first 200 years of the Roman Empire were a time of general peace and prosperity. Characteristics of the Pax Romana were a stable government and an organized military. There were no major wars or rebellions in the empire. The empire’s trade increased, the population grew, and there was an improve ...
A Republic Forms in Rome
... Over time, the plebeians gained the right to elect their own officials , called tribunes, to protect their interests. The tribunes could veto, or block, laws that they felt were harmful to plebeians. Eventually, plebeians were also chosen as consuls to the Senate. ...
... Over time, the plebeians gained the right to elect their own officials , called tribunes, to protect their interests. The tribunes could veto, or block, laws that they felt were harmful to plebeians. Eventually, plebeians were also chosen as consuls to the Senate. ...
The Roman Empire, founded by Augustus Caesar in 27 B.C. and
... aced with brick or stone and over curved wooden molds, or forms, to span spaces as vaults. The Medit erranean is an active volcanic region, and a spongy, light, tightly adhering stone called pozzolana was used to produce a concrete that was both light and extremely strong. The Romans had developed p ...
... aced with brick or stone and over curved wooden molds, or forms, to span spaces as vaults. The Medit erranean is an active volcanic region, and a spongy, light, tightly adhering stone called pozzolana was used to produce a concrete that was both light and extremely strong. The Romans had developed p ...
Unit 2
... 1. Explain the differences in government in: (a) Greece, (b) the Roman Republic, (c) the Roman Empire 2. (a) How did Alexander the Great change Greece? (b) How did Augustus change Rome? (c) How did Jesus change the Mediterranean world? 3. Identify and explain the 5 most significant Greco-Roman accom ...
... 1. Explain the differences in government in: (a) Greece, (b) the Roman Republic, (c) the Roman Empire 2. (a) How did Alexander the Great change Greece? (b) How did Augustus change Rome? (c) How did Jesus change the Mediterranean world? 3. Identify and explain the 5 most significant Greco-Roman accom ...
Roman Britain - Text, Images and Quiz (Reading Level C)
... the world has ever seen. At its height, it stretched from the Middle East, through Western Europe and North Africa, all the way to Britain! The centre of the Empire was the great city of Rome (now part of Italy). Rome had many emperors during its long history, some more famous than others. They had ...
... the world has ever seen. At its height, it stretched from the Middle East, through Western Europe and North Africa, all the way to Britain! The centre of the Empire was the great city of Rome (now part of Italy). Rome had many emperors during its long history, some more famous than others. They had ...
Lesson One: The Fall of Rome
... a year were hot, dirty, crowed, and dangerous. Anyone who could not pay the rent was forced to move out and live on the crime-infested streets. Because of this cities began to decay. Inferior Technology During the last 400 years of the empire, the scientific achievements of the Romans were limited a ...
... a year were hot, dirty, crowed, and dangerous. Anyone who could not pay the rent was forced to move out and live on the crime-infested streets. Because of this cities began to decay. Inferior Technology During the last 400 years of the empire, the scientific achievements of the Romans were limited a ...
The Roman Empire, at its height, extended from modern Sudan in
... really understand what the Romans have ever done for us. Their architecture, art and culture pervade our lives, and we’re extremely lucky that we can go and see for ourselves how they lived and where this influence comes from. Their vast civic buildings tell us of their pride and engineering prowess ...
... really understand what the Romans have ever done for us. Their architecture, art and culture pervade our lives, and we’re extremely lucky that we can go and see for ourselves how they lived and where this influence comes from. Their vast civic buildings tell us of their pride and engineering prowess ...
Unit 2 Classical Civilizations, part 2: An Age of Empires: Rome 753 B
... 6. Romans worshiped a large number of supernatural spirits as well as major gods such as Jupiter and Mars. Proper performance of ritual ensured that the gods continued to favor the Roman state. C. Expansion in Italy and the Mediterranean 1. Rome began to expand, at first slowly and then very rapidl ...
... 6. Romans worshiped a large number of supernatural spirits as well as major gods such as Jupiter and Mars. Proper performance of ritual ensured that the gods continued to favor the Roman state. C. Expansion in Italy and the Mediterranean 1. Rome began to expand, at first slowly and then very rapidl ...
Roman technology

Roman technology is the engineering practice which supported Roman civilization and made the expansion of Roman commerce and Roman military possible for almost three quarters of a millennium (753 BC–476 AD).The Roman Empire had one of the most advanced set of technologies of its time, some of which was lost during the turbulent eras of Late Antiquity and the early Middle Ages. Gradually, some of the technological feats of the Romans were rediscovered and/or improved upon, while others went ahead of what the Romans had done during the Middle Ages and the beginning of the Modern Era. Several Roman technological feats in different areas like civil engineering, construction materials, transport technology, and some inventions such as the mechanical reaper, were surprising achievements until the 19th century. The Romans achieved high levels of technology in large part because they borrowed and absorbed the culture of the pre-existing (Hellenic and others) peoples of the Mediterranean basin.