Roman Architecture - My E-town
... eliminated through the use of sewer systems that are still functional to this day such as the Cloaca Maxima (see figure 1) meaning “greatest sewer” in latin, which began construction in 600 BCE by the fifth king of rome, Lucius Tarquinius Priscus. Architecture from this early period in Rome’s histor ...
... eliminated through the use of sewer systems that are still functional to this day such as the Cloaca Maxima (see figure 1) meaning “greatest sewer” in latin, which began construction in 600 BCE by the fifth king of rome, Lucius Tarquinius Priscus. Architecture from this early period in Rome’s histor ...
Why was the capital of the Roman Empire moved? How Did
... How Did Constantinople become Rome’s New Capital? The Western Roman Empire had been so drained by taxes that it was no longer producing wealth for the state. Even the city of Rome was no longer important, either economically or strategically. The empire’s future lay in the east. In 330, Constantine ...
... How Did Constantinople become Rome’s New Capital? The Western Roman Empire had been so drained by taxes that it was no longer producing wealth for the state. Even the city of Rome was no longer important, either economically or strategically. The empire’s future lay in the east. In 330, Constantine ...
The Roman Empire
... The Roman army became a professional force instead of a citizens’ army. Julius Caesar, a general, conquered part of Gaul (present-day France) and Spain. He then marched his armies back to Rome itself. Caesar threatened to seize absolute power, but was assassinated in 44 B.C. Caesar introduced a new ...
... The Roman army became a professional force instead of a citizens’ army. Julius Caesar, a general, conquered part of Gaul (present-day France) and Spain. He then marched his armies back to Rome itself. Caesar threatened to seize absolute power, but was assassinated in 44 B.C. Caesar introduced a new ...
- Good Food Good Mood
... Roman doctors had a wide range of surgical tools, including catheters and speculums. Many modern medical terms still have Latin roots. The knee cap, for example, is the patella, which is Latin for “shallow dish” The snake was a common image in Roman art and jewellery and was believed to have powers ...
... Roman doctors had a wide range of surgical tools, including catheters and speculums. Many modern medical terms still have Latin roots. The knee cap, for example, is the patella, which is Latin for “shallow dish” The snake was a common image in Roman art and jewellery and was believed to have powers ...
The Roman Empire - White Plains Public Schools
... The Roman army became a professional force instead of a citizens’ army. Julius Caesar, a general, conquered part of Gaul (present-day France) and Spain. He then marched his armies back to Rome itself. Caesar threatened to seize absolute power, but was assassinated in 44 B.C. Caesar introduced a new ...
... The Roman army became a professional force instead of a citizens’ army. Julius Caesar, a general, conquered part of Gaul (present-day France) and Spain. He then marched his armies back to Rome itself. Caesar threatened to seize absolute power, but was assassinated in 44 B.C. Caesar introduced a new ...
DOC - Mr. Dowling
... Sometime before the first surviving written historical account, Rome was controlled by the Etruscans, a brutal civilization from the northern part of the Italian peninsula. Etruscan kings rained terror for more than a century until the Romans rebelled and expelled their ruler in 509BCE. The early Ro ...
... Sometime before the first surviving written historical account, Rome was controlled by the Etruscans, a brutal civilization from the northern part of the Italian peninsula. Etruscan kings rained terror for more than a century until the Romans rebelled and expelled their ruler in 509BCE. The early Ro ...
An excerpt from THE FALL OF THE ROMAN REPUBLIC: LESSONS
... personal patrons rather than state institutions. This instability manifested itself in the increasing role of popular generals in Roman politics, including several willing to implicitly or explicitly threaten civil war to get what they wanted. Marius himself marched on Rome, as did Lucius Cornelius ...
... personal patrons rather than state institutions. This instability manifested itself in the increasing role of popular generals in Roman politics, including several willing to implicitly or explicitly threaten civil war to get what they wanted. Marius himself marched on Rome, as did Lucius Cornelius ...
The Second Triumvirate
... • Less corrupt emperors = Nerva, Trajan, Hadrian, Antonius Pius, & Marcus Aurelius (last emperor of Pax ...
... • Less corrupt emperors = Nerva, Trajan, Hadrian, Antonius Pius, & Marcus Aurelius (last emperor of Pax ...
Daily Life in Ancient Rome
... Housing was very different in Rome for the rich and poor. The spacious, airy homes of the rich stood side by side with the small, dark apartments that housed the poor. Wealthy Romans lived in grand houses built of stone and marble. The walls were thick to keep out the noise of the city. Inside the f ...
... Housing was very different in Rome for the rich and poor. The spacious, airy homes of the rich stood side by side with the small, dark apartments that housed the poor. Wealthy Romans lived in grand houses built of stone and marble. The walls were thick to keep out the noise of the city. Inside the f ...
CH10-Lecture-ONE
... • Republican Verism: Influenced by Greeks, Etruscans & Egyptians, but celebrated their elevated position in society. • Thought head was enough, vs. the Greeks who wanted the whole body. • Wanted brutal realism, yet would put old head on young body. ...
... • Republican Verism: Influenced by Greeks, Etruscans & Egyptians, but celebrated their elevated position in society. • Thought head was enough, vs. the Greeks who wanted the whole body. • Wanted brutal realism, yet would put old head on young body. ...
Ancient Rome - Mr. Fetscher`s Class
... led to Rome for over 1200 years. In the Mediterranean, Rome was in charge. Rome had some wonderful emperors. Rome also suffered from a series of bad, corrupt and just plain crazy emperors. ...
... led to Rome for over 1200 years. In the Mediterranean, Rome was in charge. Rome had some wonderful emperors. Rome also suffered from a series of bad, corrupt and just plain crazy emperors. ...
The Roman Republic
... Generals seized more personal power, New group of soldiers (urban poor or migrants) rejoined the army New soldiers owed allegiance to their generals who promise them wealth The Republic is now in a position to be taken over by one of them ...
... Generals seized more personal power, New group of soldiers (urban poor or migrants) rejoined the army New soldiers owed allegiance to their generals who promise them wealth The Republic is now in a position to be taken over by one of them ...
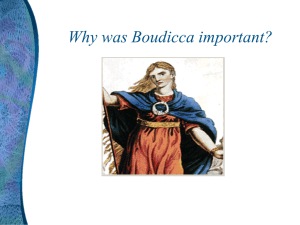
Here
... Boudicca and her army then attacked the town. They even burnt down a temple where elderly soldiers and families had been taking shelter. Next Boudicca led her army to London (it was called Londonium at that time). Here they burned down the city and killed hundreds of people living there. ...
... Boudicca and her army then attacked the town. They even burnt down a temple where elderly soldiers and families had been taking shelter. Next Boudicca led her army to London (it was called Londonium at that time). Here they burned down the city and killed hundreds of people living there. ...
9th Grade World History Overview
... 13) Chapter 16 Web Activity - “The Christian Catacombs of Rome”. 14) View Presentation on Aqueduct Construction, weigh pros/cons, and write an opinion paragraph detailing and supporting your position. 15) Complete Ancient Rome and Roman Heritage Search a Word puzzles. 16) Play Roman Jeopardy. 17) Re ...
... 13) Chapter 16 Web Activity - “The Christian Catacombs of Rome”. 14) View Presentation on Aqueduct Construction, weigh pros/cons, and write an opinion paragraph detailing and supporting your position. 15) Complete Ancient Rome and Roman Heritage Search a Word puzzles. 16) Play Roman Jeopardy. 17) Re ...
the romans - Pearland ISD
... Charismatic Jewish teacher, taught devotion to God, love for human beings Attracted large crowds through his wisdom and miraculous powers The teaching "the kingdom of God is at hand" alarmed the Romans Crucifixion in early 30s C.E.; Became "Christ," or "the anointed one" New Testament and the Old Te ...
... Charismatic Jewish teacher, taught devotion to God, love for human beings Attracted large crowds through his wisdom and miraculous powers The teaching "the kingdom of God is at hand" alarmed the Romans Crucifixion in early 30s C.E.; Became "Christ," or "the anointed one" New Testament and the Old Te ...
29. Motives for Imperialism
... that Romans didn't seek empire or expansion, rather : – result of threats to their own security – Rome acquired her power over other states & peoples as a tangent result of defending itself or its allies – honoring treaties ...
... that Romans didn't seek empire or expansion, rather : – result of threats to their own security – Rome acquired her power over other states & peoples as a tangent result of defending itself or its allies – honoring treaties ...
The Fall of Rome
... empire, but there was still a lot leaving the empire as it was being spent of foreign goods. • With less gold and silver to go around, less was put into the coins. Nice, but that meant the coins were worth less to those who used them. Merchants accordingly raised their prices to get paid the same va ...
... empire, but there was still a lot leaving the empire as it was being spent of foreign goods. • With less gold and silver to go around, less was put into the coins. Nice, but that meant the coins were worth less to those who used them. Merchants accordingly raised their prices to get paid the same va ...
Chapter 11:The Roman Empire and Christianity
... What is known about Jesus’ earl life is found in the Gospel. It is said that he was a descendant of King David and that his birth was miraculous. He was a ...
... What is known about Jesus’ earl life is found in the Gospel. It is said that he was a descendant of King David and that his birth was miraculous. He was a ...
5104 EDU-092 Olympus Pre Visit Kit_Timeline_F.indd
... Hellenistic Period (323-146 BC) Greek civilization had a powerful influence on the Roman Empire. Indeed, some modern scholars see the Roman era as a continuation of the same civilization, which they label Greco-Roman. The Roman conquest carried many features of Greek civilization to far-flung parts ...
... Hellenistic Period (323-146 BC) Greek civilization had a powerful influence on the Roman Empire. Indeed, some modern scholars see the Roman era as a continuation of the same civilization, which they label Greco-Roman. The Roman conquest carried many features of Greek civilization to far-flung parts ...
Daily Life of Romans Powerpoint - Irene C. Hernandez Middle School
... of the artisans all day. There’s no peace or quiet in this city.” ...
... of the artisans all day. There’s no peace or quiet in this city.” ...
Roman technology

Roman technology is the engineering practice which supported Roman civilization and made the expansion of Roman commerce and Roman military possible for almost three quarters of a millennium (753 BC–476 AD).The Roman Empire had one of the most advanced set of technologies of its time, some of which was lost during the turbulent eras of Late Antiquity and the early Middle Ages. Gradually, some of the technological feats of the Romans were rediscovered and/or improved upon, while others went ahead of what the Romans had done during the Middle Ages and the beginning of the Modern Era. Several Roman technological feats in different areas like civil engineering, construction materials, transport technology, and some inventions such as the mechanical reaper, were surprising achievements until the 19th century. The Romans achieved high levels of technology in large part because they borrowed and absorbed the culture of the pre-existing (Hellenic and others) peoples of the Mediterranean basin.