Chemical Equations & Reactions
... Determine the heat of reaction, ΔH, (enthalpy change) for this reaction. Determine the activation energy, Ea for this reaction. How much energy is released or absorbed during the reaction? How much energy is required for this reaction to occur? ...
... Determine the heat of reaction, ΔH, (enthalpy change) for this reaction. Determine the activation energy, Ea for this reaction. How much energy is released or absorbed during the reaction? How much energy is required for this reaction to occur? ...
Molecular Orbitals and Molecular Structure
... The unhybridised p orbitals are perpendicular to the plane of the molecule. The p orbitals of the carbon atoms are parallel and close enough to overlap sideways. This sideways overlap between the 2p orbitals produces a new molecular orbital between the two carbon atoms. This new orbital is called a ...
... The unhybridised p orbitals are perpendicular to the plane of the molecule. The p orbitals of the carbon atoms are parallel and close enough to overlap sideways. This sideways overlap between the 2p orbitals produces a new molecular orbital between the two carbon atoms. This new orbital is called a ...
handout alkenes from alcohols
... 2) Measure and record the volume of your cylcohexanol sample. 3) Add a boiling chip and 1.0 mL of phosphoric acid to the flask. 4) Swirl the solution to mix the different layers. 5) Set up the equipment for fractional distillation. 6) Gently heat the solution and distill off the liquid until 1-2 mL ...
... 2) Measure and record the volume of your cylcohexanol sample. 3) Add a boiling chip and 1.0 mL of phosphoric acid to the flask. 4) Swirl the solution to mix the different layers. 5) Set up the equipment for fractional distillation. 6) Gently heat the solution and distill off the liquid until 1-2 mL ...
Chapter 6. Electronic Structure of Atoms
... • Rutherford assumed electrons orbited nucleus as to planets orbiting the sun • however, a charged particle moving in circular path should lose energy • means that atom should be unstable according to Rutherford’s theory • Bohr noted spectra of certain elements, assumed electrons confined to specifi ...
... • Rutherford assumed electrons orbited nucleus as to planets orbiting the sun • however, a charged particle moving in circular path should lose energy • means that atom should be unstable according to Rutherford’s theory • Bohr noted spectra of certain elements, assumed electrons confined to specifi ...
슬라이드 1
... Conjugate addition to a,b-unsaturated esters can often be effected by copper catalyzed reaction with Grignard reagent. Other reactions, such as epoxide ring opening, can also be carried out under catalytic conditions. (Scheme 8.5) ...
... Conjugate addition to a,b-unsaturated esters can often be effected by copper catalyzed reaction with Grignard reagent. Other reactions, such as epoxide ring opening, can also be carried out under catalytic conditions. (Scheme 8.5) ...
Organic Pathways
... • Polystyrene is made from the monomer styrene, which in turn is made from ethene. • A copolymer is a polymer made of more than one monomer. ...
... • Polystyrene is made from the monomer styrene, which in turn is made from ethene. • A copolymer is a polymer made of more than one monomer. ...
Unit 3: Chemical Kinetics
... topics that we need to first examine - reaction mechanisms and the concept of threshold energy. ...
... topics that we need to first examine - reaction mechanisms and the concept of threshold energy. ...
CHEMISTRY 1000
... chlorides (since the pKa values for HCl and RSO3H are about -7). Therefore, if converting the alcohol into a sulfonate ester is helpful, it is reasonable to conclude that converting the alcohol into the corresponding alkyl halide would be equally helpful. ...
... chlorides (since the pKa values for HCl and RSO3H are about -7). Therefore, if converting the alcohol into a sulfonate ester is helpful, it is reasonable to conclude that converting the alcohol into the corresponding alkyl halide would be equally helpful. ...
Chemical Equations & Reactions
... Determine the heat of reaction, ΔH, (enthalpy change) for this reaction. Determine the activation energy, Ea for this reaction. How much energy is released or absorbed during the reaction? How much energy is required for this reaction to occur? ...
... Determine the heat of reaction, ΔH, (enthalpy change) for this reaction. Determine the activation energy, Ea for this reaction. How much energy is released or absorbed during the reaction? How much energy is required for this reaction to occur? ...
Chapter 18 - Sarah Mahajan Study Guides
... Rate is a measure of speed of any change that occurs within an interval of time In chemistry, the reaction rate (rate of a chemical change) = amount of reactant per unit time o For example: 0.2 mol/1 month Collision theory- atoms, molecules, and ions can react to form products when they collide with ...
... Rate is a measure of speed of any change that occurs within an interval of time In chemistry, the reaction rate (rate of a chemical change) = amount of reactant per unit time o For example: 0.2 mol/1 month Collision theory- atoms, molecules, and ions can react to form products when they collide with ...
Redox in Electrochemistry
... possible reduction half reaction in the two half cells and find their difference using the formula: ...
... possible reduction half reaction in the two half cells and find their difference using the formula: ...
Here is the Original File - University of New Hampshire
... I would like to thank the UNH Department of Chemistry, David Danico, Graham Beaton, William Butler and Sarah ...
... I would like to thank the UNH Department of Chemistry, David Danico, Graham Beaton, William Butler and Sarah ...
The Synthesis of trans-9-(2
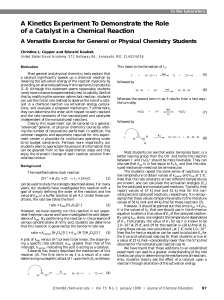
... 2. Jaworek. Christine, Lacobucci. Sarah; Wittig Reaction: The Synthesis of trans-9-(2phenylethenyl)anthracene Revisited. Journal of Chemical Education. 2002,79,(111) 3. Yusuke.O; Hikaru.S; Shigefumi.K; Total Synthesis of Amphirionin-4. Organic Letters. 2016, 18, ...
... 2. Jaworek. Christine, Lacobucci. Sarah; Wittig Reaction: The Synthesis of trans-9-(2phenylethenyl)anthracene Revisited. Journal of Chemical Education. 2002,79,(111) 3. Yusuke.O; Hikaru.S; Shigefumi.K; Total Synthesis of Amphirionin-4. Organic Letters. 2016, 18, ...
lect7
... low oxidation-state compounds of these types usually obey the 18-electron rule. CO, PR3 are 2 e- donors, NO is a 3 edonor and unsaturated organic molecules count 1 e- for each C atom which is bonded to the metal. ...
... low oxidation-state compounds of these types usually obey the 18-electron rule. CO, PR3 are 2 e- donors, NO is a 3 edonor and unsaturated organic molecules count 1 e- for each C atom which is bonded to the metal. ...
Molecular Geometry and Chemical Bonding Theory
... valence bond (VB) theory (Linus Pauling) and molecular orbital (MO) theory (Robert S. Mulliken). The molecular orbital theory does a better job of describing molecules in their ...
... valence bond (VB) theory (Linus Pauling) and molecular orbital (MO) theory (Robert S. Mulliken). The molecular orbital theory does a better job of describing molecules in their ...
General Equilibrium
... where K is the equilibrium constant, and aX is the activity of X and described by the activity coefficient X and [X]: aX = X[X] In dilute solutions, the activity coefficient approaches unity. Often, experimental conditions allow us to assume activity coefficients of one so that concentrations can ...
... where K is the equilibrium constant, and aX is the activity of X and described by the activity coefficient X and [X]: aX = X[X] In dilute solutions, the activity coefficient approaches unity. Often, experimental conditions allow us to assume activity coefficients of one so that concentrations can ...
Oxidative Addition
... such as H2 or CH3‐I. A−B bond is broken, and M−A and M−B bonds are formed. ...
... such as H2 or CH3‐I. A−B bond is broken, and M−A and M−B bonds are formed. ...
Nucleophilic substitution at saturated carbon
... SN2. It does not react by SN1 because the cation cannot become planar nor by SN2 because the nucleophile cannot approach the carbon atom from the right direction ...
... SN2. It does not react by SN1 because the cation cannot become planar nor by SN2 because the nucleophile cannot approach the carbon atom from the right direction ...
File - Dr KHALID SHADID
... • An sp2 hybrid orbital has two lobes of unequal size – the three sp2 hybrid orbitals are directed toward the corners of an equilateral triangle at angles of 120° – the unhybridized 2p orbital is perpendicular to the plane of the three sp2 hybrid orbitals ...
... • An sp2 hybrid orbital has two lobes of unequal size – the three sp2 hybrid orbitals are directed toward the corners of an equilateral triangle at angles of 120° – the unhybridized 2p orbital is perpendicular to the plane of the three sp2 hybrid orbitals ...
Woodward–Hoffmann rules

The Woodward–Hoffmann rules, devised by Robert Burns Woodward and Roald Hoffmann, are a set of rules in organic chemistry predicting the barrier heights of pericyclic reactions based upon conservation of orbital symmetry. The Woodward–Hoffmann rules can be applied to understand electrocyclic reactions, cycloadditions (including cheletropic reactions), sigmatropic reactions, and group transfer reactions. Reactions are classified as allowed if the electronic barrier is low, and forbidden if the barrier is high. Forbidden reactions can still take place but require significantly more energy.The Woodward–Hoffmann rules were first formulated to explain the striking stereospecificity of electrocyclic reactions under thermal and photochemical control. Thermolysis of the substituted cyclobutene trans-1,2,3,4-tetramethylcyclobutene (1) gave only one diastereomer, the (E,E)-3,4-dimethyl-2,4-hexadiene (2) as shown below; the (Z,Z) and the (E,Z) diastereomers were not detected in the reaction. Similarly, thermolysis of cis-1,2,3,4-tetramethylcyclobutene (3) gave only the (E,Z) diastereomer (4).Due to their elegance and simplicity, the Woodward–Hoffmann rules are credited with first exemplifying the power of molecular orbital theory to experimental chemists. Hoffmann was awarded the 1981 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for this work, shared with Kenichi Fukui who developed a similar model using frontier molecular orbital (FMO) theory; because Woodward had died two years before, he was not eligible to win what would have been his second Nobel Prize for Chemistry.