WebQuest * Human Senses
... a. What structures integrate taste into memories and where are these structures found? ...
... a. What structures integrate taste into memories and where are these structures found? ...
module 6 The Cerebral Cortex and Our Divided Brain Module
... areas. Each lobe performs many functions and interacts with other areas of the cortex. 6-2. Summarize some of the findings on the functions of the motor cortex and the sensory cortex, and discuss the importance of the association areas. The motor cortex, an arch-shaped region at the rear of the fron ...
... areas. Each lobe performs many functions and interacts with other areas of the cortex. 6-2. Summarize some of the findings on the functions of the motor cortex and the sensory cortex, and discuss the importance of the association areas. The motor cortex, an arch-shaped region at the rear of the fron ...
Stephen D. Krashen Second Language Acquisition Theory
... Conclusions The more comprehensible input one receives in low- ...
... Conclusions The more comprehensible input one receives in low- ...
Module 07_lecture
... debunked • Brain is divided into two hemispheres but works as a single entity. • Both sides continually communicate via the corpus callosum, except in those with split brains. ...
... debunked • Brain is divided into two hemispheres but works as a single entity. • Both sides continually communicate via the corpus callosum, except in those with split brains. ...
The Brain - Central Connecticut State University
... sing familiar songs and comprehend speech. Disrupts speaking ...
... sing familiar songs and comprehend speech. Disrupts speaking ...
Chapter 2
... • Hypothalamus: feeding, fleeing, mating, fighting, homeostasis • Cerebellum: involved in motor control ...
... • Hypothalamus: feeding, fleeing, mating, fighting, homeostasis • Cerebellum: involved in motor control ...
xpx tampa bay
... • 100 billion neurons • Every neuron may be touched by as many as 10,000 other nerve cell axons • 1000 trillion different possible synaptic connections (more connections in one brain than stars in the universe) • 16 billion neurons in the cerebral cortex alone • Neurons form dense connected plexus i ...
... • 100 billion neurons • Every neuron may be touched by as many as 10,000 other nerve cell axons • 1000 trillion different possible synaptic connections (more connections in one brain than stars in the universe) • 16 billion neurons in the cerebral cortex alone • Neurons form dense connected plexus i ...
Option A Neural Development Study Guide A1 A2
... What is meant by the term “neural migration”? How do synapses develop and what happens to those not used? ...
... What is meant by the term “neural migration”? How do synapses develop and what happens to those not used? ...
article
... This oppositional behavior between the right and left hands disappears quickly after the split-brain surgery. Split-brain patients then are able to engage in virtually all the behaviors that anyone else can perform. In fact, it takes special tests to demonstrate that their left and right hemisphere ...
... This oppositional behavior between the right and left hands disappears quickly after the split-brain surgery. Split-brain patients then are able to engage in virtually all the behaviors that anyone else can perform. In fact, it takes special tests to demonstrate that their left and right hemisphere ...
Nervous System
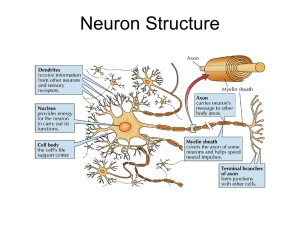
... PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Messages about your environment travel through the nervous system called neurons. A neuron is a nerve cell that is specialized to transfer messages in the form of fast-moving electrical energy. These electrical messages are called impulses. A neuron has a large region i ...
... PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Messages about your environment travel through the nervous system called neurons. A neuron is a nerve cell that is specialized to transfer messages in the form of fast-moving electrical energy. These electrical messages are called impulses. A neuron has a large region i ...
The Brain and The Nervous System
... • B. Patients with brain damage are unable to send neural information through the corpus callosum. • C. The corpus callosum ensures that each hemisphere of the brain is able to function independently. • D. The corpus callosum is found in the cerebral cortex, and connects the two hemispheres of the b ...
... • B. Patients with brain damage are unable to send neural information through the corpus callosum. • C. The corpus callosum ensures that each hemisphere of the brain is able to function independently. • D. The corpus callosum is found in the cerebral cortex, and connects the two hemispheres of the b ...
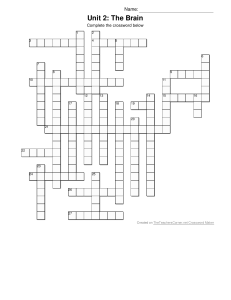
Crossword Puzzle
... and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron 4. an impairment of language as a result of damage to any of several cortical areas 9. located at the back of the frontal lobe, the part of the cortex that controls voluntary movement 10. Limbic system structure that regulates hunger, thirst, and ...
... and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron 4. an impairment of language as a result of damage to any of several cortical areas 9. located at the back of the frontal lobe, the part of the cortex that controls voluntary movement 10. Limbic system structure that regulates hunger, thirst, and ...
How Does the Brain Work?
... Reproduced with permission from the Dana Alliance for Brain Initiatives, www.dana.org ...
... Reproduced with permission from the Dana Alliance for Brain Initiatives, www.dana.org ...
the brain - WordPress.com
... accounts for two-thirds of the total weight of the brain. One hemisphere, usually the left, is functionally dominant, controlling language and speech. The other hemisphere interprets visual and spatial information. The cerebral hemispheres consist of an inner core of myelinated nerve fibres, t ...
... accounts for two-thirds of the total weight of the brain. One hemisphere, usually the left, is functionally dominant, controlling language and speech. The other hemisphere interprets visual and spatial information. The cerebral hemispheres consist of an inner core of myelinated nerve fibres, t ...
Biopsychology - WordPress.com
... • Psychophysiology ~ also studies the neural bases of thought, memory, attention, perception ...
... • Psychophysiology ~ also studies the neural bases of thought, memory, attention, perception ...
Sample
... and Wernicke’s and Broca’s areas in the left hemisphere. These are collectively found in the perisylvian region of the cerebrum. ...
... and Wernicke’s and Broca’s areas in the left hemisphere. These are collectively found in the perisylvian region of the cerebrum. ...
Chapter 3
... medulla- controls breathing, respiration pons- controls sleep, arousal cerebellum- controls basic motor activity ...
... medulla- controls breathing, respiration pons- controls sleep, arousal cerebellum- controls basic motor activity ...
Unit 3B Study Guide
... C) the angular gyrus. 18. When asked to describe a picture that showed two boys stealing cookies behind a woman's back, a patient replied, “Mother is away her working her work to get her better, but when she's looking the two boys looking the other part.” Which brain region has most likely been dama ...
... C) the angular gyrus. 18. When asked to describe a picture that showed two boys stealing cookies behind a woman's back, a patient replied, “Mother is away her working her work to get her better, but when she's looking the two boys looking the other part.” Which brain region has most likely been dama ...
Overview and Integration
... Norman Geschwind (1974) reintroduced Wernicke's language circuit in the mid-twentieth century, and the WernickeGeschwind model of brain and language function is still the basis for contemporary understanding ...
... Norman Geschwind (1974) reintroduced Wernicke's language circuit in the mid-twentieth century, and the WernickeGeschwind model of brain and language function is still the basis for contemporary understanding ...
Allison Bynum Neurobiology A.1 – A.3 Allison Bynum A.1 Neural
... Reasoning Language Complex thought Visual processing Motor movement Remembering Speech ...
... Reasoning Language Complex thought Visual processing Motor movement Remembering Speech ...
Lateralization of brain function

The longitudinal fissure separates the human brain into two distinct cerebral hemispheres, connected by the corpus callosum. The hemispheres exhibit strong, but not complete, bilateral symmetry in both structure and function. For example, structurally, the lateral sulcus generally is longer in the left hemisphere than in the right hemisphere, and functionally, Broca's area and Wernicke's area are located in the left cerebral hemisphere for about 95% of right-handers, but about 70% of left-handers.Broad generalizations are often made in ""pop"" psychology about one side or the other having characteristic labels, such as ""logical"" for the left side or ""creative"" for the right. These labels are not supported by studies on lateralization, as lateralization does not add specialized usage from either hemisphere. Both hemispheres contribute to both kinds of processes, and experimental evidence provides little support for correlating the structural differences between the sides with such broadly defined functional differences.The extent of any modularity, or specialization of brain function by area, remains under investigation. If a specific region of the brain, or even an entire hemisphere, is injured or destroyed, its functions can sometimes be assumed by a neighboring region in the same hemisphere or the corresponding region in the other hemisphere, depending upon the area damaged and the patient's age. When injury interferes with pathways from one area to another, alternative (indirect) connections may develop to communicate information with detached areas, despite the inefficiencies.Brain function lateralization is evident in the phenomena of right- or left-handedness and of right or left ear preference, but a person's preferred hand is not a clear indication of the location of brain function. Although 95% of right-handed people have left-hemisphere dominance for language, 18.8% of left-handed people have right-hemisphere dominance for language function. Additionally, 19.8% of the left-handed have bilateral language functions. Even within various language functions (e.g., semantics, syntax, prosody), degree (and even hemisphere) of dominance may differ.Additionally, although some functions are lateralized, these are only a tendency. The trend across many individuals may also vary significantly as to how any specific function is implemented. The areas of exploration of this causal or effectual difference of a particular brain function include its gross anatomy, dendritic structure, and neurotransmitter distribution. The structural and chemical variance of a particular brain function, between the two hemispheres of one brain or between the same hemisphere of two different brains, is still being studied. Short of having undergone a hemispherectomy (removal of a cerebral hemisphere), no one is a ""left-brain only"" or ""right-brain only"" person.