Introduction to the Brain
... Copyright Headway, 2009. This is one of a range of factsheets made available by Headway. We have taken great care to ensure all information is accurate but these factsheets are only intended as a guide and recommend that medical or professional support should be sought. Headway will not be held resp ...
... Copyright Headway, 2009. This is one of a range of factsheets made available by Headway. We have taken great care to ensure all information is accurate but these factsheets are only intended as a guide and recommend that medical or professional support should be sought. Headway will not be held resp ...
Neuroanatomy- anatomy of nerve cell (neuron)
... Contra lateral control- the left hemisphere controls the motor movement of the right hand. Hemispheric Specialization (aka brain lateralization)- outdated theory suggesting that each hemisphere controls all specific functions. It’s factual however that the left is where most language takes place. Ri ...
... Contra lateral control- the left hemisphere controls the motor movement of the right hand. Hemispheric Specialization (aka brain lateralization)- outdated theory suggesting that each hemisphere controls all specific functions. It’s factual however that the left is where most language takes place. Ri ...
The concept of mood in psychology paper final
... distinctiveness of to single or other of the two brain parts. It is accomplished; thus, that the dominant exploit of any right or left hemisphere verify an individual’s means of thinking and individuality. In accordance with the attributed distinctiveness, the left brain may possibly be the rational ...
... distinctiveness of to single or other of the two brain parts. It is accomplished; thus, that the dominant exploit of any right or left hemisphere verify an individual’s means of thinking and individuality. In accordance with the attributed distinctiveness, the left brain may possibly be the rational ...
Study Guide
... The part of the brain that controls involuntary actions, such as the beating of your heart, breathing, and digestion is called the medulla. The cerebellum controls balance and coordination and makes sure your muscles work in the right order. Nerves are long threads of specialized cells. Jumping acro ...
... The part of the brain that controls involuntary actions, such as the beating of your heart, breathing, and digestion is called the medulla. The cerebellum controls balance and coordination and makes sure your muscles work in the right order. Nerves are long threads of specialized cells. Jumping acro ...
The Great Brain Drain Review - Reeths
... a. Uses radio waves and magnetic fields to produce computer generated images to distinguish among different types of brain tissue. MRI b. Uses glucose to develop a visual display of brain activity. PET c. Measures electrical activity across the surface of the brain. EEG V. As a summer camp counselor ...
... a. Uses radio waves and magnetic fields to produce computer generated images to distinguish among different types of brain tissue. MRI b. Uses glucose to develop a visual display of brain activity. PET c. Measures electrical activity across the surface of the brain. EEG V. As a summer camp counselor ...
The Great Brain Drain Review - Reeths
... a. Uses radio waves and magnetic fields to produce computer generated images to distinguish among different types of brain tissue. MRI b. Uses glucose to develop a visual display of brain activity. PET c. Measures electrical activity across the surface of the brain. EEG V. As a summer camp counselor ...
... a. Uses radio waves and magnetic fields to produce computer generated images to distinguish among different types of brain tissue. MRI b. Uses glucose to develop a visual display of brain activity. PET c. Measures electrical activity across the surface of the brain. EEG V. As a summer camp counselor ...
1. The left and right hemispheres communicate with each other
... 5.Recovery of brain function a. is least likely if the brain injury occurs during early childhood b. is better following a single large stroke than a series of small strokes c. is maximal if the brain injury occurs during adolescence d. is much less pronounced several years after the brain injury th ...
... 5.Recovery of brain function a. is least likely if the brain injury occurs during early childhood b. is better following a single large stroke than a series of small strokes c. is maximal if the brain injury occurs during adolescence d. is much less pronounced several years after the brain injury th ...
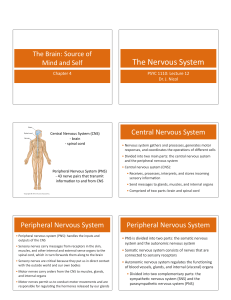
The Nervous System
... Cerebral Cortex • Where higher order thinking takes place, and the wiring of the brain is most complex • Divided into two halves: the lek and right hemispheres • Lek and right hemispheres are connected b ...
... Cerebral Cortex • Where higher order thinking takes place, and the wiring of the brain is most complex • Divided into two halves: the lek and right hemispheres • Lek and right hemispheres are connected b ...
CNS=Central Nervous System
... • Also known as the cerebral cortex, is divided into four lobes: frontal, parietal, occipital and temporal – Each lobe has its own particular responsibilities: • Frontal: ____________________________ ___________________________________ • Parietal: ___________________________ ________________________ ...
... • Also known as the cerebral cortex, is divided into four lobes: frontal, parietal, occipital and temporal – Each lobe has its own particular responsibilities: • Frontal: ____________________________ ___________________________________ • Parietal: ___________________________ ________________________ ...
DESIRED RESULTS (STAGE 1) - Anoka
... To underrstand, student will need to consider such questions as... ...
... To underrstand, student will need to consider such questions as... ...
The body`s information system is built from billions of interconnected
... The brain is sculpted by our genes but also by our experiences. Plasticity refers to the brain’s ability to modify itself after some types of injury or illness. the brain is capable of changing its structure and function in response to changing environmental conditions. Our Divided Brain The brain i ...
... The brain is sculpted by our genes but also by our experiences. Plasticity refers to the brain’s ability to modify itself after some types of injury or illness. the brain is capable of changing its structure and function in response to changing environmental conditions. Our Divided Brain The brain i ...
Neurons
... balancing task when subject (right-handed person) either vocalize or remain silent Results: ...
... balancing task when subject (right-handed person) either vocalize or remain silent Results: ...
THE BRAIN The brain can be divided into three main regions
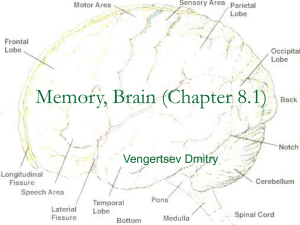
... 4. Cerebral cortex: Largest and most complex part of the human brain. Includes the brain areas that are responsible for the most complex mental activities, including learning, remembering, thinking, and consciousness. LOBES OF THE BRAIN Each cerebral hemisphere is divided into four lobes. Each is de ...
... 4. Cerebral cortex: Largest and most complex part of the human brain. Includes the brain areas that are responsible for the most complex mental activities, including learning, remembering, thinking, and consciousness. LOBES OF THE BRAIN Each cerebral hemisphere is divided into four lobes. Each is de ...
Lecture 2 - wseh2elt
... Besides, such patients have problems naming objects, coming up with related words or sound distortions: table – chair; clip - plick ...
... Besides, such patients have problems naming objects, coming up with related words or sound distortions: table – chair; clip - plick ...
Brain Facts
... • Contraction of skeletal muscles • Reflexes deviate from normal in certain conditions • Reflex testing is valuable diagnostic tool – Patellar Reflex: extension of lower leg – Achilles Reflex: extension of foot – Babinski Reflex: extension of big toe ...
... • Contraction of skeletal muscles • Reflexes deviate from normal in certain conditions • Reflex testing is valuable diagnostic tool – Patellar Reflex: extension of lower leg – Achilles Reflex: extension of foot – Babinski Reflex: extension of big toe ...
Chapter 4 Outline
... (4) Involved in determining the proper order of behaviors and knowing when to stop V. THE TWO HEMISPHERES OF THE BRAIN A. Split brains: A house divided 1. Corpus callosum, which connects the cerebral hemispheres in normal brains, is severed 2. This surgery has been performed in animal studies and fo ...
... (4) Involved in determining the proper order of behaviors and knowing when to stop V. THE TWO HEMISPHERES OF THE BRAIN A. Split brains: A house divided 1. Corpus callosum, which connects the cerebral hemispheres in normal brains, is severed 2. This surgery has been performed in animal studies and fo ...
Brain Structure and Function
... Left and Right Hemispheres Left hemisphere for most people is the dominant hemisphere- responsible for production of language, mathematical ability, problem solving, logic Right hemisphere thought to be responsible for creativity and spatial ability ...
... Left and Right Hemispheres Left hemisphere for most people is the dominant hemisphere- responsible for production of language, mathematical ability, problem solving, logic Right hemisphere thought to be responsible for creativity and spatial ability ...
The Brain for Not-So
... Neurogenesis does not stop at birth Occurs in normal adult brain Adds neurons in hippocampus ...
... Neurogenesis does not stop at birth Occurs in normal adult brain Adds neurons in hippocampus ...
The Brain
... d. Occipital lobe- vision- not marked by a fissure- process visual information- visual cortex there e. Temporal lobe- has auditory cortex- hearingf. Corpus callosum- band of fibers that connect the two hemispheres- allows the right and left hemisphere to communicate with each other. Lesson 4- Latera ...
... d. Occipital lobe- vision- not marked by a fissure- process visual information- visual cortex there e. Temporal lobe- has auditory cortex- hearingf. Corpus callosum- band of fibers that connect the two hemispheres- allows the right and left hemisphere to communicate with each other. Lesson 4- Latera ...
Nolte Chapter 22: Cerebral Cortex
... activities. Wernicke’s would leave Broca’s area unchecked so that words would be produced without reagard for their meaning. This could also happen with destruction of the arcuate (which connects the two), but this lesion would leave comprehension in tact and result in “conduction aphasia” where sub ...
... activities. Wernicke’s would leave Broca’s area unchecked so that words would be produced without reagard for their meaning. This could also happen with destruction of the arcuate (which connects the two), but this lesion would leave comprehension in tact and result in “conduction aphasia” where sub ...
Lateralization of brain function

The longitudinal fissure separates the human brain into two distinct cerebral hemispheres, connected by the corpus callosum. The hemispheres exhibit strong, but not complete, bilateral symmetry in both structure and function. For example, structurally, the lateral sulcus generally is longer in the left hemisphere than in the right hemisphere, and functionally, Broca's area and Wernicke's area are located in the left cerebral hemisphere for about 95% of right-handers, but about 70% of left-handers.Broad generalizations are often made in ""pop"" psychology about one side or the other having characteristic labels, such as ""logical"" for the left side or ""creative"" for the right. These labels are not supported by studies on lateralization, as lateralization does not add specialized usage from either hemisphere. Both hemispheres contribute to both kinds of processes, and experimental evidence provides little support for correlating the structural differences between the sides with such broadly defined functional differences.The extent of any modularity, or specialization of brain function by area, remains under investigation. If a specific region of the brain, or even an entire hemisphere, is injured or destroyed, its functions can sometimes be assumed by a neighboring region in the same hemisphere or the corresponding region in the other hemisphere, depending upon the area damaged and the patient's age. When injury interferes with pathways from one area to another, alternative (indirect) connections may develop to communicate information with detached areas, despite the inefficiencies.Brain function lateralization is evident in the phenomena of right- or left-handedness and of right or left ear preference, but a person's preferred hand is not a clear indication of the location of brain function. Although 95% of right-handed people have left-hemisphere dominance for language, 18.8% of left-handed people have right-hemisphere dominance for language function. Additionally, 19.8% of the left-handed have bilateral language functions. Even within various language functions (e.g., semantics, syntax, prosody), degree (and even hemisphere) of dominance may differ.Additionally, although some functions are lateralized, these are only a tendency. The trend across many individuals may also vary significantly as to how any specific function is implemented. The areas of exploration of this causal or effectual difference of a particular brain function include its gross anatomy, dendritic structure, and neurotransmitter distribution. The structural and chemical variance of a particular brain function, between the two hemispheres of one brain or between the same hemisphere of two different brains, is still being studied. Short of having undergone a hemispherectomy (removal of a cerebral hemisphere), no one is a ""left-brain only"" or ""right-brain only"" person.