Objective 1 | Explain why psychologists are concerned with human
... specific brain areas, by recording the brain’s surface electrical activity, and by displaying neural activity with computer-aided brain scans, neuroscientists explore the connections among brain, mind, and behavior. Pages: 68-70 Objective 12 | Describe the components of the brainstem, and summarize ...
... specific brain areas, by recording the brain’s surface electrical activity, and by displaying neural activity with computer-aided brain scans, neuroscientists explore the connections among brain, mind, and behavior. Pages: 68-70 Objective 12 | Describe the components of the brainstem, and summarize ...
Physiological bases of mental and physical work
... thought processes in the mind. This presumably results from some of the same capabilities of the prefrontal cortex that allow it to plan motor activities. The prefrontal association area is frequently described as important for elaboration of thoughts to store on a short-term basis “working memori ...
... thought processes in the mind. This presumably results from some of the same capabilities of the prefrontal cortex that allow it to plan motor activities. The prefrontal association area is frequently described as important for elaboration of thoughts to store on a short-term basis “working memori ...
The Structures of the Brain
... meaningless words. • Reading aloud involves angular gyruswhich takes words from visual cortex and moves it to auditory cortex while Wernicke’s area gives meaning • Nerve fibers connect the areas • Geschwind assembled clues into process of reading aloud • Register in visual area • Relayed to angular ...
... meaningless words. • Reading aloud involves angular gyruswhich takes words from visual cortex and moves it to auditory cortex while Wernicke’s area gives meaning • Nerve fibers connect the areas • Geschwind assembled clues into process of reading aloud • Register in visual area • Relayed to angular ...
Structure of the Nervous System
... 4 pockets of gray matter – relay motor information to spinal cord Permit coordinated, steady body movements ...
... 4 pockets of gray matter – relay motor information to spinal cord Permit coordinated, steady body movements ...
Chapter 2
... areas of the cerebral cortex that are not involved in primary motor or sensory functions involved in higher mental functions such as learning, remembering, thinking, and speaking ...
... areas of the cerebral cortex that are not involved in primary motor or sensory functions involved in higher mental functions such as learning, remembering, thinking, and speaking ...
Brain Damage & Neuroplasticity
... • if you understand the functional organization of the brain in a healthy person, you will be able to understand functional changes following brain damage? AND (if you understand this) • you will be able to understand problems associated with psychiatric disorders? ...
... • if you understand the functional organization of the brain in a healthy person, you will be able to understand functional changes following brain damage? AND (if you understand this) • you will be able to understand problems associated with psychiatric disorders? ...
Active Reading - Red Hook Central Schools
... Read the passage below. Then answer the questions that follow. ...
... Read the passage below. Then answer the questions that follow. ...
Neurotransmitters: Acetylcholine (Ach) transmitter plays a role in
... the cerebral hemispheres. (Higher level functioning). Glial Cells (glue cells) – support, nourish, and protect neurons, along with playing a role in learning and thinking. *Each hemisphere cortex is subdivided into four lobes* Frontal Lobes – involved in speaking and muscle movements, and making pla ...
... the cerebral hemispheres. (Higher level functioning). Glial Cells (glue cells) – support, nourish, and protect neurons, along with playing a role in learning and thinking. *Each hemisphere cortex is subdivided into four lobes* Frontal Lobes – involved in speaking and muscle movements, and making pla ...
EXC 7770 Psychoneurological & Medical Issues in Special Education
... with the integration of psychological observations on behavior and the mind with neurological observations on the brain and nervous system http://www2.merriam-webster.com/cgi-bin/mwmednlm ...
... with the integration of psychological observations on behavior and the mind with neurological observations on the brain and nervous system http://www2.merriam-webster.com/cgi-bin/mwmednlm ...
1244509Health Nervous System 2012
... without oxygen. After that cells begin die. The slowest speed at which information travels between neurons is 260 mph!!! ...
... without oxygen. After that cells begin die. The slowest speed at which information travels between neurons is 260 mph!!! ...
Brain Power Point
... The left brain Left - function - sequential, logical, remembers names, timeoriented, mathematical, takes one thing at a time, language - controls the right side of the body ...
... The left brain Left - function - sequential, logical, remembers names, timeoriented, mathematical, takes one thing at a time, language - controls the right side of the body ...
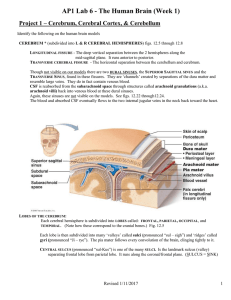
Sheep Brain Dissection Instructions
... pituitary gland. Use your fingers or a teasing needle to gently probe the parts and see how they are connected to each other. What does that opening inside the corpus callosum lead to? How many different kinds of tissue can you see and feel? The corpus callosum is a bundle of white fibers See a larg ...
... pituitary gland. Use your fingers or a teasing needle to gently probe the parts and see how they are connected to each other. What does that opening inside the corpus callosum lead to? How many different kinds of tissue can you see and feel? The corpus callosum is a bundle of white fibers See a larg ...
File - Biology with Radjewski
... world and translating it into language • Damage causes people to not see motion ...
... world and translating it into language • Damage causes people to not see motion ...
The Nervous System - AP Psychology-NWHS
... cerebral cortex plays a key role in memory, attention, perceptual awareness, thought, language, and consciousness Thalamus: relays and translates incoming messages from the ...
... cerebral cortex plays a key role in memory, attention, perceptual awareness, thought, language, and consciousness Thalamus: relays and translates incoming messages from the ...
Nervous System
... Lies below and behind the cerebral hemispheres Its surface is highly folded It helps coordinate muscle action It receives sensory impulses from muscles, tendons, joints, eyes and ears, as well as input from other brain centers • It processes information about body position • Controls posture by keep ...
... Lies below and behind the cerebral hemispheres Its surface is highly folded It helps coordinate muscle action It receives sensory impulses from muscles, tendons, joints, eyes and ears, as well as input from other brain centers • It processes information about body position • Controls posture by keep ...
Imaging shows structural changes in mild traumatic brain injury
... “You have the CPU and the memory, but they are worthless unless they are connected to each other. The white matter of the brain has the same function as the cables of the computer.” When white matter is damaged, areas of the brain may appear healthy but they are actually “unplugged” and cannot funct ...
... “You have the CPU and the memory, but they are worthless unless they are connected to each other. The white matter of the brain has the same function as the cables of the computer.” When white matter is damaged, areas of the brain may appear healthy but they are actually “unplugged” and cannot funct ...
the brain - Mayfield City Schools
... angular gyrus leaves a person able to speak and understand, but unable to read aloud ...
... angular gyrus leaves a person able to speak and understand, but unable to read aloud ...
Lab Activity Sheets
... Countless neuron cell bodies, dendrites, and axons form billions of synapses in these ridges. Most motor impulses for voluntary muscle contraction begin here as conscious thought. POSTCENTRAL GYRUS * (one of many GYRI) A landmark gyrus just posterior to the central sulcus. It is also called ...
... Countless neuron cell bodies, dendrites, and axons form billions of synapses in these ridges. Most motor impulses for voluntary muscle contraction begin here as conscious thought. POSTCENTRAL GYRUS * (one of many GYRI) A landmark gyrus just posterior to the central sulcus. It is also called ...
Concepts of Neurobiology
... THREE PARTS OF THE BRAIN 1. Forebrain A. Cerebrum Consists of right and left hemisphere connected by a large group of nerves called the corpus callosum. Each hemisphere is divided into four lobes: Frontal lobes Parietal lobes Temporal lobes Occipital lobes B. Diencephalon The diencepha ...
... THREE PARTS OF THE BRAIN 1. Forebrain A. Cerebrum Consists of right and left hemisphere connected by a large group of nerves called the corpus callosum. Each hemisphere is divided into four lobes: Frontal lobes Parietal lobes Temporal lobes Occipital lobes B. Diencephalon The diencepha ...
Lateralization of brain function

The longitudinal fissure separates the human brain into two distinct cerebral hemispheres, connected by the corpus callosum. The hemispheres exhibit strong, but not complete, bilateral symmetry in both structure and function. For example, structurally, the lateral sulcus generally is longer in the left hemisphere than in the right hemisphere, and functionally, Broca's area and Wernicke's area are located in the left cerebral hemisphere for about 95% of right-handers, but about 70% of left-handers.Broad generalizations are often made in ""pop"" psychology about one side or the other having characteristic labels, such as ""logical"" for the left side or ""creative"" for the right. These labels are not supported by studies on lateralization, as lateralization does not add specialized usage from either hemisphere. Both hemispheres contribute to both kinds of processes, and experimental evidence provides little support for correlating the structural differences between the sides with such broadly defined functional differences.The extent of any modularity, or specialization of brain function by area, remains under investigation. If a specific region of the brain, or even an entire hemisphere, is injured or destroyed, its functions can sometimes be assumed by a neighboring region in the same hemisphere or the corresponding region in the other hemisphere, depending upon the area damaged and the patient's age. When injury interferes with pathways from one area to another, alternative (indirect) connections may develop to communicate information with detached areas, despite the inefficiencies.Brain function lateralization is evident in the phenomena of right- or left-handedness and of right or left ear preference, but a person's preferred hand is not a clear indication of the location of brain function. Although 95% of right-handed people have left-hemisphere dominance for language, 18.8% of left-handed people have right-hemisphere dominance for language function. Additionally, 19.8% of the left-handed have bilateral language functions. Even within various language functions (e.g., semantics, syntax, prosody), degree (and even hemisphere) of dominance may differ.Additionally, although some functions are lateralized, these are only a tendency. The trend across many individuals may also vary significantly as to how any specific function is implemented. The areas of exploration of this causal or effectual difference of a particular brain function include its gross anatomy, dendritic structure, and neurotransmitter distribution. The structural and chemical variance of a particular brain function, between the two hemispheres of one brain or between the same hemisphere of two different brains, is still being studied. Short of having undergone a hemispherectomy (removal of a cerebral hemisphere), no one is a ""left-brain only"" or ""right-brain only"" person.