neuron and nervous system
... Nervous System – body’s speedy, electrochemical communication network consisting of nerve cells Central Nervous System (CNS) – brain and spinal cord **Neural networks – interconnected neural cells; more connections made as experience gained Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) – sensory and motor neuron ...
... Nervous System – body’s speedy, electrochemical communication network consisting of nerve cells Central Nervous System (CNS) – brain and spinal cord **Neural networks – interconnected neural cells; more connections made as experience gained Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) – sensory and motor neuron ...
Nervous System
... up the nerve impulse along the axon Myelin is a fatty substance that protects the axon Synapse- space between neurons, messages go from one cell to the next. ...
... up the nerve impulse along the axon Myelin is a fatty substance that protects the axon Synapse- space between neurons, messages go from one cell to the next. ...
Synthetic neurons
... together • Connect central nervous system (spinal cord and brain) to all muscles in the body ...
... together • Connect central nervous system (spinal cord and brain) to all muscles in the body ...
ntro to Nervous system study guide
... Nervous system Quiz Review 1. What is the function of the nervous system? What other system has this same function? What is the difference between them? ...
... Nervous system Quiz Review 1. What is the function of the nervous system? What other system has this same function? What is the difference between them? ...
The Nervous System
... 2. Responds and adapts to changes that occur both inside and outside the body (Ex: pain, temperature, pregnancy) ...
... 2. Responds and adapts to changes that occur both inside and outside the body (Ex: pain, temperature, pregnancy) ...
The nervous system
... nervous system (CNS): brain and spinal cord Peripheral nervous system (PNS)- the nerves ...
... nervous system (CNS): brain and spinal cord Peripheral nervous system (PNS)- the nerves ...
Chapter 9 Nervous
... Na ions are transferred out into extracellular fluid. K ions are transferred into cell within cytoplasm. This is threshold potential. The permeability of the cell membrane increases, allowing Na to rush into the cell. Cells interior takes a positive charge. (Called depolarization) Depolarization swe ...
... Na ions are transferred out into extracellular fluid. K ions are transferred into cell within cytoplasm. This is threshold potential. The permeability of the cell membrane increases, allowing Na to rush into the cell. Cells interior takes a positive charge. (Called depolarization) Depolarization swe ...
Overview of the Day
... chemical messengers that allow neurons to communicate with one another between neurons is a small space (1 millionth of an inch thick) called synaptic cleft when action potential reaches knob-like terminals at axon's end, it triggers release of neurotransmitter they cross synaptic cleft and bi ...
... chemical messengers that allow neurons to communicate with one another between neurons is a small space (1 millionth of an inch thick) called synaptic cleft when action potential reaches knob-like terminals at axon's end, it triggers release of neurotransmitter they cross synaptic cleft and bi ...
The Nervous System
... transfer messages (impulses)around the body by electrical energy • sensory neurons –collect information and send to CNS • motor neurons – respond to information sent from CNS ...
... transfer messages (impulses)around the body by electrical energy • sensory neurons –collect information and send to CNS • motor neurons – respond to information sent from CNS ...
Print › Nervous System | Quizlet
... Transmit information from the central nervous system to the muscles making them move. ...
... Transmit information from the central nervous system to the muscles making them move. ...
Ch 3 Biopsychology & the Foundations of Neuroscience
... organisms adapt over time to their unique environments. O 4.Because the human brain is born already programmed for language, we can say that innate behavioral tendency. language is a(n) ________ The Nervous & Endocrine form the body's two O 5 .____________________ communication systems. ...
... organisms adapt over time to their unique environments. O 4.Because the human brain is born already programmed for language, we can say that innate behavioral tendency. language is a(n) ________ The Nervous & Endocrine form the body's two O 5 .____________________ communication systems. ...
The Nervous System
... The Spinal Cord and Reflexes (simple, automatic response to sensory stimuli) ...
... The Spinal Cord and Reflexes (simple, automatic response to sensory stimuli) ...
the nervous system
... • Cells carry messages from one part of the body to another • The messages in the nervous system are electrical signals called impulses • The cells that transmit the impulses are called neurons – Made of: • Dendrite • Axon • Myelin Sheath ...
... • Cells carry messages from one part of the body to another • The messages in the nervous system are electrical signals called impulses • The cells that transmit the impulses are called neurons – Made of: • Dendrite • Axon • Myelin Sheath ...
The Nervous System - Kirchner-WHS
... system is the function of everything. ► It sends signals notify the brain to react to the situation. ► Reflexes, movement, muscles, everything! ...
... system is the function of everything. ► It sends signals notify the brain to react to the situation. ► Reflexes, movement, muscles, everything! ...
Nervous System - Cloudfront.net
... Sensory neurons take information from sensory receptors to the CNS. Interneurons occur within the CNS and ...
... Sensory neurons take information from sensory receptors to the CNS. Interneurons occur within the CNS and ...
Slide 1
... The Nervous System • The control center for the entire body. • Made up of brain, spinal cord, and neurons. ...
... The Nervous System • The control center for the entire body. • Made up of brain, spinal cord, and neurons. ...
Ch. 3 Discovering Psy Behaving Brain Video
... Discovering Psychology Video Series: “The Behaving Brain” pt. 1 1. In the beginning of the video, Philip Zimbardo compared our brain to a _____________. 2. The human brain houses approximately _____________ number of brain cells. 3. Neurons and glia are designed to do 3 things: a. __________________ ...
... Discovering Psychology Video Series: “The Behaving Brain” pt. 1 1. In the beginning of the video, Philip Zimbardo compared our brain to a _____________. 2. The human brain houses approximately _____________ number of brain cells. 3. Neurons and glia are designed to do 3 things: a. __________________ ...
Nervous System Period 7 - Mercer Island School District
... The nervous system maintains homeostasis by sending electrochemical signals throughout the body, coordinating and executing both the voluntary and involuntary processes that maintain homeostasis ...
... The nervous system maintains homeostasis by sending electrochemical signals throughout the body, coordinating and executing both the voluntary and involuntary processes that maintain homeostasis ...
Biological Basis of Behavior
... • Seratonin is the brain chemical that is associated with moods, concentration and attention Thinking about the information in the last slides, explain what happens in the brain with people who are depressed ...
... • Seratonin is the brain chemical that is associated with moods, concentration and attention Thinking about the information in the last slides, explain what happens in the brain with people who are depressed ...
Nervous Tissue
... The part of the neuron which immediately surrounds the nucleus Usually used synonymously with neuron or soma ...
... The part of the neuron which immediately surrounds the nucleus Usually used synonymously with neuron or soma ...
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM: Communication
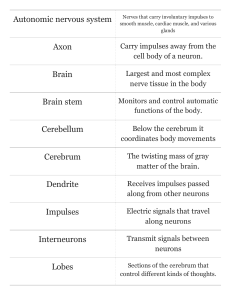
... effectors (muscles or glands). The goal is usually to maintain stable conditions (especially internal) – Homeostasis. Motor neurons. - Somatic Nervous System (skeletal muscles) - Autonomic Nervous System (smooth muscles, glands) C. Neurons: Nerve cells. Unique structure – cell body with many extensi ...
... effectors (muscles or glands). The goal is usually to maintain stable conditions (especially internal) – Homeostasis. Motor neurons. - Somatic Nervous System (skeletal muscles) - Autonomic Nervous System (smooth muscles, glands) C. Neurons: Nerve cells. Unique structure – cell body with many extensi ...
Neurotoxin
Neurotoxins are substances that are poisonous or destructive to nerve tissue. Neurotoxins are an extensive class of exogenous chemical neurological insults that can adversely affect function in both developing and mature nervous tissue. The term can also be used to classify endogenous compounds, which, when abnormally contact, can prove neurologically toxic. Though neurotoxins are often neurologically destructive, their ability to specifically target neural components is important in the study of nervous systems. Common examples of neurotoxins include lead, ethanol (drinking alcohol), Manganese glutamate, nitric oxide (NO), botulinum toxin (e.g. Botox), tetanus toxin, and tetrodotoxin. Some substances such as nitric oxide and glutamate are in fact essential for proper function of the body and only exert neurotoxic effects at excessive concentrations.Neurotoxins inhibit neuron control over ion concentrations across the cell membrane, or communication between neurons across a synapse. Local pathology of neurotoxin exposure often includes neuron excitotoxicity or apoptosis but can also include glial cell damage. Macroscopic manifestations of neurotoxin exposure can include widespread central nervous system damage such as intellectual disability, persistent memory impairments, epilepsy, and dementia. Additionally, neurotoxin-mediated peripheral nervous system damage such as neuropathy or myopathy is common. Support has been shown for a number of treatments aimed at attenuating neurotoxin-mediated injury, such as antioxidant, and antitoxin administration.