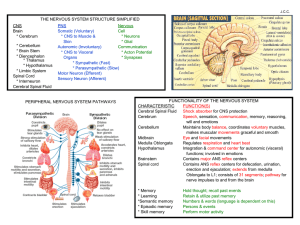
CNS Brain * Cerebrum * Cerebellum * Brain Stem * Diencephalon
... Maintains body balance, coordinates voluntary muscles, makes muscular movements graceful and smooth Midbrain Eye and facial movements Medulla Oblongata Regulates respiration and heart beat Hypothalamus Integration & command center for autonomic (visceral) functions; involved in emotions Brainstem Co ...
... Maintains body balance, coordinates voluntary muscles, makes muscular movements graceful and smooth Midbrain Eye and facial movements Medulla Oblongata Regulates respiration and heart beat Hypothalamus Integration & command center for autonomic (visceral) functions; involved in emotions Brainstem Co ...
Chapter 12-13 Summary
... change allows sodium ions to enter the cell, causing depolarization. Once begun the action potential or nerve impulse continues over the entire surface of the axon. Electrical condition of resting state are restored by the diffusion of potassium ions out of the cell (repolarization) ion concentratio ...
... change allows sodium ions to enter the cell, causing depolarization. Once begun the action potential or nerve impulse continues over the entire surface of the axon. Electrical condition of resting state are restored by the diffusion of potassium ions out of the cell (repolarization) ion concentratio ...
Nervous system 1 - INAYA Medical College
... Neurons What is neuron? Morphological classification of neurons Functional classification of neurons Parts of the brain & functions of each part Short notes on spinal cord, meninges, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) ...
... Neurons What is neuron? Morphological classification of neurons Functional classification of neurons Parts of the brain & functions of each part Short notes on spinal cord, meninges, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) ...
Nervous Tissue
... • Point of stimulus only place ions can pass – (+) ions toward (-) areas and (-) ions to (+) areas – Inside (+) ions move from stimuli site to neighboring () areas ...
... • Point of stimulus only place ions can pass – (+) ions toward (-) areas and (-) ions to (+) areas – Inside (+) ions move from stimuli site to neighboring () areas ...
Chapter 2 (The Brain) Study Guide 1. What is a neuron? What are
... Chapter 2 (The Brain) Study Guide 1. What is a neuron? What are the three basic types of neurons? What is the difference between a neuron with myelin compared to a neuron that is not myelinated? 2. What is stimulus threshold? All-or-none principle? (domino example in class) 3. What is a synapse? 4. ...
... Chapter 2 (The Brain) Study Guide 1. What is a neuron? What are the three basic types of neurons? What is the difference between a neuron with myelin compared to a neuron that is not myelinated? 2. What is stimulus threshold? All-or-none principle? (domino example in class) 3. What is a synapse? 4. ...
Madison Pejsa Pd.4
... control of the reflexes and such essential internal mechanisms as respiration and heartbeat. Cerebellum- A large portion of the brain, serving to coordinate voluntary movements, posture, and balance in humans, being in back of and below the cerebrum and consisting of two lateral lobes and a central ...
... control of the reflexes and such essential internal mechanisms as respiration and heartbeat. Cerebellum- A large portion of the brain, serving to coordinate voluntary movements, posture, and balance in humans, being in back of and below the cerebrum and consisting of two lateral lobes and a central ...
Nervous System
... A) Sensory neurons convey signals from the CNS to sensory receptors. B) Motor neurons convey signals from the CNS to effector cells. C) Interneurons integrate data and relay appropriate signals to other interneurons or to motor neurons. D) The PNS includes nerves and ganglia. E) The CNS consists of ...
... A) Sensory neurons convey signals from the CNS to sensory receptors. B) Motor neurons convey signals from the CNS to effector cells. C) Interneurons integrate data and relay appropriate signals to other interneurons or to motor neurons. D) The PNS includes nerves and ganglia. E) The CNS consists of ...
Nervous System
... A) Sensory neurons convey signals from the CNS to sensory receptors. B) Motor neurons convey signals from the CNS to effector cells. C) Interneurons integrate data and relay appropriate signals to other interneurons or to motor neurons. D) The PNS includes nerves and ganglia. E) The CNS consists of ...
... A) Sensory neurons convey signals from the CNS to sensory receptors. B) Motor neurons convey signals from the CNS to effector cells. C) Interneurons integrate data and relay appropriate signals to other interneurons or to motor neurons. D) The PNS includes nerves and ganglia. E) The CNS consists of ...
Neuroscience - Instructional Resources
... size of the brain. They are not fully equipped, properly positioned, or completely functioning. 30,000 neurons would fit in the space the size of a pinhead. At birth, the brain’s cerebral cortex has 100 billion neurons; but few neurons are connected. ...
... size of the brain. They are not fully equipped, properly positioned, or completely functioning. 30,000 neurons would fit in the space the size of a pinhead. At birth, the brain’s cerebral cortex has 100 billion neurons; but few neurons are connected. ...
List of vocabulary used in understanding the nervous
... membrane that make use of the countervailing gradients of sodium and potassium ions across the membrane. Potassium ion concentration is high inside cells and low outside; sodium ion concentration is the opposite. The sodium and potassium ion concentration gradients are restored by an active transpor ...
... membrane that make use of the countervailing gradients of sodium and potassium ions across the membrane. Potassium ion concentration is high inside cells and low outside; sodium ion concentration is the opposite. The sodium and potassium ion concentration gradients are restored by an active transpor ...
PSY110 Psychology
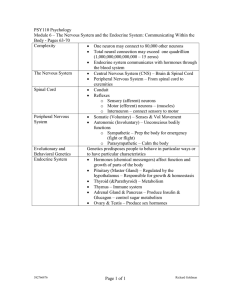
... Complexity One neuron may connect to 80,000 other neurons Total neural connection may exceed one quadrillion (1,000,000,000,000,000 – 15 zeros) Endocrine system communicates with hormones through the blood system The Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) – Brain & Spinal Cord Periphe ...
... Complexity One neuron may connect to 80,000 other neurons Total neural connection may exceed one quadrillion (1,000,000,000,000,000 – 15 zeros) Endocrine system communicates with hormones through the blood system The Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) – Brain & Spinal Cord Periphe ...
File
... alerts the higher brain to incoming messages and thus controls levels of arousal; when asleep, it is subdued. ...
... alerts the higher brain to incoming messages and thus controls levels of arousal; when asleep, it is subdued. ...
File
... They are highly specialized cells that transmit messages (nerve impulses) from one part of the body to another. You will take a closer look at the neuron structure and its function during lecture. Prior to, make sure to read this section so you have a better understanding of its parts and its respon ...
... They are highly specialized cells that transmit messages (nerve impulses) from one part of the body to another. You will take a closer look at the neuron structure and its function during lecture. Prior to, make sure to read this section so you have a better understanding of its parts and its respon ...
Document
... learning and other conscious mental functions. • Thalamus= A midbrain structure that plays a major role in relaying information from the various sensory receptors to other ...
... learning and other conscious mental functions. • Thalamus= A midbrain structure that plays a major role in relaying information from the various sensory receptors to other ...
Unit VIII: Animal Structure and Function, Part II
... info. To spinal cord 4. Synapses with motor neuron in spinal cord 5. Motor neuron conveys signal to quadriceps 6. Synapse with interneuron in spinal cord 7. Interneurons inhibit other motor neurons (hamstring) 8. Prevents the hamstring from contracting ...
... info. To spinal cord 4. Synapses with motor neuron in spinal cord 5. Motor neuron conveys signal to quadriceps 6. Synapse with interneuron in spinal cord 7. Interneurons inhibit other motor neurons (hamstring) 8. Prevents the hamstring from contracting ...
Review Senses and Nervous System Test
... 5. What is pathway of light thru eye 6. What is visual field and visual pathway to brain 7. Eye reflexes (pupil dialate/photpupillary reflex) 8. Mecahnoreceptors in hearing 9. Ottis media 10. Mechanisms of hearing 11. Mechanisms of equilibrium (static and dynamic) 12. Types of deafness 13. What are ...
... 5. What is pathway of light thru eye 6. What is visual field and visual pathway to brain 7. Eye reflexes (pupil dialate/photpupillary reflex) 8. Mecahnoreceptors in hearing 9. Ottis media 10. Mechanisms of hearing 11. Mechanisms of equilibrium (static and dynamic) 12. Types of deafness 13. What are ...
The nervous system
... the cells to one another, to centers throughout the body or to other neurons. These neurons operate on excitation or inhibition and although nerve cells can vary in size and location their communication with one another determines their function. These nerves conduct impulses from sensory receptors ...
... the cells to one another, to centers throughout the body or to other neurons. These neurons operate on excitation or inhibition and although nerve cells can vary in size and location their communication with one another determines their function. These nerves conduct impulses from sensory receptors ...
eating spaghetti!
... nerve impulse in the second neuron. The electrical signal is changing from positive to negative, and it moves the nerve impulse along a neuron. Neurons are in a fiber-like bundle called a nerve, and the impulses are all traveling in the same direction. ...
... nerve impulse in the second neuron. The electrical signal is changing from positive to negative, and it moves the nerve impulse along a neuron. Neurons are in a fiber-like bundle called a nerve, and the impulses are all traveling in the same direction. ...
BIOL241AddlGuideFinalSUM2012
... Because brain anatomy (structures) is being tested in the laboratory, this exam has a strong emphasis on functions, the senses and more general topics in the Nervous System. Be sure to study: • The events, chemicals, and structures involved in transmission at a neural synapse • The “anatomy” of an a ...
... Because brain anatomy (structures) is being tested in the laboratory, this exam has a strong emphasis on functions, the senses and more general topics in the Nervous System. Be sure to study: • The events, chemicals, and structures involved in transmission at a neural synapse • The “anatomy” of an a ...
What is the Nervous System?
... 2. Motor Neurons - project axons out from the central nervous system to control muscles ...
... 2. Motor Neurons - project axons out from the central nervous system to control muscles ...
Toxicology of the Nervous System
... week may be linked to fatigue, headaches, inability to concentrate and hair loss, all symptoms of low-level mercury poisoning. In a study of 123 fish-loving subjects, the researchers found that 89% had blood levels of methylmercury that exceeded the EPA standard by as much as 10 times. How Much Tuna ...
... week may be linked to fatigue, headaches, inability to concentrate and hair loss, all symptoms of low-level mercury poisoning. In a study of 123 fish-loving subjects, the researchers found that 89% had blood levels of methylmercury that exceeded the EPA standard by as much as 10 times. How Much Tuna ...
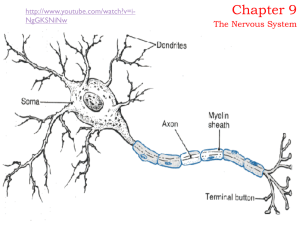
Chapter 9 Nerves
... Dendrites and the cell body provide receptive surfaces A single AXON arises from the cell body and may be enclosed in a myelin sheath and a neurilemma. ...
... Dendrites and the cell body provide receptive surfaces A single AXON arises from the cell body and may be enclosed in a myelin sheath and a neurilemma. ...
Document
... a. They follow an all-or-none principle. c. They travel from neuron to neuron. b. They flow at various speeds. d. They flow in only one direction. __C__13. The somatic nervous system regulates activities that are a. unconscious control b. involuntary c. conscious control ...
... a. They follow an all-or-none principle. c. They travel from neuron to neuron. b. They flow at various speeds. d. They flow in only one direction. __C__13. The somatic nervous system regulates activities that are a. unconscious control b. involuntary c. conscious control ...
Neurotoxin
Neurotoxins are substances that are poisonous or destructive to nerve tissue. Neurotoxins are an extensive class of exogenous chemical neurological insults that can adversely affect function in both developing and mature nervous tissue. The term can also be used to classify endogenous compounds, which, when abnormally contact, can prove neurologically toxic. Though neurotoxins are often neurologically destructive, their ability to specifically target neural components is important in the study of nervous systems. Common examples of neurotoxins include lead, ethanol (drinking alcohol), Manganese glutamate, nitric oxide (NO), botulinum toxin (e.g. Botox), tetanus toxin, and tetrodotoxin. Some substances such as nitric oxide and glutamate are in fact essential for proper function of the body and only exert neurotoxic effects at excessive concentrations.Neurotoxins inhibit neuron control over ion concentrations across the cell membrane, or communication between neurons across a synapse. Local pathology of neurotoxin exposure often includes neuron excitotoxicity or apoptosis but can also include glial cell damage. Macroscopic manifestations of neurotoxin exposure can include widespread central nervous system damage such as intellectual disability, persistent memory impairments, epilepsy, and dementia. Additionally, neurotoxin-mediated peripheral nervous system damage such as neuropathy or myopathy is common. Support has been shown for a number of treatments aimed at attenuating neurotoxin-mediated injury, such as antioxidant, and antitoxin administration.