Human Physiology
... Causes damage to liver, heart, lungs, muscles, pancreas, stomach, intestines Alcohol Poisoning-usually caused by rapid intake of alcohol, slowing of breathing, body feels cool or clammy, unconscious or semiconscious, skin is bluish, vomitting, Long term effects on the brain-Damage to the frontal lob ...
... Causes damage to liver, heart, lungs, muscles, pancreas, stomach, intestines Alcohol Poisoning-usually caused by rapid intake of alcohol, slowing of breathing, body feels cool or clammy, unconscious or semiconscious, skin is bluish, vomitting, Long term effects on the brain-Damage to the frontal lob ...
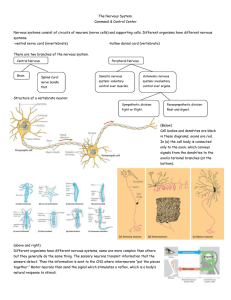
Nervous
... The nervous system also has cells that are essential for the structure of the nervous system called supporting cells or Glia. Some of these are: Astrocyte: glial cell that provides structural and metabolic support for neurons. Blood-brain barrier: a specialized capillary arrangement in the brain th ...
... The nervous system also has cells that are essential for the structure of the nervous system called supporting cells or Glia. Some of these are: Astrocyte: glial cell that provides structural and metabolic support for neurons. Blood-brain barrier: a specialized capillary arrangement in the brain th ...
Assignment 2 - Gordon State College
... Name __________________________________ These questions can be answered from your textbook, class notes, and/or lecture slides. Complete this sheet and turn it in for 5 points extra credit on Test 1. It will not be graded but will be scanned for completeness and reasonable answers. 1. Communication ...
... Name __________________________________ These questions can be answered from your textbook, class notes, and/or lecture slides. Complete this sheet and turn it in for 5 points extra credit on Test 1. It will not be graded but will be scanned for completeness and reasonable answers. 1. Communication ...
Nervous System - EMTStudyCenter.com
... 6. The different charge between the outside and the inside of a neuron at rest is called action potential. synaptic potential. resting membrane potential. equilibrium potential. 7. The stage in an action potential that immediately follows depolarization is polarization. repolarization. threshold. th ...
... 6. The different charge between the outside and the inside of a neuron at rest is called action potential. synaptic potential. resting membrane potential. equilibrium potential. 7. The stage in an action potential that immediately follows depolarization is polarization. repolarization. threshold. th ...
Study Concepts for Exam V - Nervous System
... Nervous system defects arising during pregnancy Divisions of the CNS and PNS, and what parts serve what functions Types of reflex arcs The definitions and differences in location of nuclei vs. ganglia The parts of the brain at the level of detail discussed in lecture. Know at least one major functio ...
... Nervous system defects arising during pregnancy Divisions of the CNS and PNS, and what parts serve what functions Types of reflex arcs The definitions and differences in location of nuclei vs. ganglia The parts of the brain at the level of detail discussed in lecture. Know at least one major functio ...
Assignment 1 - Gordon State College
... 1. Communication in the nervous system takes place via _____________ or nerve cells. 2. The human brain is estimated to have (how many) _____________________neurons. 3. Cells that provide nutrition and support for neurons, remove waste products, and enhance the speed of communication are called ____ ...
... 1. Communication in the nervous system takes place via _____________ or nerve cells. 2. The human brain is estimated to have (how many) _____________________neurons. 3. Cells that provide nutrition and support for neurons, remove waste products, and enhance the speed of communication are called ____ ...
Neurotransmission
... The nervous system is a network of specialized cells, which coordinate the actions of an individual by sending signals from one part of the body to the other. ...
... The nervous system is a network of specialized cells, which coordinate the actions of an individual by sending signals from one part of the body to the other. ...
36.1 The Nervous System Neurons: Basic units of
... Neurons: a long cell that consists of 3 regions a cell body, dendrites and axon and conducts an impulse. Dendrite - branch like extensions of the neuron that receive impulses and carry them to the cell body. White matter - Composed of myelin which coats the axons – this area of the brain is high in ...
... Neurons: a long cell that consists of 3 regions a cell body, dendrites and axon and conducts an impulse. Dendrite - branch like extensions of the neuron that receive impulses and carry them to the cell body. White matter - Composed of myelin which coats the axons – this area of the brain is high in ...
Vocabulary: Chapter 1 Body Control Systems Neuron
... muscles and organs. Retina- an area at the back of the eye that contains sensory receptors for light. Dendrite- part of a neuron that collects information from other neurons. Nerve impulse- message that travels from the dendrites of a neuron to the axon. Axon- part of the neuron that carries message ...
... muscles and organs. Retina- an area at the back of the eye that contains sensory receptors for light. Dendrite- part of a neuron that collects information from other neurons. Nerve impulse- message that travels from the dendrites of a neuron to the axon. Axon- part of the neuron that carries message ...
Neuron Structure
... • 3 substances in choc act as cannabinoids (mimic cannibis (marijuana)) • Active ingredient in marijuana is THC (tetrahydrocannabiol) • When THC binds to receptors, person feels high!!! • No THC in chocolate, but there are chemicals in choc that act like THC • You would have to eat 25 lbs of choc to ...
... • 3 substances in choc act as cannabinoids (mimic cannibis (marijuana)) • Active ingredient in marijuana is THC (tetrahydrocannabiol) • When THC binds to receptors, person feels high!!! • No THC in chocolate, but there are chemicals in choc that act like THC • You would have to eat 25 lbs of choc to ...
Nervous - Lamont High
... • 3 substances in choc act as cannabinoids (mimic cannibis (marijuana)) • Active ingredient in marijuana is THC (tetrahydrocannabiol) • When THC binds to receptors, person feels high!!! • No THC in chocolate, but there are chemicals in choc that act like THC • You would have to eat 25 lbs of choc to ...
... • 3 substances in choc act as cannabinoids (mimic cannibis (marijuana)) • Active ingredient in marijuana is THC (tetrahydrocannabiol) • When THC binds to receptors, person feels high!!! • No THC in chocolate, but there are chemicals in choc that act like THC • You would have to eat 25 lbs of choc to ...
Notes Outline I (Part I)
... __________________ and in the PNS are called ___________________. 18. _____________________ receive imput from other neurons (axons). 19. Axons and dendrites are called ___________________ ________________. 20. Very long axons are otherwise know as ________________ _______________. 21. Movement of s ...
... __________________ and in the PNS are called ___________________. 18. _____________________ receive imput from other neurons (axons). 19. Axons and dendrites are called ___________________ ________________. 20. Very long axons are otherwise know as ________________ _______________. 21. Movement of s ...
Parts and Functions of a Nervous System
... Nerve cells or ______________ are highly specialized body cells that convey impulses from one part of the body to the CNS or vice versa. Neurons have important properties like ______________ or the ability to respond to stimuli and ________________ or the ability to transmit a signal. A neuron consi ...
... Nerve cells or ______________ are highly specialized body cells that convey impulses from one part of the body to the CNS or vice versa. Neurons have important properties like ______________ or the ability to respond to stimuli and ________________ or the ability to transmit a signal. A neuron consi ...
Nervous System
... Lies between the cerebellum and the spinal cord, controls your body’s involuntary actions those that occur automatically Spinal Cord: The spinal cord is the link between your brain and the peripheral nervous system. Peripheral Nervous system: Consist of a network of nerves that branch out from the c ...
... Lies between the cerebellum and the spinal cord, controls your body’s involuntary actions those that occur automatically Spinal Cord: The spinal cord is the link between your brain and the peripheral nervous system. Peripheral Nervous system: Consist of a network of nerves that branch out from the c ...
The Nervous System
... Nervous System Injuries Concussions • Bruise-like injury of brain • Occurs when soft tissue collides against skull • Can cause headache, dizziness, confusion, memory loss, brain damage ...
... Nervous System Injuries Concussions • Bruise-like injury of brain • Occurs when soft tissue collides against skull • Can cause headache, dizziness, confusion, memory loss, brain damage ...
The Nervous System
... Responds and adapts to changes that occur both inside and outside the body (Ex: pain, temperature, pregnancy) ...
... Responds and adapts to changes that occur both inside and outside the body (Ex: pain, temperature, pregnancy) ...
sensory neurons
... spinal cord 3. Impulse sent to brain and back to hand. 4. Hand pulls back before pain is registered by brain ...
... spinal cord 3. Impulse sent to brain and back to hand. 4. Hand pulls back before pain is registered by brain ...
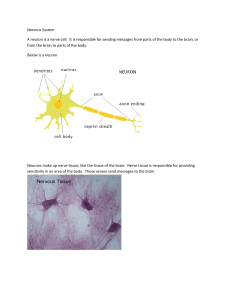
Nervous System A neuron is a nerve cell. It is responsible for
... Below you will find a plastic model of the brain. The brain is responsible for sending and receiving all the signals that make the organs of our bodies function properly. The brain is why we blink, breathe and our hearts beat without thinking about it or being able to really stop it for very long. ...
... Below you will find a plastic model of the brain. The brain is responsible for sending and receiving all the signals that make the organs of our bodies function properly. The brain is why we blink, breathe and our hearts beat without thinking about it or being able to really stop it for very long. ...
Nervous System
... impulses At resting potential the axon has negative voltage Action potential gated channels allow positive sodium ions to move freely into axon, voltage becomes positive. Myelinated axons: action potential concentrated at the nodes. ...
... impulses At resting potential the axon has negative voltage Action potential gated channels allow positive sodium ions to move freely into axon, voltage becomes positive. Myelinated axons: action potential concentrated at the nodes. ...
notes - Other Places you want to go
... 1. Neurons pass signals to other neurons 2. Neurons pass signals to muscle or gland cells 3. Neurons receive signals, process the information, and send out new signals to other neurons Neurotransmitter – chemicals that travel across the synapse, transmitting a signal from the end of an axon to the r ...
... 1. Neurons pass signals to other neurons 2. Neurons pass signals to muscle or gland cells 3. Neurons receive signals, process the information, and send out new signals to other neurons Neurotransmitter – chemicals that travel across the synapse, transmitting a signal from the end of an axon to the r ...
The NERVOUS System
... -nerves extending from the CNS -these nerves link all of the parts of the nervous system ...
... -nerves extending from the CNS -these nerves link all of the parts of the nervous system ...
Nervous System
... of the physical movement of the body as well as responding to the action of all the senses of hearing, sight, smell, taste, and touch Enables animals to react to the internal and external stimuli in their environment ...
... of the physical movement of the body as well as responding to the action of all the senses of hearing, sight, smell, taste, and touch Enables animals to react to the internal and external stimuli in their environment ...
Nervous System
... Most stimuli are received by receptors located on the membrane of nerve cells. ...
... Most stimuli are received by receptors located on the membrane of nerve cells. ...
“Definitions” section of your binder Central nervous system
... messages travel to and from the brain Synapse: the gap that exists between individual nerve cells Neurotransmitters: the chemicals released by neurons which determine the rate at which other neurons fire. ...
... messages travel to and from the brain Synapse: the gap that exists between individual nerve cells Neurotransmitters: the chemicals released by neurons which determine the rate at which other neurons fire. ...
The Nervous System
... Neurotransmitters: chemical messengers that traverse the synaptic gaps between neurons Agonist – mimic neurotransmitters Example: Morphine mimics endorphins Antagonist – block neurotransmitters Example: Poison blocks muscle movement Acetylcholine (Ach) – Enables muscle action, learning, and memory * ...
... Neurotransmitters: chemical messengers that traverse the synaptic gaps between neurons Agonist – mimic neurotransmitters Example: Morphine mimics endorphins Antagonist – block neurotransmitters Example: Poison blocks muscle movement Acetylcholine (Ach) – Enables muscle action, learning, and memory * ...
Neurotoxin
Neurotoxins are substances that are poisonous or destructive to nerve tissue. Neurotoxins are an extensive class of exogenous chemical neurological insults that can adversely affect function in both developing and mature nervous tissue. The term can also be used to classify endogenous compounds, which, when abnormally contact, can prove neurologically toxic. Though neurotoxins are often neurologically destructive, their ability to specifically target neural components is important in the study of nervous systems. Common examples of neurotoxins include lead, ethanol (drinking alcohol), Manganese glutamate, nitric oxide (NO), botulinum toxin (e.g. Botox), tetanus toxin, and tetrodotoxin. Some substances such as nitric oxide and glutamate are in fact essential for proper function of the body and only exert neurotoxic effects at excessive concentrations.Neurotoxins inhibit neuron control over ion concentrations across the cell membrane, or communication between neurons across a synapse. Local pathology of neurotoxin exposure often includes neuron excitotoxicity or apoptosis but can also include glial cell damage. Macroscopic manifestations of neurotoxin exposure can include widespread central nervous system damage such as intellectual disability, persistent memory impairments, epilepsy, and dementia. Additionally, neurotoxin-mediated peripheral nervous system damage such as neuropathy or myopathy is common. Support has been shown for a number of treatments aimed at attenuating neurotoxin-mediated injury, such as antioxidant, and antitoxin administration.