3-8_NeuronDiversity_SalmaA
... to the effector cells. Muscular output involves peripheral nervous system. ...
... to the effector cells. Muscular output involves peripheral nervous system. ...
Nervous System Notes
... neurotransmitters(chemicals) to be released at the terminal, to stimulate the next neuron in the chain. ...
... neurotransmitters(chemicals) to be released at the terminal, to stimulate the next neuron in the chain. ...
2222222222222222222 System • Responsible for coordinating the
... All animals have a nervous system Humans have a dorsally located ___________________(vertebrae) Anterior end of the nerve cord is ______________________ and is dominant controller of the whole nervous system ...
... All animals have a nervous system Humans have a dorsally located ___________________(vertebrae) Anterior end of the nerve cord is ______________________ and is dominant controller of the whole nervous system ...
click - Uplift Education
... 15) When a neuron is at resting membrane potential, which ions are more concentrated in the interstitial fluid (outside the cell)? When a neuron is a resting membrane potential, which ions are more concentrated in the cytosol (inside the cell)? What processes position the ions in these locations? 16 ...
... 15) When a neuron is at resting membrane potential, which ions are more concentrated in the interstitial fluid (outside the cell)? When a neuron is a resting membrane potential, which ions are more concentrated in the cytosol (inside the cell)? What processes position the ions in these locations? 16 ...
Name
... _____ 1. Sensory receptors found in the skin, which are specialized to detect temperature, pressure changes and pain. _____ 2. Specialized cells that myelinate the fibers of neurons found in the PNS _____ 3. Junction or point of close contact between neurons. _____ 4. Bundle of nerve processes insid ...
... _____ 1. Sensory receptors found in the skin, which are specialized to detect temperature, pressure changes and pain. _____ 2. Specialized cells that myelinate the fibers of neurons found in the PNS _____ 3. Junction or point of close contact between neurons. _____ 4. Bundle of nerve processes insid ...
Neurotox I
... The effects of toxicant exposure will be markedly affected not only by dose/concentration, but also by timing. Insults by the same dose/concentration at different times during development may result in markedly different sequelae. ...
... The effects of toxicant exposure will be markedly affected not only by dose/concentration, but also by timing. Insults by the same dose/concentration at different times during development may result in markedly different sequelae. ...
Unit 2 Review
... 7. Another name for a neural impulse is an ______________________________. 8. Explain how neural communication is both an electrical and chemical process. ...
... 7. Another name for a neural impulse is an ______________________________. 8. Explain how neural communication is both an electrical and chemical process. ...
The Nervous System
... Diseases of the Nervous System Cerebral Palsy – caused by abnormalities in parts of the brain that control muscle movements. The early signs of cerebral palsy usually appear before a child reaches 3 years of age. Most common symptoms are a lack of muscle coordination when performing voluntary movem ...
... Diseases of the Nervous System Cerebral Palsy – caused by abnormalities in parts of the brain that control muscle movements. The early signs of cerebral palsy usually appear before a child reaches 3 years of age. Most common symptoms are a lack of muscle coordination when performing voluntary movem ...
Health - Nervous System Review
... 1. Largest part of the brain where learning, intelligence, and judgment occur 3. Sweet, sour, salty, and bitter 5. Nervous system that consists of the brain and spinal column 6. Carries messages to your brain and spinal cord from receptors in your skin 8. Special cell in our skin that allows us to s ...
... 1. Largest part of the brain where learning, intelligence, and judgment occur 3. Sweet, sour, salty, and bitter 5. Nervous system that consists of the brain and spinal column 6. Carries messages to your brain and spinal cord from receptors in your skin 8. Special cell in our skin that allows us to s ...
psy221 tutorial kit - Covenant University
... Note that it is everything that lies between the boundary of one neurone and another. Synapses take different forms such as axo-axonic, axodendritic etc. ...
... Note that it is everything that lies between the boundary of one neurone and another. Synapses take different forms such as axo-axonic, axodendritic etc. ...
Brain Questions
... 2- What, kind of neurons carry signals to the central nervous system? What, kind of neurons interpret these signals? What, kind of neurons send signals out to the peripheral nervous system? 3- The central nervous system is composed of what? The peripheral nervous system is composed of what? 4- What ...
... 2- What, kind of neurons carry signals to the central nervous system? What, kind of neurons interpret these signals? What, kind of neurons send signals out to the peripheral nervous system? 3- The central nervous system is composed of what? The peripheral nervous system is composed of what? 4- What ...
The Nervous System – Use notebook paper if
... interact with other organ systems to serve the needs of cells for oxygen, food, waste removal, and maintaining homeostasis? ...
... interact with other organ systems to serve the needs of cells for oxygen, food, waste removal, and maintaining homeostasis? ...
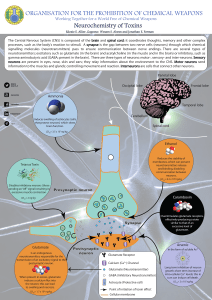
Working Together for a World Free of Chemical Weapons
... Induces swelling of astrocytes (cells that protect neurons) which slows brain function. ...
... Induces swelling of astrocytes (cells that protect neurons) which slows brain function. ...
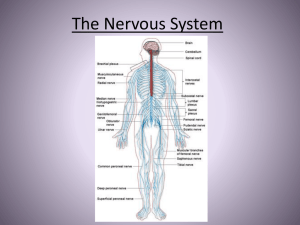
The Nervous System
... • Allows body to respond to stimuli • Structures • 1. Central Nervous System: • - brain • - spinal cord • 2. Peripheral Nervous System - nerves leading away from cns ...
... • Allows body to respond to stimuli • Structures • 1. Central Nervous System: • - brain • - spinal cord • 2. Peripheral Nervous System - nerves leading away from cns ...
Neurotoxin
Neurotoxins are substances that are poisonous or destructive to nerve tissue. Neurotoxins are an extensive class of exogenous chemical neurological insults that can adversely affect function in both developing and mature nervous tissue. The term can also be used to classify endogenous compounds, which, when abnormally contact, can prove neurologically toxic. Though neurotoxins are often neurologically destructive, their ability to specifically target neural components is important in the study of nervous systems. Common examples of neurotoxins include lead, ethanol (drinking alcohol), Manganese glutamate, nitric oxide (NO), botulinum toxin (e.g. Botox), tetanus toxin, and tetrodotoxin. Some substances such as nitric oxide and glutamate are in fact essential for proper function of the body and only exert neurotoxic effects at excessive concentrations.Neurotoxins inhibit neuron control over ion concentrations across the cell membrane, or communication between neurons across a synapse. Local pathology of neurotoxin exposure often includes neuron excitotoxicity or apoptosis but can also include glial cell damage. Macroscopic manifestations of neurotoxin exposure can include widespread central nervous system damage such as intellectual disability, persistent memory impairments, epilepsy, and dementia. Additionally, neurotoxin-mediated peripheral nervous system damage such as neuropathy or myopathy is common. Support has been shown for a number of treatments aimed at attenuating neurotoxin-mediated injury, such as antioxidant, and antitoxin administration.