CHAPTER 10
... Genetic information written in codons is translated into amino acid sequences of proteins – The sequence of nucleotides in DNA provides a code for constructing a protein – Protein construction requires a conversion of a nucleotide sequence to an amino acid sequence – Transcription rewrites the DNA ...
... Genetic information written in codons is translated into amino acid sequences of proteins – The sequence of nucleotides in DNA provides a code for constructing a protein – Protein construction requires a conversion of a nucleotide sequence to an amino acid sequence – Transcription rewrites the DNA ...
The process represented in the diagram below occurs in many cells
... Scientists have found a gene in the DNA of a certain plant that could be the key to increasing the amount of lycopene, a cancerfighting substance, in tomatoes. 32 The process of inserting this gen ...
... Scientists have found a gene in the DNA of a certain plant that could be the key to increasing the amount of lycopene, a cancerfighting substance, in tomatoes. 32 The process of inserting this gen ...
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... separates the 2 strands • RNA polymerase then uses one strand of DNA as a template for assembling an mRNA complementary strand • This creates a strand of mRNA which can carry the genetic code out of the nucleus to complete the second step of protein synthesis. ...
... separates the 2 strands • RNA polymerase then uses one strand of DNA as a template for assembling an mRNA complementary strand • This creates a strand of mRNA which can carry the genetic code out of the nucleus to complete the second step of protein synthesis. ...
Unit 1: Cells, Cell Reproduction, and Development
... What is in the DNA backbone, and why are they considered antiparallel? ...
... What is in the DNA backbone, and why are they considered antiparallel? ...
Objectives • Explain the "one gene–one polypeptide" hypothesis
... mold needed, such as a vitamin or an amino acid. Beadle and Tatum also showed that each mutant was defective in a single gene. Their research led them to propose the "one gene–one enzyme" hypothesis. This hypothesis states that the function of an individual gene is to dictate the production of a spe ...
... mold needed, such as a vitamin or an amino acid. Beadle and Tatum also showed that each mutant was defective in a single gene. Their research led them to propose the "one gene–one enzyme" hypothesis. This hypothesis states that the function of an individual gene is to dictate the production of a spe ...
DNA Replication Graphic Organizer
... REVIEW: Explain the TWO things an enzyme does in chemical reactions in the body… ...
... REVIEW: Explain the TWO things an enzyme does in chemical reactions in the body… ...
Unit 1: Cells - Loudoun County Public Schools
... 1. Understand the history of DNA. a) Understand the contributions of all scientists that led to the development of the Double Helix structure by Watson, Crick, Franklin and Chargaff. 2. Explain how the genetic code is contained in DNA a) DNA is a macromolecule (polymer) made up of repeating subunits ...
... 1. Understand the history of DNA. a) Understand the contributions of all scientists that led to the development of the Double Helix structure by Watson, Crick, Franklin and Chargaff. 2. Explain how the genetic code is contained in DNA a) DNA is a macromolecule (polymer) made up of repeating subunits ...
Genetics - FAQ`s - El Camino College
... primary carrier of genetic (hereditary) information. It’s made up of nucleic acids, which consist of phosphates, sugars and four chemical bases (adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine). WHAT IS A CHROMOSOME? A threadlike structure found in the nucleus of the cell that contains the hereditary materi ...
... primary carrier of genetic (hereditary) information. It’s made up of nucleic acids, which consist of phosphates, sugars and four chemical bases (adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine). WHAT IS A CHROMOSOME? A threadlike structure found in the nucleus of the cell that contains the hereditary materi ...
APC004 DNA Quantification/Nanodrop
... Add Your DNA sample to the Nanodrop and click Measure. A measurement will appear. If the sample is very high in concentration it is advisable to dilute it 1:5 or 1:10 as Genomic DNA can be very viscous and may yield in incorrect readings. ...
... Add Your DNA sample to the Nanodrop and click Measure. A measurement will appear. If the sample is very high in concentration it is advisable to dilute it 1:5 or 1:10 as Genomic DNA can be very viscous and may yield in incorrect readings. ...
Gene Expression
... • Proteins (enzymes) can be used to make all the other molecules a cell needs: carbohydrates, lipids and nucleic acids. • A segment of DNA that carries the instructions to make (codes for) a protein is called a gene. ...
... • Proteins (enzymes) can be used to make all the other molecules a cell needs: carbohydrates, lipids and nucleic acids. • A segment of DNA that carries the instructions to make (codes for) a protein is called a gene. ...
1. Which of the following enzymes will untangle DNA? A
... C) Carbon base, ribose, and phosphate D) Carbon base, glucose, and carboxyl ...
... C) Carbon base, ribose, and phosphate D) Carbon base, glucose, and carboxyl ...
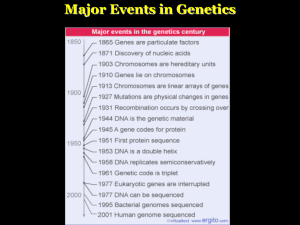
Major Events in Genetics
... issue as Wilkins and Franklin in April 1953 that DNA was a double helix through observations of the X-ray crystallographic images of DNA • Watson and Crick reasoned that there must be additional specificity of pairing – Dictated by the structure of the bases • Each base pair forms a different number ...
... issue as Wilkins and Franklin in April 1953 that DNA was a double helix through observations of the X-ray crystallographic images of DNA • Watson and Crick reasoned that there must be additional specificity of pairing – Dictated by the structure of the bases • Each base pair forms a different number ...
Modeling DNA
... ᷿model of a DNA molecule using the materials provided by your teacher. Label the following parts of your DNA molecule: Sugar-phosphate backbone, adenine, thyamine, guanine, cytosine, hydrogen bond ...
... ᷿model of a DNA molecule using the materials provided by your teacher. Label the following parts of your DNA molecule: Sugar-phosphate backbone, adenine, thyamine, guanine, cytosine, hydrogen bond ...
Name
... make a specific protein. 5. Information is stored on the RNA molecule in a triplet code called a ________________. 6. Codons are a sequence of __________ nitrogen bases that code for a specific amino acid. 7. The mRNA strand will leave the nucleus and attach itself to a __________________, the site ...
... make a specific protein. 5. Information is stored on the RNA molecule in a triplet code called a ________________. 6. Codons are a sequence of __________ nitrogen bases that code for a specific amino acid. 7. The mRNA strand will leave the nucleus and attach itself to a __________________, the site ...
15-Work-Experience - College Admissions Strategies
... Tip: The above essay was modified below to answer another application’s question that stated, “Describe a time you collaborated with others in a way that seemed natural at first but became exceptional.” Only the parts highlighted in yellow have been modified. I have always had a passion for science, ...
... Tip: The above essay was modified below to answer another application’s question that stated, “Describe a time you collaborated with others in a way that seemed natural at first but became exceptional.” Only the parts highlighted in yellow have been modified. I have always had a passion for science, ...
Section 1.1 Name:
... Review of Old Information: Recall that the DNA is the hereditary information for all living things. In this molecule is the code for all of our traits. However, one important question remains… how do we get from the genetic code from DNA in the nucleus, to the production of our phenotypes (or what w ...
... Review of Old Information: Recall that the DNA is the hereditary information for all living things. In this molecule is the code for all of our traits. However, one important question remains… how do we get from the genetic code from DNA in the nucleus, to the production of our phenotypes (or what w ...
Make an Animal Activity: Coyote
... Transcribe the DNA strand into mRNA. Don't forget the special base pair rules for RNA! Separate the triplets into codons by putting a mark after every 3 (three) bases. 2. Translate the mRNA into an amino acid chain. Use the amino acid chart to find the amino acid that corresponds to each codon. Reme ...
... Transcribe the DNA strand into mRNA. Don't forget the special base pair rules for RNA! Separate the triplets into codons by putting a mark after every 3 (three) bases. 2. Translate the mRNA into an amino acid chain. Use the amino acid chart to find the amino acid that corresponds to each codon. Reme ...
1 BIOL 213 Fourth Exam All atoms, chemical bonding and structures
... Draw the correct and complete chemical structures and complementary base pairing for the following template DNA deoxynucleotides and primer RNA nucleotides as it exists to initiate DNA synthesis on the template strand. 3' - GT………………….5' 5' - CU………………….3' ...
... Draw the correct and complete chemical structures and complementary base pairing for the following template DNA deoxynucleotides and primer RNA nucleotides as it exists to initiate DNA synthesis on the template strand. 3' - GT………………….5' 5' - CU………………….3' ...
1 Unit 9: Modern Genetics Advance Organizer Topic: DNA, RNA
... - Contains ______________ information and instructions for making ___________ which control cell activities. - Made of monomers called ______________ (monomers of nucleic acids). Draw a model of DNA: ...
... - Contains ______________ information and instructions for making ___________ which control cell activities. - Made of monomers called ______________ (monomers of nucleic acids). Draw a model of DNA: ...
Gene Control of Cellular Activities
... The cut up pieces are then separated in a gel using the negative charge of the DNA to move it across an agrose gel. The smaller pieces will move faster then the larger pieces. ...
... The cut up pieces are then separated in a gel using the negative charge of the DNA to move it across an agrose gel. The smaller pieces will move faster then the larger pieces. ...
Sc9 - a 3.1(student notes)
... The sequence of the proteins ______________________ that the cell is able to interpret. o This is called the _____________________. ...
... The sequence of the proteins ______________________ that the cell is able to interpret. o This is called the _____________________. ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.