
Genetic Code Review.cwk
... 18. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about translation. a. Before translation occurs, messenger RNAis transcribed from DNAin the nucleus. b. Translation occurs in the nucleus. c. It is the job of transfer RNAto bring the proper amino acid into the ribosome to be attached to the growin ...
... 18. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about translation. a. Before translation occurs, messenger RNAis transcribed from DNAin the nucleus. b. Translation occurs in the nucleus. c. It is the job of transfer RNAto bring the proper amino acid into the ribosome to be attached to the growin ...
Biology 2.3 2.4 - Sleeping Dog Studios
... Lipids are nonpolar molecules that are not soluble or mostly insoluble in water. They will not dissolve into ...
... Lipids are nonpolar molecules that are not soluble or mostly insoluble in water. They will not dissolve into ...
i. building blocks
... (1) Hydrogen bonds between amino hydrogens and carboxyl oxygens b) Results in an -helix configuration or a - sheet configuration 3. Tertiary structure a) The 3-dimensional folding of the polypeptide chain b) Do to interaction of R-groups of amino acids some distance away from each other (1) These ...
... (1) Hydrogen bonds between amino hydrogens and carboxyl oxygens b) Results in an -helix configuration or a - sheet configuration 3. Tertiary structure a) The 3-dimensional folding of the polypeptide chain b) Do to interaction of R-groups of amino acids some distance away from each other (1) These ...
DNA EXTRACTION
... BACKGROUND The genomes of all living organisms consist of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). There are two interconnected strands in the structure of DNA (double helix). The strands of a DNA molecule contain nucleotides which have three essential parts: a sugar, a phosphate and a base. There are four diff ...
... BACKGROUND The genomes of all living organisms consist of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). There are two interconnected strands in the structure of DNA (double helix). The strands of a DNA molecule contain nucleotides which have three essential parts: a sugar, a phosphate and a base. There are four diff ...
Quiz 2 Practice - philipdarrenjones.com
... quizzing each other on them. More work for you in the short term, but you’ll thank me later! ☺ ...
... quizzing each other on them. More work for you in the short term, but you’ll thank me later! ☺ ...
2013 - (canvas.brown.edu).
... D) the 5' ends of both strands are at one end of the helix. E) the bases occupy the interior of the helix. Circle the correct answer. 9. [2 points] Nucleosomes: A) are important features of chromosome organization in bacteria. B) contain proteins that are rich in acidic amino acids. C) are composed ...
... D) the 5' ends of both strands are at one end of the helix. E) the bases occupy the interior of the helix. Circle the correct answer. 9. [2 points] Nucleosomes: A) are important features of chromosome organization in bacteria. B) contain proteins that are rich in acidic amino acids. C) are composed ...
Semester 2 – Final Exam Review2016
... cystic fibrosis. What do their genotypes have to be in order to have a child with cystic fibrosis (assuming she didn’t fool around with the milk man). 7. Be able to interpret a pedigree. Use their Pedigree Worksheet to help you practice! Chapter 12 & 13: 1. What is DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) mad ...
... cystic fibrosis. What do their genotypes have to be in order to have a child with cystic fibrosis (assuming she didn’t fool around with the milk man). 7. Be able to interpret a pedigree. Use their Pedigree Worksheet to help you practice! Chapter 12 & 13: 1. What is DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) mad ...
Genetics IB Syllabus
... base pairing. Helicase unwinds the double helix and separates the two strands by breaking hydrogen bonds. DNA polymerase links nucleotides together to form a new strand, using the pre-existing strand as a template. Transcription is the synthesis of mRNA copied from the DNA base sequences by RN ...
... base pairing. Helicase unwinds the double helix and separates the two strands by breaking hydrogen bonds. DNA polymerase links nucleotides together to form a new strand, using the pre-existing strand as a template. Transcription is the synthesis of mRNA copied from the DNA base sequences by RN ...
3. Organic Compounds
... phosphate, and a base. The sugar, ribose in RNA and deoxyribose in DNA, contain 5 carbons. They differ only in that an –OH group in ribose is replaced by a –H in DNA. The main energy-carrying molecule in the cell is ATP. ATP is an RNA nucleotide with 3 phosphate groups attached to it in a chain. The ...
... phosphate, and a base. The sugar, ribose in RNA and deoxyribose in DNA, contain 5 carbons. They differ only in that an –OH group in ribose is replaced by a –H in DNA. The main energy-carrying molecule in the cell is ATP. ATP is an RNA nucleotide with 3 phosphate groups attached to it in a chain. The ...
BIOL 105 S 2013 Practice Quiz Supp DNA
... Which of the following tasks is not accomplished by DNA? A) undergoes mutations that can provide variation B) provides energy for the cell C) stores information D) replicates to pass a copy to the next generation Answer B Which of the following statements is incorrect concerning deoxyribonucleic aci ...
... Which of the following tasks is not accomplished by DNA? A) undergoes mutations that can provide variation B) provides energy for the cell C) stores information D) replicates to pass a copy to the next generation Answer B Which of the following statements is incorrect concerning deoxyribonucleic aci ...
fatty acids
... Steroid hormones and steroids: not composed of glycerol and fatty acids, but have ringlike structures similar to sugars Consist mainly of hydrocarbons and are therefore hydrophobic Testosterone: release into the blood stream from testis, development of male sexual characteristics, lipid soluble so ...
... Steroid hormones and steroids: not composed of glycerol and fatty acids, but have ringlike structures similar to sugars Consist mainly of hydrocarbons and are therefore hydrophobic Testosterone: release into the blood stream from testis, development of male sexual characteristics, lipid soluble so ...
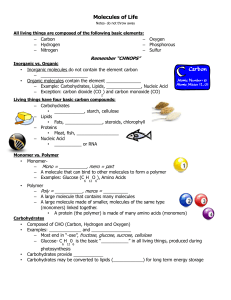
Molecules of Life
... Some types of proteins can contain other elements like S, P, Fe, and Cu (Sulfur, Phosphorous, Iron, Copper) Made of small units (monomers) called ____________ __________. Examples: – Proteins make up muscle, __________ and hair – Hemoglobin (______________) is a protein that carries oxygenated blood ...
... Some types of proteins can contain other elements like S, P, Fe, and Cu (Sulfur, Phosphorous, Iron, Copper) Made of small units (monomers) called ____________ __________. Examples: – Proteins make up muscle, __________ and hair – Hemoglobin (______________) is a protein that carries oxygenated blood ...
bio12_sm_07_1
... out of the nucleus to be coded into proteins at a ribosome; rRNA, which combines with proteins to form catalytic portions of ribosomes that facilitate peptide production; and tRNA, which are small clover-leaf shaped RNA units that translate mRNA code into amino acids during translation at the riboso ...
... out of the nucleus to be coded into proteins at a ribosome; rRNA, which combines with proteins to form catalytic portions of ribosomes that facilitate peptide production; and tRNA, which are small clover-leaf shaped RNA units that translate mRNA code into amino acids during translation at the riboso ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis
... Every three bases on DNA stands for ONE amino acid Each three-letter unit on mRNA is called a codon Most amino acids have more than one codon! The code is nearly universal among living organisms ...
... Every three bases on DNA stands for ONE amino acid Each three-letter unit on mRNA is called a codon Most amino acids have more than one codon! The code is nearly universal among living organisms ...
Stem Cells, Cancer, and Human Health
... are called point mutations A substitution mutation occurs when one base is substituted for another in a DNA sequence ...
... are called point mutations A substitution mutation occurs when one base is substituted for another in a DNA sequence ...
ch4 reading guide key
... 3. All four groups of organic molecules require genetic instructions because enzymes control their synthesis. 4. A genome is the complete set of genetic instructions in a cell. 5. Nucleotides are building blocks of nucleic acids. 6. Three parts of a nucleotide are a sugar, a phosphate group, and on ...
... 3. All four groups of organic molecules require genetic instructions because enzymes control their synthesis. 4. A genome is the complete set of genetic instructions in a cell. 5. Nucleotides are building blocks of nucleic acids. 6. Three parts of a nucleotide are a sugar, a phosphate group, and on ...
Final Review Answer Key - Mercer Island School District
... Translation occurs in the ribosome. The mRNA is attaches to a ribosome and a tRNA complementary to start codon. A tRNA with a complementary anticodon to the next codon (series of 3 nucleotides) attaches bringing the corresponding amino acid. The amino acids are joined together and the mRNA slides do ...
... Translation occurs in the ribosome. The mRNA is attaches to a ribosome and a tRNA complementary to start codon. A tRNA with a complementary anticodon to the next codon (series of 3 nucleotides) attaches bringing the corresponding amino acid. The amino acids are joined together and the mRNA slides do ...
Biology Chapter 2 Organic Molecules Students 9-25
... 1. Look at the monosaccharides (single sugars) below. How many different elements do they contain? What are they? ...
... 1. Look at the monosaccharides (single sugars) below. How many different elements do they contain? What are they? ...
2. If 20% of the DNA in a guinea pig cell is adenine, what
... acids in equal proportions. In fact, each strand would produce the two in alternating order; for example, in the z strand would produce a polypeptide chain of isoleucine followed by tyrosine followed by isoleucine, then tyrosine, and so on. ...
... acids in equal proportions. In fact, each strand would produce the two in alternating order; for example, in the z strand would produce a polypeptide chain of isoleucine followed by tyrosine followed by isoleucine, then tyrosine, and so on. ...
DNA Replication
... as a template for the attachment of complementary bases. Addition of new amino acids can’t begin, though, until an RNA primer is added by the enzyme primase. Once primed, DNA polymerase adds new nucleotides to the DNA molecule. The nitrogen base adenine always pairs with guanine and cytosine always ...
... as a template for the attachment of complementary bases. Addition of new amino acids can’t begin, though, until an RNA primer is added by the enzyme primase. Once primed, DNA polymerase adds new nucleotides to the DNA molecule. The nitrogen base adenine always pairs with guanine and cytosine always ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.

















![Recombinant DNA technology.ppt [Compatibility Mode]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/022508436_1-26bb714d45e9a2e7cd265480e0da1a03-300x300.png)




