Biology_EOC_Review_best_version2011_2
... What provides immediate energy? What is used for long term stored energy? How does heating affect the function of an enzyme? Shape is a characteristics responsible for deterring the function of an enzyme. If pectinase is mixed with pectin what factors will slow the ...
... What provides immediate energy? What is used for long term stored energy? How does heating affect the function of an enzyme? Shape is a characteristics responsible for deterring the function of an enzyme. If pectinase is mixed with pectin what factors will slow the ...
The Organization of the Human Body
... Nonpolar covalent: atoms share equally one atom does not attract the shared electrons more strongly than the other atom Polar covalent: atoms share unequally one atom attracts the shared electron more strongly than the other ...
... Nonpolar covalent: atoms share equally one atom does not attract the shared electrons more strongly than the other atom Polar covalent: atoms share unequally one atom attracts the shared electron more strongly than the other ...
Self_Assembly_in_Nanotechnology
... • Two strands of DNA can bond together using hydrogen bonds between base pairs. – In DNA thymine always pairs with adenine and cytosine always base pairs with guanine via hydrogen bonds. – The most common form of DNA is the double helix. – It is called the B or right handed DNA structure. ...
... • Two strands of DNA can bond together using hydrogen bonds between base pairs. – In DNA thymine always pairs with adenine and cytosine always base pairs with guanine via hydrogen bonds. – The most common form of DNA is the double helix. – It is called the B or right handed DNA structure. ...
Chapter 1 Review Understanding Concepts
... 17. RNA nucleotides contain the five-carbon sugar ribose and contain the nitrogenous base uracil, whereas DNA contains the five-carbon sugar deoxyribose and the nitrogenous base thymine instead of uracil. 18. DNA possesses hydrogen bonds as two DNA strands run antiparallel to each other, allowing hy ...
... 17. RNA nucleotides contain the five-carbon sugar ribose and contain the nitrogenous base uracil, whereas DNA contains the five-carbon sugar deoxyribose and the nitrogenous base thymine instead of uracil. 18. DNA possesses hydrogen bonds as two DNA strands run antiparallel to each other, allowing hy ...
Systematic Implications of DNA variation in subfamily
... appropriate to the taxonomic level(s) being investigated; “slow” genes versus “fast” genes It is desirable that sequences can be readily aligned The biology of the gene (or other DNA sequence) must be understood to assure homology ...
... appropriate to the taxonomic level(s) being investigated; “slow” genes versus “fast” genes It is desirable that sequences can be readily aligned The biology of the gene (or other DNA sequence) must be understood to assure homology ...
Lecture 9
... (1) synthesis of small organic molecules (2) join small molecules (monomers) into big molecules (polymers) (3) aggregrate molecules into droplets which have different properties than their nonliving constituents. (4) origin of heredity, so “droplets” can pass on their molecules to offspring Evolutio ...
... (1) synthesis of small organic molecules (2) join small molecules (monomers) into big molecules (polymers) (3) aggregrate molecules into droplets which have different properties than their nonliving constituents. (4) origin of heredity, so “droplets” can pass on their molecules to offspring Evolutio ...
ACADEMIC BIOLOGY MIDTERM REVIEW GUIDE
... 10. What are sex-linked traits? 11. Who shows more sex linked traits? 12. What is a carrier? Can a male be a carrier? 13. Be able to solve sex-linked punnett squares and give genotypic and phenotypic ratio of offspring. 14. Name two sex linked traits 15. What can be learned by looking at a karyotype ...
... 10. What are sex-linked traits? 11. Who shows more sex linked traits? 12. What is a carrier? Can a male be a carrier? 13. Be able to solve sex-linked punnett squares and give genotypic and phenotypic ratio of offspring. 14. Name two sex linked traits 15. What can be learned by looking at a karyotype ...
short_answer_Barcoding_exam_Key
... 38. What is unique about the ddNTPS that make them useful in DNA sequencing? (3) The oxygen molecule is not present, so a covalent bond with another nucleotide at that the phosphate can’t occur, which causes elongation to stop at various points during PCR These nucleotides also fluoresce in differen ...
... 38. What is unique about the ddNTPS that make them useful in DNA sequencing? (3) The oxygen molecule is not present, so a covalent bond with another nucleotide at that the phosphate can’t occur, which causes elongation to stop at various points during PCR These nucleotides also fluoresce in differen ...
Nucleotides, nucleic acids and the genetic material It all started with
... required to unwind the double helix and to synthesize a new strand of DNA. We will approach the study of the moelcular mechanism of DNA replication from the point of view of the machinery that is required to accomplish it. The unwound helix, with each strand • being synthesized into a new double hel ...
... required to unwind the double helix and to synthesize a new strand of DNA. We will approach the study of the moelcular mechanism of DNA replication from the point of view of the machinery that is required to accomplish it. The unwound helix, with each strand • being synthesized into a new double hel ...
Nucleotides, nucleic acids and the genetic material
... once supercoiling has been eliminated by the topoisomerase. The two strands very much want to bind together because of their hydrogen bonding affinity for each other, so the helicase activity requires energy (in the form of ATP ) to break the strands apart. ...
... once supercoiling has been eliminated by the topoisomerase. The two strands very much want to bind together because of their hydrogen bonding affinity for each other, so the helicase activity requires energy (in the form of ATP ) to break the strands apart. ...
DNA Lesson Plan - Penn Arts and Sciences
... shows the glycosidic bonds that form between the sugars and nitrogenous bases. The nucleosides are then linked via phosphoester bonds to phosphate groups: figure 5a shows the phosphate group and the ester linkages to the nucleosides: these are cyclic nucleotides. Nucleotides link to other nucleotide ...
... shows the glycosidic bonds that form between the sugars and nitrogenous bases. The nucleosides are then linked via phosphoester bonds to phosphate groups: figure 5a shows the phosphate group and the ester linkages to the nucleosides: these are cyclic nucleotides. Nucleotides link to other nucleotide ...
Unoshan_project
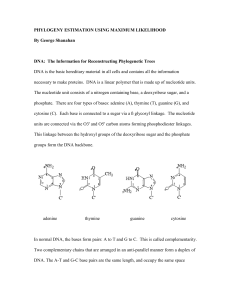
... The nucleotide unit consists of a nitrogen containing base, a deoxyribose sugar, and a phosphate. There are four types of bases: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C). Each base is connected to a sugar via a ß glycosyl linkage. The nucleotide units are connected via the O3' and O5' ...
... The nucleotide unit consists of a nitrogen containing base, a deoxyribose sugar, and a phosphate. There are four types of bases: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C). Each base is connected to a sugar via a ß glycosyl linkage. The nucleotide units are connected via the O3' and O5' ...
Biotechnology
... Biotechnology • Biotechnology is the manipulation of organisms or their components to make useful products • The applications of DNA technology affect everything from agriculture, to criminal law, to medical research ...
... Biotechnology • Biotechnology is the manipulation of organisms or their components to make useful products • The applications of DNA technology affect everything from agriculture, to criminal law, to medical research ...
Chapter 26 - RNA Metabolism
... • DNA is continuously unwound as RNA pol catalyzes a processive elongation of RNA chain (about 17 bp at a time) transcription bubble • Mechanism of elongation reaction almost identical to that for DNA polymerase • Incoming ribonucleotide triphosphates (RTPs) form correct H bonds to template • New ph ...
... • DNA is continuously unwound as RNA pol catalyzes a processive elongation of RNA chain (about 17 bp at a time) transcription bubble • Mechanism of elongation reaction almost identical to that for DNA polymerase • Incoming ribonucleotide triphosphates (RTPs) form correct H bonds to template • New ph ...
Chapter 20~ DNA Technology & Genomics
... Single circular chromosome ◦ haploid ◦ naked DNA no histone proteins ...
... Single circular chromosome ◦ haploid ◦ naked DNA no histone proteins ...
E co
... each end of the blunt-ended DNA. EcoRI digestion removes all but the terminal one,leaving the desired 5’-overhangs.(b)cloning vectors often have polylinkers consisting of a multiple array of restriction sites at their coning sites, so restriction fragments generated by a variety of endonucleases can ...
... each end of the blunt-ended DNA. EcoRI digestion removes all but the terminal one,leaving the desired 5’-overhangs.(b)cloning vectors often have polylinkers consisting of a multiple array of restriction sites at their coning sites, so restriction fragments generated by a variety of endonucleases can ...
Chapter 13 DNA Technology
... - “sticky ends” (single chain segments or tails created on the cut piece of DNA….easily bind to complementary strands of DNA. ** Pieces of DNA cut with the same restriction enzyme can bind to form a new sequence of nucleotides…..therefore, DNA HAS BEEN TRANSFERRED OR ISOLATED!!!!!!! See fig.13-1 on ...
... - “sticky ends” (single chain segments or tails created on the cut piece of DNA….easily bind to complementary strands of DNA. ** Pieces of DNA cut with the same restriction enzyme can bind to form a new sequence of nucleotides…..therefore, DNA HAS BEEN TRANSFERRED OR ISOLATED!!!!!!! See fig.13-1 on ...
Organic Compounds
... up organisms and carry out life processes. Carbohydrates are organic molecules that consist of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. They are made up of repeating units called saccharides. They provide cells with energy, store energy, and form structural tissues. Lipids are organic compounds that consist of ...
... up organisms and carry out life processes. Carbohydrates are organic molecules that consist of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. They are made up of repeating units called saccharides. They provide cells with energy, store energy, and form structural tissues. Lipids are organic compounds that consist of ...
Genetic Engineering
... Antibodies- help destroy microbes that invade the body ( only effective against bacteria) Insulin – protein produced by genetic engineering to treat diabetes ...
... Antibodies- help destroy microbes that invade the body ( only effective against bacteria) Insulin – protein produced by genetic engineering to treat diabetes ...
Structure and Replication of DNA
... • Replication bubbles are the “unzipped” sections where replication occurs all along the molecule • At the end of each replication bubble is a replication fork: a Y-shaped region where new DNA strands are elongating • Helicase: enzyme that unzips the double helix at the replication forks • Single-s ...
... • Replication bubbles are the “unzipped” sections where replication occurs all along the molecule • At the end of each replication bubble is a replication fork: a Y-shaped region where new DNA strands are elongating • Helicase: enzyme that unzips the double helix at the replication forks • Single-s ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.