CAP5510 - Bioinformatics - UF CISE
... • Building proteins from DNA – Promoter sequence: start of a gene – 13 nucleotides. ...
... • Building proteins from DNA – Promoter sequence: start of a gene – 13 nucleotides. ...
CH 20 DNA TECHNOLOGY - Ed W. Clark High School
... A. Recombinant DNA is DNA in which nucleotide sequences from two different sources are combined into one DNA molecule. B. The methods for making recombinant DNA is called genetic engjneering C. Biotechnology allows for the manipulation of organisms and their components to make useful products. II. U ...
... A. Recombinant DNA is DNA in which nucleotide sequences from two different sources are combined into one DNA molecule. B. The methods for making recombinant DNA is called genetic engjneering C. Biotechnology allows for the manipulation of organisms and their components to make useful products. II. U ...
1 Biotechnology: Old and New
... ammonium cyanate in a laboratory, proving that an organic compound made by living organisms can be made from inorganic compounds in the laboratory. ...
... ammonium cyanate in a laboratory, proving that an organic compound made by living organisms can be made from inorganic compounds in the laboratory. ...
Homework #2
... c) If trisomies and monsomies entailing chromosome 13 and 22 are letha, what proportion of the surviving offspring will be carriers of the translocation? ...
... c) If trisomies and monsomies entailing chromosome 13 and 22 are letha, what proportion of the surviving offspring will be carriers of the translocation? ...
Genetics/DNA PowerPoint
... DNA nucleotides are made of three basic components: a 5-carbon sugar called deoxyribose, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. – The deoxyribose and phosphates make up the “backbone” of DNA while the nitrogenous bases make up the “rungs” of the DNA ladder. ...
... DNA nucleotides are made of three basic components: a 5-carbon sugar called deoxyribose, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. – The deoxyribose and phosphates make up the “backbone” of DNA while the nitrogenous bases make up the “rungs” of the DNA ladder. ...
BSC 2010C
... Explain the chromosomal basis of sex determination. Explain sex linked inheritance and give examples. Characterize alterations in chromosome numbers and common associated disorders in humans. Explain the structure of DNA, including the double helix, arrangement of nucleotides, and pairing of nitroge ...
... Explain the chromosomal basis of sex determination. Explain sex linked inheritance and give examples. Characterize alterations in chromosome numbers and common associated disorders in humans. Explain the structure of DNA, including the double helix, arrangement of nucleotides, and pairing of nitroge ...
Genetics - LLI Manassas
... estimates about 19,000 genes. The Encyclopedia of DNA Elements project (ENCODE) found that each part of a gene can be used in many different proteins, these parts are spliced together to form the more than 100,000 distinct proteins. Also, different cells can produce different proteins, and they can ...
... estimates about 19,000 genes. The Encyclopedia of DNA Elements project (ENCODE) found that each part of a gene can be used in many different proteins, these parts are spliced together to form the more than 100,000 distinct proteins. Also, different cells can produce different proteins, and they can ...
Macromolecule Expert Sheets
... 9. What kind of molecules will result when a protein is completely hydrolyzed? A mixture of various amino acids will result. 10. What makes different kinds of proteins unique? The sequence of amino acids (primary structure) 11. Explain how a protein’s shape is determined. Some of the side chains for ...
... 9. What kind of molecules will result when a protein is completely hydrolyzed? A mixture of various amino acids will result. 10. What makes different kinds of proteins unique? The sequence of amino acids (primary structure) 11. Explain how a protein’s shape is determined. Some of the side chains for ...
Student Handout - University of California, Irvine
... Uses of Gel Electrophoresis: Gel electrophoresis is used to provide genetic information in a wide range of data fields. Human DNA can be analyzed to provide ________________ in criminal cases, to diagnose _____________ diseases, and to solve _______________ cases. Samples can be obtained from any ...
... Uses of Gel Electrophoresis: Gel electrophoresis is used to provide genetic information in a wide range of data fields. Human DNA can be analyzed to provide ________________ in criminal cases, to diagnose _____________ diseases, and to solve _______________ cases. Samples can be obtained from any ...
UNIT 3 Biochem Test Study Guide
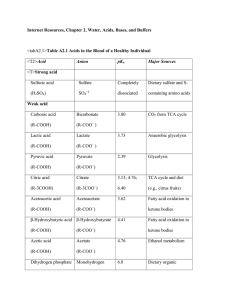
... ●Chapter 6 in the book, especially page 167 (take a book home if needed) & 924-928 ●all your notes from Unit 3 Concepts Listed Below: What does organic mean? Indicators used in the lab (Identifying Organic Compound) and what each identifies How to make models of molecules, how to draw them and how t ...
... ●Chapter 6 in the book, especially page 167 (take a book home if needed) & 924-928 ●all your notes from Unit 3 Concepts Listed Below: What does organic mean? Indicators used in the lab (Identifying Organic Compound) and what each identifies How to make models of molecules, how to draw them and how t ...
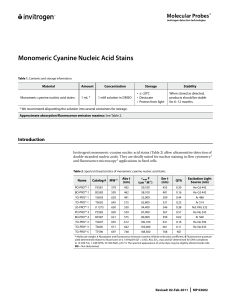
Monomeric Cyanine Nucleic Acid Stains
... in 10 mM Tris, 1 mM EDTA, 50 mM NaCl, pH 7.4. The spectral appearance of some dyes may be slightly altered inside cells. ND = Not determined. ...
... in 10 mM Tris, 1 mM EDTA, 50 mM NaCl, pH 7.4. The spectral appearance of some dyes may be slightly altered inside cells. ND = Not determined. ...
Eukaryotic Transcription In all species, transcription begins with the
... One strand of the DNA, the template strand (or noncoding strand), is used as a template for RNA synthesis. As transcription proceeds, RNA polymerase traverses the template strand and uses base pairing complementarity with the DNA template to create an RNA copy. RNA polymerase traverses the template ...
... One strand of the DNA, the template strand (or noncoding strand), is used as a template for RNA synthesis. As transcription proceeds, RNA polymerase traverses the template strand and uses base pairing complementarity with the DNA template to create an RNA copy. RNA polymerase traverses the template ...
BIOLOGY 12 MUTATIONS FRAMESHIFT MUTATIONS
... Ultraviolet light, nuclear radiation, and certain chemicals can damage DNA by altering nucleotide bases so that they look like other nucleotide bases. ...
... Ultraviolet light, nuclear radiation, and certain chemicals can damage DNA by altering nucleotide bases so that they look like other nucleotide bases. ...
Bleomycin - Clemson University
... • Treatment is discontinued in 2% of patients because of side effects • Because of allergic reactions in some lymphoma patients, a very small dose is administered (1-2 units) • Normal dose ranges from 0.25 unit per kilogram of body mass twice a week to 1 unit daily ...
... • Treatment is discontinued in 2% of patients because of side effects • Because of allergic reactions in some lymphoma patients, a very small dose is administered (1-2 units) • Normal dose ranges from 0.25 unit per kilogram of body mass twice a week to 1 unit daily ...
DNA, RNA and Protein Synthesis
... b. The figure below lists 64 mRNA codons and the corresponding amino acid they encode for in most organisms. ...
... b. The figure below lists 64 mRNA codons and the corresponding amino acid they encode for in most organisms. ...
Document
... Probably not. The sidechain of arginine is positively charged at physiological pH’s and is thus most likely to interact ionically with negatively charged molecules, such as phosphates of the RNA backbone. The backbone does not have any sequence specific information, and thus is unlikely to be used t ...
... Probably not. The sidechain of arginine is positively charged at physiological pH’s and is thus most likely to interact ionically with negatively charged molecules, such as phosphates of the RNA backbone. The backbone does not have any sequence specific information, and thus is unlikely to be used t ...
File
... protein the gene codes for) • To do this, we would need “molecular scissors” to cut the gene sequence from our original source and “molecular glue” to insert the gene sequence into the host organism’s DNA ...
... protein the gene codes for) • To do this, we would need “molecular scissors” to cut the gene sequence from our original source and “molecular glue” to insert the gene sequence into the host organism’s DNA ...
Big Picture
... •Phospholipids are the molecules that form much of the cell membrane. • Fats and Oils Fats and oils are lipids that store energy. When an organism has used up most of its carbohydrates, it can get energy from these lipids. ...
... •Phospholipids are the molecules that form much of the cell membrane. • Fats and Oils Fats and oils are lipids that store energy. When an organism has used up most of its carbohydrates, it can get energy from these lipids. ...
Carbon Compounds
... ● There are two kinds of nucleic acids: ribonucleic acid (RNA) and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). ● RNA contains the sugar ribose and DNA contains the sugar deoxyribose. ...
... ● There are two kinds of nucleic acids: ribonucleic acid (RNA) and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). ● RNA contains the sugar ribose and DNA contains the sugar deoxyribose. ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.