From RNA to protein
... Functional (transfer) - tRNA Molecules that carry amino acids to the growing polypeptide: ~ 32 different kinds of tRNA in a typical eukaryotic cell • Each is the product of a separate gene. • They are small containing ~ 80 nucleotides. • Double and single stranded regions • The unpaired regions for ...
... Functional (transfer) - tRNA Molecules that carry amino acids to the growing polypeptide: ~ 32 different kinds of tRNA in a typical eukaryotic cell • Each is the product of a separate gene. • They are small containing ~ 80 nucleotides. • Double and single stranded regions • The unpaired regions for ...
Restriction Enzymes
... sequences known as restriction sites. • Found in bacteria and have evolved to provide a defense mechanism against invading viruses. • In bacteria they selectively cut up foreign DNA in a process called restriction • To cut the DNA, restriction enzyme makes two incisions, each strand of the DNA doubl ...
... sequences known as restriction sites. • Found in bacteria and have evolved to provide a defense mechanism against invading viruses. • In bacteria they selectively cut up foreign DNA in a process called restriction • To cut the DNA, restriction enzyme makes two incisions, each strand of the DNA doubl ...
markscheme File
... Award [1 max] for any of the following which refer to the comparison of BR-R and SU-R in graph 2. BR-R performs (slightly) better when combined with SU-R; SU-R performs less well when combined with BR-R; Award [2 max] to a candidate who combines these marks into a single statement: ...
... Award [1 max] for any of the following which refer to the comparison of BR-R and SU-R in graph 2. BR-R performs (slightly) better when combined with SU-R; SU-R performs less well when combined with BR-R; Award [2 max] to a candidate who combines these marks into a single statement: ...
Biology Organic Molecules Notes
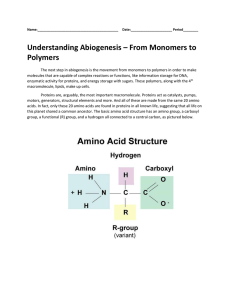
... 2.) Are long chains of amino acids Joined together by peptide bonds Dipeptide: two amino acids Polypeptide: very long chain of amino acids Proteins all have a different shape but are all globular ...
... 2.) Are long chains of amino acids Joined together by peptide bonds Dipeptide: two amino acids Polypeptide: very long chain of amino acids Proteins all have a different shape but are all globular ...
limited warranty
... minutes later, mix the diluted DNA and SuperFection™ reagent followed by 20 minutes incubation at room temperature to allow DNA complex generation. Step 3: Add the mixture of SuperFection™/DNA complex directly to the cell growth medium. Incubate at 37°C and 5% CO2 for 4 hours. Step 4: Replace the DN ...
... minutes later, mix the diluted DNA and SuperFection™ reagent followed by 20 minutes incubation at room temperature to allow DNA complex generation. Step 3: Add the mixture of SuperFection™/DNA complex directly to the cell growth medium. Incubate at 37°C and 5% CO2 for 4 hours. Step 4: Replace the DN ...
Jet-swirl nozzle design for producing nanoscale polymer
... • The enzyme RNA polymerase reads a specific nucleotide sequence • (gene) from the DNA template while proteins called transcription factors facilitate the copying • Copies are made in the form of Ribonucleic acid (RNA) • RNA resembles DNA except: – -base thymine [T] and adenine [A] are replace with ...
... • The enzyme RNA polymerase reads a specific nucleotide sequence • (gene) from the DNA template while proteins called transcription factors facilitate the copying • Copies are made in the form of Ribonucleic acid (RNA) • RNA resembles DNA except: – -base thymine [T] and adenine [A] are replace with ...
Quantification of nucleic acids
... in 100 ml TEN buffer (10 mM Tris, 1 mM sodium ethylene diamine ...
... in 100 ml TEN buffer (10 mM Tris, 1 mM sodium ethylene diamine ...
Modification of Amino Acids
... Mutation: Levels of Hereditary Change Gene (Point) Mutation: One allele changes to a different allele. Effects are limited to that locus. ...
... Mutation: Levels of Hereditary Change Gene (Point) Mutation: One allele changes to a different allele. Effects are limited to that locus. ...
Oligonucleotide 5` End Labeling with Radiochemicals
... The techniques for end labeling oligonucleotides with radioisotopes have driven nucleic acid probe technology. Oligonucleotide probes can be custom made based on sequence information of the target DNA or RNA in several hours on a DNA synthesizer. Use of a DNA synthesizer eliminates the usual cumbers ...
... The techniques for end labeling oligonucleotides with radioisotopes have driven nucleic acid probe technology. Oligonucleotide probes can be custom made based on sequence information of the target DNA or RNA in several hours on a DNA synthesizer. Use of a DNA synthesizer eliminates the usual cumbers ...
Mutation - NIU Department of Biological Sciences
... Mutations can be classified according to their effects on the protein (or mRNA) produced by the gene that is mutated. 1. Silent mutations (synonymous mutations). Since the genetic code is degenerate, several codons produce the same amino acid. Especially, third base changes often have no effect on t ...
... Mutations can be classified according to their effects on the protein (or mRNA) produced by the gene that is mutated. 1. Silent mutations (synonymous mutations). Since the genetic code is degenerate, several codons produce the same amino acid. Especially, third base changes often have no effect on t ...
Radioisotopes in biology
... Protein-ligand interactions -interactions are influenced by physical parameters such as pH, temperature and ionic concentration. -It is important to allow the system to reach equilibrium The dissociation constant Kd for a particular interaction can be determined experimentally, through e.g. a scatch ...
... Protein-ligand interactions -interactions are influenced by physical parameters such as pH, temperature and ionic concentration. -It is important to allow the system to reach equilibrium The dissociation constant Kd for a particular interaction can be determined experimentally, through e.g. a scatch ...
D._Eating_before_an_Event - Wapakoneta High School Wrestling
... rettub tunaep ,egasuas ,eseehc ,sgod toh ,sregrubmaH ٭ peeD ٭-fried or fried foods like doughnuts, french fries, hash browns, and chips ,eseehc maerc ,gnisserd dalas raluger ,esiannoyam ekil stnemidnoC ٭ margarine or butter 4. A liquid meal can be taken up to one hour before an event. For exam ...
... rettub tunaep ,egasuas ,eseehc ,sgod toh ,sregrubmaH ٭ peeD ٭-fried or fried foods like doughnuts, french fries, hash browns, and chips ,eseehc maerc ,gnisserd dalas raluger ,esiannoyam ekil stnemidnoC ٭ margarine or butter 4. A liquid meal can be taken up to one hour before an event. For exam ...
Class: AP Bio Unit: Genetics Estimated Date Target Reading
... 11/04/11 Describe how environmental conditions can effect gene expression and how there is a range of gene expression. Differentiate between autosomal inheritance and sexlinked inheritance. ...
... 11/04/11 Describe how environmental conditions can effect gene expression and how there is a range of gene expression. Differentiate between autosomal inheritance and sexlinked inheritance. ...
problem set
... expression of the gene (Fig. 5.31). One common method by which expressed proteins are purified is via the attachment of an amino acid sequence such as a polyhistidine sequence (Histag) that serves as a tag for affinity purification. Mammalian cell expression systems offer the advantage that posttran ...
... expression of the gene (Fig. 5.31). One common method by which expressed proteins are purified is via the attachment of an amino acid sequence such as a polyhistidine sequence (Histag) that serves as a tag for affinity purification. Mammalian cell expression systems offer the advantage that posttran ...
File - Mr. Lambdin`s Biology
... • Caused by a “fresh” mutation or has occurred only by chance in the child and does not occur in either of the parents. ...
... • Caused by a “fresh” mutation or has occurred only by chance in the child and does not occur in either of the parents. ...
Fall 2009
... 4. Define the term homeostasis? What process is used for it to be maintained? What are some examples of how we maintain homeostasis? 5. What is the relationship between adaptation and natural selection? 6. Identify the different elements of scientific inquiry and differentiate between dependent vari ...
... 4. Define the term homeostasis? What process is used for it to be maintained? What are some examples of how we maintain homeostasis? 5. What is the relationship between adaptation and natural selection? 6. Identify the different elements of scientific inquiry and differentiate between dependent vari ...
Unit E - Images
... – The validity of a signature on a will, – If a corporation is complying with environmental laws, – The origin of physical evidence at a crime scene ...
... – The validity of a signature on a will, – If a corporation is complying with environmental laws, – The origin of physical evidence at a crime scene ...
File
... Protein synthesis – genes…contain all the information needed to duplicate cells (i.e., “blueprints”). Genes specify sequence of amino acids in proteins Gene expression–important for determining phenotypes of organism 3. ATP—how cells store energy for their use …ATP is the energy carrier of cells ...
... Protein synthesis – genes…contain all the information needed to duplicate cells (i.e., “blueprints”). Genes specify sequence of amino acids in proteins Gene expression–important for determining phenotypes of organism 3. ATP—how cells store energy for their use …ATP is the energy carrier of cells ...
No Slide Title
... 21. An ultracentrifuge consists of a rotor that spins tubes containing materials and is: (A) a component on a new type of microscope to allow cell components to be easily visualized (B) the laboratory tool developed by Robert Hooke in the 1660s that he used to discover cells (C) a tool used by cell ...
... 21. An ultracentrifuge consists of a rotor that spins tubes containing materials and is: (A) a component on a new type of microscope to allow cell components to be easily visualized (B) the laboratory tool developed by Robert Hooke in the 1660s that he used to discover cells (C) a tool used by cell ...
PreAP Lesson Plan 8/25-8/29
... 8/27- 9A(R): SWBAT compare the 8/28 structure and functions of different types of biomolecules including carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. ...
... 8/27- 9A(R): SWBAT compare the 8/28 structure and functions of different types of biomolecules including carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.