Trikenol plus
... microorganism, because it can degrade sebum triglycerides. This leads to an increase in the amount of free fatty acids existing in the scalp, especially oleic acid, which has a strong irritating ability that can cause the stimulation of mitosis in cells of the basal layer. ...
... microorganism, because it can degrade sebum triglycerides. This leads to an increase in the amount of free fatty acids existing in the scalp, especially oleic acid, which has a strong irritating ability that can cause the stimulation of mitosis in cells of the basal layer. ...
p53 regulation and function in normal cells and tumors
... damaged sites in DNA and is postulated to have a role in DNA repair or apoptosis. Mutations of p53 have been found in more than 50% of human cancers1. However, loss of p53 function has been estimated to occur in almost 80% of human cancers, due not only to mutation but also to defects in activating ...
... damaged sites in DNA and is postulated to have a role in DNA repair or apoptosis. Mutations of p53 have been found in more than 50% of human cancers1. However, loss of p53 function has been estimated to occur in almost 80% of human cancers, due not only to mutation but also to defects in activating ...
LESSON 4 Understanding Genetic Tests to Detect BRCA1
... be used to compare the sequences of two or more proteins or nucleic acid molecules, or to compare a single sequence to a collection of sequences in a database. Additional information about BLAST can be found in the Appendix. 20. Specifically, students will be performing a Nucleotide BLAST, comparing ...
... be used to compare the sequences of two or more proteins or nucleic acid molecules, or to compare a single sequence to a collection of sequences in a database. Additional information about BLAST can be found in the Appendix. 20. Specifically, students will be performing a Nucleotide BLAST, comparing ...
... 26. (12 pts) Please do one of the following two choices: Choice A: You haven’t eaten in a while but your liver has been actively metabolizing, consuming ATP. You then have a large influx of glucose due to eating lunch. i) What will happen to glycogen levels in the liver cell? Describe the regulatory ...
Initiation of transcription by Pol II Separate basal and activated
... 3.Zinc-finger nucleases 4.Transcription activator-like effector nucleases (TALENs) 5.Triple-helix–forming oligonucleotides conjugated to restriction endonucleases 6.CRE/LOX system ...
... 3.Zinc-finger nucleases 4.Transcription activator-like effector nucleases (TALENs) 5.Triple-helix–forming oligonucleotides conjugated to restriction endonucleases 6.CRE/LOX system ...
Chem*3560 Lecture 23: Phospholipid Biosynthesis
... Phospholipids are major components of membrane bilayers, so are structural components of the cell, whereas triacylglycerols are stored as the bodies main energy reserve. Phosphatidic acid itself tends to disrupt bilayer structure, and must be modified by adding a polar headgroup. The head group is a ...
... Phospholipids are major components of membrane bilayers, so are structural components of the cell, whereas triacylglycerols are stored as the bodies main energy reserve. Phosphatidic acid itself tends to disrupt bilayer structure, and must be modified by adding a polar headgroup. The head group is a ...
Improved production of poly-γ-glutamate by newly Bacillus subtilis
... The D-glutamate content was over 50% in every γ-PGA produced under the conditions used, suggesting that the bacterium possesses a synthetic pathway to produce D-glutamate, the main precursor of γ-PGA, from L-glutamate.To obtain a clue as to the nature of the D-glutamate synthetic pathway in B. subti ...
... The D-glutamate content was over 50% in every γ-PGA produced under the conditions used, suggesting that the bacterium possesses a synthetic pathway to produce D-glutamate, the main precursor of γ-PGA, from L-glutamate.To obtain a clue as to the nature of the D-glutamate synthetic pathway in B. subti ...
the association of chloroplast dna with photosynthetic membrane
... and stroma membrane areas, circular vesicles with a peripheral grana area were scored as indicated in the Materials and methods section. The grana membrane area is enriched in grana, but is not uniformly covered with grana (Figs. 6, 7, 11, 15). The stroma membrane areas are enriched in stroma membra ...
... and stroma membrane areas, circular vesicles with a peripheral grana area were scored as indicated in the Materials and methods section. The grana membrane area is enriched in grana, but is not uniformly covered with grana (Figs. 6, 7, 11, 15). The stroma membrane areas are enriched in stroma membra ...
Genetics - Michael
... crops and domesticated animals. In many early cultures, including those that were the precursors of some of today’s countries, the priests and royal families kept detailed records of lineages and bloodlines in order to establish a hierarchy of power. In the process, they also discovered that some tr ...
... crops and domesticated animals. In many early cultures, including those that were the precursors of some of today’s countries, the priests and royal families kept detailed records of lineages and bloodlines in order to establish a hierarchy of power. In the process, they also discovered that some tr ...
CHAPTER 6
... • The process of b-oxidation begins with the formation of a thiol ester bond between the FA and the thiol group of CoA • Acyl-CoA synthetase condenses fatty acids with CoA, with simultaneous hydrolysis of ATP to AMP and PPi (acyl-CoA ligase or fatty acid thiokinase) ...
... • The process of b-oxidation begins with the formation of a thiol ester bond between the FA and the thiol group of CoA • Acyl-CoA synthetase condenses fatty acids with CoA, with simultaneous hydrolysis of ATP to AMP and PPi (acyl-CoA ligase or fatty acid thiokinase) ...
The Large Loop Repair and Mismatch Repair Pathways
... mitotic growth. NER functions to repair bulky DNA lesions, such as thymine dimers and other helix-distorting lesions. During NER the damaged nucleotide is recognized and bound by several NER proteins, and the DNA surrounding the lesion is unwound. The single-stranded DNA containing the lesion is rem ...
... mitotic growth. NER functions to repair bulky DNA lesions, such as thymine dimers and other helix-distorting lesions. During NER the damaged nucleotide is recognized and bound by several NER proteins, and the DNA surrounding the lesion is unwound. The single-stranded DNA containing the lesion is rem ...
402_06_watersoluble2..
... In pernicious anemia, give 100 g IM q 4 weeks; Studies indicate that 1 mg/day P.O. will work also. A sublingual 1mg “dot” product may be better. A 1mg nasal solution 0.5mg/0.1ml) is marketed and is convenient. High IM doses are used for methylmalonic acidurea, an inborn error of metabolism. Increas ...
... In pernicious anemia, give 100 g IM q 4 weeks; Studies indicate that 1 mg/day P.O. will work also. A sublingual 1mg “dot” product may be better. A 1mg nasal solution 0.5mg/0.1ml) is marketed and is convenient. High IM doses are used for methylmalonic acidurea, an inborn error of metabolism. Increas ...
Capillary electrophoresis tandem mass spectrometry of bromine
... (NYITR-NH2 ) was allowed to react with DBEP. Brominecontaining ions (291/293 m/z) appeared again in the MS/MS spectrum together with a 70 m/z ion (immonium ion of N) and a series of *b ions (832, 676, 576, 463 m/z corresponding to labeled NYITR, NYIT, NYI, NY sequences) along with a series of *a ion ...
... (NYITR-NH2 ) was allowed to react with DBEP. Brominecontaining ions (291/293 m/z) appeared again in the MS/MS spectrum together with a 70 m/z ion (immonium ion of N) and a series of *b ions (832, 676, 576, 463 m/z corresponding to labeled NYITR, NYIT, NYI, NY sequences) along with a series of *a ion ...
Chpt8_RecombineDNA.doc
... The previous chapter on mutation and repair of DNA dealt mainly with small changes in DNA sequence, usually single base pairs, resulting from errors in replication or damage to DNA. The DNA sequence of a chromosome can change in large segments as well, by the processes of recombination and transposi ...
... The previous chapter on mutation and repair of DNA dealt mainly with small changes in DNA sequence, usually single base pairs, resulting from errors in replication or damage to DNA. The DNA sequence of a chromosome can change in large segments as well, by the processes of recombination and transposi ...
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System, 3e
... and polarity without hydrogen bonds. Hydrogen bonds hold the double helix of DNA together and contribute to the overall shape of protein molecules. However, unlike covalent bonds, hydrogen bonds are not permanent bonds, so they can easily and temporarily be broken, a characteristic that is important ...
... and polarity without hydrogen bonds. Hydrogen bonds hold the double helix of DNA together and contribute to the overall shape of protein molecules. However, unlike covalent bonds, hydrogen bonds are not permanent bonds, so they can easily and temporarily be broken, a characteristic that is important ...
model for Escherichia coli chromosome packaging supports
... Figure 2. (A) Graphical illustration of the transcriptional regulatory network describing the regulatory interplay between the TFs and their target genes as applied in our polymer model. Black nodes represent TF genes, dark gray nodes represent the target genes and links represent regulatory interac ...
... Figure 2. (A) Graphical illustration of the transcriptional regulatory network describing the regulatory interplay between the TFs and their target genes as applied in our polymer model. Black nodes represent TF genes, dark gray nodes represent the target genes and links represent regulatory interac ...
Protein structure
... During the translation of a gene into a protein, the protein is formed by the sequential joining of amino acids end-to-end to form a long chain-like molecule (polymer). A polymer of amino acids is often referred to as a polypeptide. The genome is capable of coding for 20 different amino acids whose ...
... During the translation of a gene into a protein, the protein is formed by the sequential joining of amino acids end-to-end to form a long chain-like molecule (polymer). A polymer of amino acids is often referred to as a polypeptide. The genome is capable of coding for 20 different amino acids whose ...
Four Amino Acids Are Converted to Succinyl
... produced from isoleucine, valine, & methionine. • All essential. • Propionyl-CoA, an intermediate on these pathways, is also a product of β-oxidation of fatty acids with an odd number of C atoms. • Methionin could be metabolised to cystein ...
... produced from isoleucine, valine, & methionine. • All essential. • Propionyl-CoA, an intermediate on these pathways, is also a product of β-oxidation of fatty acids with an odd number of C atoms. • Methionin could be metabolised to cystein ...
REAL-TIME PCR
... fluorescein (from the donor probe) is directly transferred to the acceptor dye by FRET. The acceptor fluorophore emits light at a different wavelength. Subsequently the fluorescent signal can be detected and measured. This happens during the annealing phase and first part of the extension phase of t ...
... fluorescein (from the donor probe) is directly transferred to the acceptor dye by FRET. The acceptor fluorophore emits light at a different wavelength. Subsequently the fluorescent signal can be detected and measured. This happens during the annealing phase and first part of the extension phase of t ...
Lipids (lec 1, 2, 3)..
... Formed only from fatty acid and alcohol. The most common type is neutral fat. Neutral fats: the most important and most abundant group of fats in nature. They may be fats or oils which have the same chemical structure and same chemical properties, but differ in the state at room temperature, fats ar ...
... Formed only from fatty acid and alcohol. The most common type is neutral fat. Neutral fats: the most important and most abundant group of fats in nature. They may be fats or oils which have the same chemical structure and same chemical properties, but differ in the state at room temperature, fats ar ...
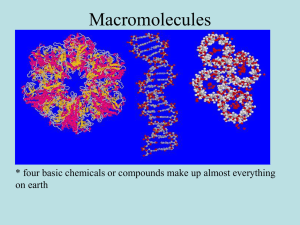
Macromolecules - Saint Paul Public Schools
... QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. ...
... QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. ...
Title: Rescuing discarded spectra: Full - e
... Mutations in both RNA and peptides were analyzed through an in-house script (publicly available at https://switchlab.svn.cloudforge.com/sequencing). All the protein variants identified by SPIDER and the RNA variants found by SAMTools were compared to the reference genome, as well as to a database wi ...
... Mutations in both RNA and peptides were analyzed through an in-house script (publicly available at https://switchlab.svn.cloudforge.com/sequencing). All the protein variants identified by SPIDER and the RNA variants found by SAMTools were compared to the reference genome, as well as to a database wi ...
ribosome binding site Prokaryotic mRNAs have a ribosome binding
... • Large subunit contains peptidyl transferase center (for formation of peptide bond) ...
... • Large subunit contains peptidyl transferase center (for formation of peptide bond) ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.