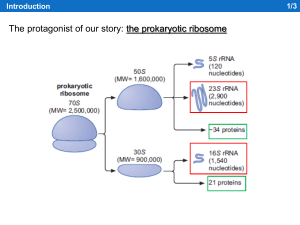
Ribosomal frameshifting in decoding antizyme mRNAs from yeast
... effector of an autoregulatory circuit which is conserved in animals, fungi and protists. Stimulatory signals encoded 50 and 30 of the shift site act to program the frameshifting. Despite overall conservation, many individual branches have evolved specific features surrounding the frameshift site. Am ...
... effector of an autoregulatory circuit which is conserved in animals, fungi and protists. Stimulatory signals encoded 50 and 30 of the shift site act to program the frameshifting. Despite overall conservation, many individual branches have evolved specific features surrounding the frameshift site. Am ...
Microbial Cause of Calcium Lactate Defect in Cheddar Cheese
... formation in Cheddar cheese. Institute of Food Technologists. Chou, Y. E. E., C.G.; Luedecke, L.O.; Bates, M.P.; Clark, S. 2003. Nonstarter lactic acid bacteria and aging temperature affect calcium lactate crystallization in cheddar cheese. Journal of Dairy Science. 86:2516-2524. Coyne, V. E., M. D. ...
... formation in Cheddar cheese. Institute of Food Technologists. Chou, Y. E. E., C.G.; Luedecke, L.O.; Bates, M.P.; Clark, S. 2003. Nonstarter lactic acid bacteria and aging temperature affect calcium lactate crystallization in cheddar cheese. Journal of Dairy Science. 86:2516-2524. Coyne, V. E., M. D. ...
Similarities: Differences Differences
... • 2 important genera are Sulfolobus and Thermoproteus •Can be chemoheterotrophic or chemoautotrophic ...
... • 2 important genera are Sulfolobus and Thermoproteus •Can be chemoheterotrophic or chemoautotrophic ...
Answers to Problems in Text - pdf
... 1.91 Converting 30°C from the Celsius to Fahrenheit temperature scales gives 86°F. You are most likely to be wearing a T-shirt and shorts. 1.93 Cells that have been exposed to several cycles of freezing and thawing will have expanded quite a bit. The expansion process tends to break open the cells t ...
... 1.91 Converting 30°C from the Celsius to Fahrenheit temperature scales gives 86°F. You are most likely to be wearing a T-shirt and shorts. 1.93 Cells that have been exposed to several cycles of freezing and thawing will have expanded quite a bit. The expansion process tends to break open the cells t ...
RiboT
... RiboT with mutations in the PTC A-site (normally lethal!) - were functional in cellular protein synthesis - gained the ability to bypass translation arrest caused by the SecM sequence ...
... RiboT with mutations in the PTC A-site (normally lethal!) - were functional in cellular protein synthesis - gained the ability to bypass translation arrest caused by the SecM sequence ...
A Rapid Chromosome Mapping Method for Cloned Fragments of Yeast DNA.
... containing virtually any yeast gene in which mutants can be found [see BOTSTEIN and DAVIS (1982) for review]. Recombinant DNA methods have, in addition, allowed the identification of interesting DNA segments corresponding to no mapped yeast gene. T h e classical mapping methods referred to can be ap ...
... containing virtually any yeast gene in which mutants can be found [see BOTSTEIN and DAVIS (1982) for review]. Recombinant DNA methods have, in addition, allowed the identification of interesting DNA segments corresponding to no mapped yeast gene. T h e classical mapping methods referred to can be ap ...
D-lactic acidosis: Turning sugar into acids in the gastrointestinal tract
... because organic acids accumulated within the GI tract, one can renal failure, the degree of organic acid accumulation could be infer that bacterial overgrowth may still be a potential hazard; a much greater for a given rate of production in the GI tract. To analyze the acid-base consequences from a ...
... because organic acids accumulated within the GI tract, one can renal failure, the degree of organic acid accumulation could be infer that bacterial overgrowth may still be a potential hazard; a much greater for a given rate of production in the GI tract. To analyze the acid-base consequences from a ...
CHAPTER 15
... C11. Answer: An anticodon that was 3–UUG–5 would recognize the two codons. To recognize 5–AAA–3, it would have to be modified to 3–UUI–5. C12. Answer: All tRNA molecules have some basic features in common. They all have a cloverleaf structure with three stem-loop structures. The second stem-lo ...
... C11. Answer: An anticodon that was 3–UUG–5 would recognize the two codons. To recognize 5–AAA–3, it would have to be modified to 3–UUI–5. C12. Answer: All tRNA molecules have some basic features in common. They all have a cloverleaf structure with three stem-loop structures. The second stem-lo ...
Biosc_48_Chapter_5_lecture
... 3. If more amino acids are consumed than are needed, the excess amino acids can be used for energy or converted into carbohydrates or fat. 4. Our bodies can make 12 of the 20 amino acids from other molecules. Eight of them (9 in children) must come from the diet and are called essential amino acids. ...
... 3. If more amino acids are consumed than are needed, the excess amino acids can be used for energy or converted into carbohydrates or fat. 4. Our bodies can make 12 of the 20 amino acids from other molecules. Eight of them (9 in children) must come from the diet and are called essential amino acids. ...
Ribosome Profiling
... the information about gene expression, which is studied by the commonly used techniques such as Microarray and RNA sequencing, RP can give information about ribosome speed along a coding sequence. The technique has helped scientists to identify many non-canonical translational initiation sites, paus ...
... the information about gene expression, which is studied by the commonly used techniques such as Microarray and RNA sequencing, RP can give information about ribosome speed along a coding sequence. The technique has helped scientists to identify many non-canonical translational initiation sites, paus ...
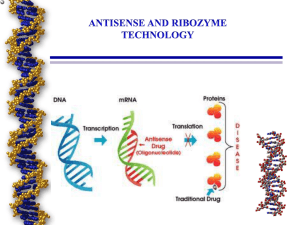
Antisense Transcript and RNA Processing
... was required for viability but could not produce stable atpB transcripts. Based on strand-specific RT-PCR, S1 nuclease protection, and RNA gel blots, evidence was obtained that the PSþ genome stabilizes atpB mRNA by generating an atpB antisense transcript, which attenuates the degradation of the pol ...
... was required for viability but could not produce stable atpB transcripts. Based on strand-specific RT-PCR, S1 nuclease protection, and RNA gel blots, evidence was obtained that the PSþ genome stabilizes atpB mRNA by generating an atpB antisense transcript, which attenuates the degradation of the pol ...
PowerPoint Presentation Materials to accompany
... Three stem-loop structures; Variable region An acceptor stem and 3’ single strand region ...
... Three stem-loop structures; Variable region An acceptor stem and 3’ single strand region ...
Lecture 25 Cofactors and Coenzymes
... two groups- organic cofactors and inorganic cofactors. Coenzymes are organic cofactors which are again divided into two groups- cosubstrates and prosthetic groups. Cofactors which bound loosely to an enzyme are termed as coenzymes and cofactors which bound tightly to an enzyme are termed as prosthet ...
... two groups- organic cofactors and inorganic cofactors. Coenzymes are organic cofactors which are again divided into two groups- cosubstrates and prosthetic groups. Cofactors which bound loosely to an enzyme are termed as coenzymes and cofactors which bound tightly to an enzyme are termed as prosthet ...
VITAMINS-5
... avocado, and sweet potatoes are also good sources • When found in foods, most pantothenic acid is in the form of CoA or acyl carrier protein (ACP) 1. CoA and ACP are hydrolyzed into 4'phosphopantetheine 2. The 4'-phospho-pantetheine is then dephosphorylated into pantetheine 3. Pantetheine hydrolysed ...
... avocado, and sweet potatoes are also good sources • When found in foods, most pantothenic acid is in the form of CoA or acyl carrier protein (ACP) 1. CoA and ACP are hydrolyzed into 4'phosphopantetheine 2. The 4'-phospho-pantetheine is then dephosphorylated into pantetheine 3. Pantetheine hydrolysed ...
Chapter 11 Vitamins and proteins
... regular basis as part of a healthy diet. Thirteen vitamins are required but they generally cannot be synthesised by humans, except for vitamin D. If, however, vitamins are present in excess or are deficient, diseases such as beriberi, scurvy, anaemia, rickets and skin disorders may occur. Some vitam ...
... regular basis as part of a healthy diet. Thirteen vitamins are required but they generally cannot be synthesised by humans, except for vitamin D. If, however, vitamins are present in excess or are deficient, diseases such as beriberi, scurvy, anaemia, rickets and skin disorders may occur. Some vitam ...
Application to Modify an Approved Exempt or Notifiable Low Risk
... dealing with GMOs and then sign the application form. I have read, considered and understand my responsibilities under the Gene Technology Act 2000 and agree to undertake the GMO dealing outlined in this application in accordance with the relevant Office of the Gene Technology Regulator guidelines a ...
... dealing with GMOs and then sign the application form. I have read, considered and understand my responsibilities under the Gene Technology Act 2000 and agree to undertake the GMO dealing outlined in this application in accordance with the relevant Office of the Gene Technology Regulator guidelines a ...
File Ref.No.7054/GA - IV - J1/2013/CU UNIVERSITY OF CALICUT
... Coenzymes and cofactors:Definition: examples of a) metal ions b) coenzymes c) prosthetic group.. Coenzymes and their functions - NAD, NADP+,FAD, FMN, lipoic acid, TPP, pyridoxal phosphate and biotin.( structure and one reaction each) ...
... Coenzymes and cofactors:Definition: examples of a) metal ions b) coenzymes c) prosthetic group.. Coenzymes and their functions - NAD, NADP+,FAD, FMN, lipoic acid, TPP, pyridoxal phosphate and biotin.( structure and one reaction each) ...
Lecture 2: Evolution and Genetic Algorithms
... In Genetic Algorithm (GA) terminology, the genotype is the full set of genes that any individual in the population has. The phenotype is the individual potential solution to the problem, that the genotype 'encodes'. So if you are evolving with a GA the control structure, the 'nervous system' of a ro ...
... In Genetic Algorithm (GA) terminology, the genotype is the full set of genes that any individual in the population has. The phenotype is the individual potential solution to the problem, that the genotype 'encodes'. So if you are evolving with a GA the control structure, the 'nervous system' of a ro ...
Bacterial disease resistance of transgenic hybrid poplar expressing
... studied in detail. Many antimicrobial genes have been isolated and attempts are being made to engineer pathogen resistance in plants by introducing these genes. Antimicrobial peptides have been isolated from several plant and animal species and characterized (Rao 1995, Broekaert et al. 1997, Hancock ...
... studied in detail. Many antimicrobial genes have been isolated and attempts are being made to engineer pathogen resistance in plants by introducing these genes. Antimicrobial peptides have been isolated from several plant and animal species and characterized (Rao 1995, Broekaert et al. 1997, Hancock ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.