Abstract Dissertation Makhalova
... side effect of chemotherapy with DNA reactive drugs such as cisplatin. The underlying mechanisms, however, are still not clear. Platinum compounds are known to exert their antineoplastic activity by forming distinct Pt-DNA adducts. Both the DNA repair rates and the extent of tolerance to persisting ...
... side effect of chemotherapy with DNA reactive drugs such as cisplatin. The underlying mechanisms, however, are still not clear. Platinum compounds are known to exert their antineoplastic activity by forming distinct Pt-DNA adducts. Both the DNA repair rates and the extent of tolerance to persisting ...
THINK ABOUT IT
... The Molecular Basis of Heredity One of the most interesting discoveries of molecular biology is the nearuniversal nature of the genetic code. Although some organisms show slight variations in the amino acids assigned to particular codons, the code is always read three bases at a time and in the same ...
... The Molecular Basis of Heredity One of the most interesting discoveries of molecular biology is the nearuniversal nature of the genetic code. Although some organisms show slight variations in the amino acids assigned to particular codons, the code is always read three bases at a time and in the same ...
The Genetic Code
... molecule, and that the sequence of bases in DNA is a kind of code in which different combinations of bases could specify the 20 amino acids. • A particular stretch of DNA (a gene) contains the information to specify the amino acid sequence of one protein. • The information encoded in the base sequen ...
... molecule, and that the sequence of bases in DNA is a kind of code in which different combinations of bases could specify the 20 amino acids. • A particular stretch of DNA (a gene) contains the information to specify the amino acid sequence of one protein. • The information encoded in the base sequen ...
The Genetic Code
... molecule, and that the sequence of bases in DNA is a kind of code in which different combinations of bases could specify the 20 amino acids. • A particular stretch of DNA (a gene) contains the information to specify the amino acid sequence of one protein. • The information encoded in the base sequen ...
... molecule, and that the sequence of bases in DNA is a kind of code in which different combinations of bases could specify the 20 amino acids. • A particular stretch of DNA (a gene) contains the information to specify the amino acid sequence of one protein. • The information encoded in the base sequen ...
幻灯片 1 - TUST
... b). Functional genomics is concerned with the way in which the genome functions. That is, it examines the transcripts produced by the genome and the array of proteins they encode. c). Comparative genomics is third area of study, in which genomes from different organisms are compared to look for sign ...
... b). Functional genomics is concerned with the way in which the genome functions. That is, it examines the transcripts produced by the genome and the array of proteins they encode. c). Comparative genomics is third area of study, in which genomes from different organisms are compared to look for sign ...
4 – 2 Chemical Compounds in Living Things
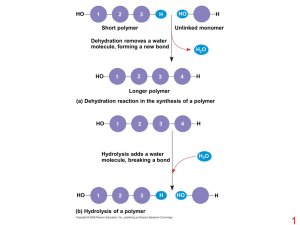
... Forms 4 very strong and stable covalent bonds Commonly bonds w/ O, N, P, S (& itself) Forms chains of almost unlimited length by bonding w/ other carbon atoms. Bonds btwn C can be single, double, or triple Long chains can close to form rings (see Figure 3-1) o Polymerization Process wher ...
... Forms 4 very strong and stable covalent bonds Commonly bonds w/ O, N, P, S (& itself) Forms chains of almost unlimited length by bonding w/ other carbon atoms. Bonds btwn C can be single, double, or triple Long chains can close to form rings (see Figure 3-1) o Polymerization Process wher ...
Viruses and Bacteria
... from differential gene expression, the expression of different genes by cells within the same genome In each type of differentiated cell, a unique subset of genes is expressed Many key stages of gene expression can be regulated in eukaryotic cells ...
... from differential gene expression, the expression of different genes by cells within the same genome In each type of differentiated cell, a unique subset of genes is expressed Many key stages of gene expression can be regulated in eukaryotic cells ...
Polypeptide Synthesis -Making Proteins
... RNA is built complimentary to the DNA in the 5’ to 3’ direction A U, ...
... RNA is built complimentary to the DNA in the 5’ to 3’ direction A U, ...
The protein that assesses distances
... Trieste, and Kuni Iwasa, from the US National Institutes of Health (NIH), have answered this question by means of a theoretical study. Both Florescu and Iwasa were at the Max Planck Institute for Physics of Complex Systems in Dresden when they started their work for this research. “It is indeed a ...
... Trieste, and Kuni Iwasa, from the US National Institutes of Health (NIH), have answered this question by means of a theoretical study. Both Florescu and Iwasa were at the Max Planck Institute for Physics of Complex Systems in Dresden when they started their work for this research. “It is indeed a ...
Guidelines and Assignments
... 1. (MT1) A. How is the 5-mC distributed within the human genome? B. Do all human genes have CpG island at their promoters? C. How bisulfite treatment may affect the CpG methylation status? D. What methods can be used to detect the methylation status of DNA? Please describe at least four different me ...
... 1. (MT1) A. How is the 5-mC distributed within the human genome? B. Do all human genes have CpG island at their promoters? C. How bisulfite treatment may affect the CpG methylation status? D. What methods can be used to detect the methylation status of DNA? Please describe at least four different me ...
Document
... “The linear sequence of nucleotides in a gene determines the linear sequence of amino acids in a protein.” Mutant alleles of trpA gene differed in the position of the mutation at the DNA level, which corresponded to position of amino acid substitution in the gene product. Colinearity of mutations an ...
... “The linear sequence of nucleotides in a gene determines the linear sequence of amino acids in a protein.” Mutant alleles of trpA gene differed in the position of the mutation at the DNA level, which corresponded to position of amino acid substitution in the gene product. Colinearity of mutations an ...
DNA and the Genome
... This is followed by elongation, in which free RNA nucleotides enter the transcription bubble and align with the complementary base pairs on the DNA moving from 3’ to 5’. The RNA nucleotides are held in place by hydrogen bonding while strong covalent bonds form between the phosphate of one nucleotide ...
... This is followed by elongation, in which free RNA nucleotides enter the transcription bubble and align with the complementary base pairs on the DNA moving from 3’ to 5’. The RNA nucleotides are held in place by hydrogen bonding while strong covalent bonds form between the phosphate of one nucleotide ...
The Genetic Material
... same overall genetic content. – One member of each homologous pair of chromosomes is inherited from each parent. ...
... same overall genetic content. – One member of each homologous pair of chromosomes is inherited from each parent. ...
The Genetic Code and Translation
... – There are 64 different codons, but only 20 amino acids. (So, there may be more than one codon for an amino acid.) – AUG codes for methionine (the “start” codon) • Signals the beginning of protein production ...
... – There are 64 different codons, but only 20 amino acids. (So, there may be more than one codon for an amino acid.) – AUG codes for methionine (the “start” codon) • Signals the beginning of protein production ...
L22 RNA, QC
... themselves. In both prokaryotes and eukaryotes the two main types of non-coding RNA are: Ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs), which are the most abundant RNAs in the cell, making up over 80% of the total in actively dividing bacteria. These molecules are components of ribosomes, the structures on which protein s ...
... themselves. In both prokaryotes and eukaryotes the two main types of non-coding RNA are: Ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs), which are the most abundant RNAs in the cell, making up over 80% of the total in actively dividing bacteria. These molecules are components of ribosomes, the structures on which protein s ...
Brooker Chapter 9
... • Prepared cell extracts from type IIIS cells and added to type IIR cells for transformation in culture medium • Only the DNA enriched extract was able to convert type IIR into type IIIS ...
... • Prepared cell extracts from type IIIS cells and added to type IIR cells for transformation in culture medium • Only the DNA enriched extract was able to convert type IIR into type IIIS ...
Biophysics : Aspects of Amino Acids Sequence in Proteins and
... genetic codes are triplets i.e. one coding includes substrate without changing themselves. three nucleotides out of four. There are twenty amino acids responsible for formation of protein chains. The reaction rate constant is given by the formula: Among many combinations of genetic codes first half ...
... genetic codes are triplets i.e. one coding includes substrate without changing themselves. three nucleotides out of four. There are twenty amino acids responsible for formation of protein chains. The reaction rate constant is given by the formula: Among many combinations of genetic codes first half ...
UNIT 2 BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY ORGANIC MOLECULES
... -(Hair, fingernails are made of fibrous protein: collagen)Collagen is the most abundant protein by mass in animals. -Hemoglobin is an oxygen carrying protein - The most numerous class of proteins are the enzymes. ( end in –ase) Enzymes: speed up chemical reactions Monomer of Proteins: Amino acid : 2 ...
... -(Hair, fingernails are made of fibrous protein: collagen)Collagen is the most abundant protein by mass in animals. -Hemoglobin is an oxygen carrying protein - The most numerous class of proteins are the enzymes. ( end in –ase) Enzymes: speed up chemical reactions Monomer of Proteins: Amino acid : 2 ...
Blank notes - local.brookings.k12.sd.us
... Combine with proteins to form ribosomes Bacterial ribosomes different size than eukaryotic ribosomes ...
... Combine with proteins to form ribosomes Bacterial ribosomes different size than eukaryotic ribosomes ...
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY EXAM II
... Describe physical and genetic mapping, discussing the following; What is the basis for each type? What types of techniques are used in each type of mapping? (list several) What type of data is obtained? Why are both techniques necessary? (how do they complement each other?) ...
... Describe physical and genetic mapping, discussing the following; What is the basis for each type? What types of techniques are used in each type of mapping? (list several) What type of data is obtained? Why are both techniques necessary? (how do they complement each other?) ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.