
Nerve activates contraction - Jackson County School District
... • Silences (same as above, just turn gene off) • Methylation of DNA • mRNA processing before it leaves the nucleus • Gene regulation in Bacteria: • The Operon- A group, or cluster, of genes (that make work together) or a segment of DNA that functions as a single transcription unit. It is comprised o ...
... • Silences (same as above, just turn gene off) • Methylation of DNA • mRNA processing before it leaves the nucleus • Gene regulation in Bacteria: • The Operon- A group, or cluster, of genes (that make work together) or a segment of DNA that functions as a single transcription unit. It is comprised o ...
PCR-technique Applications
... by E. Börje Lindström This learning object has been funded by the European Commissions FP6 BioMinE project ...
... by E. Börje Lindström This learning object has been funded by the European Commissions FP6 BioMinE project ...
CHAPTER 14: DNA: THE GENETIC MATERIAL
... c. Nitrogen containing base: Purine or pyrimidine 1) Purines = adenine (A), guanine (G) 2) Pyrimidines = thymine (T), cytosine (C), RNA contains uracil (U) not T 3. DNA and RNA composed of repeating units a. Called nucleotides b. Nitrogen base distinguishes nucleotide identity 4. Numbering scheme fo ...
... c. Nitrogen containing base: Purine or pyrimidine 1) Purines = adenine (A), guanine (G) 2) Pyrimidines = thymine (T), cytosine (C), RNA contains uracil (U) not T 3. DNA and RNA composed of repeating units a. Called nucleotides b. Nitrogen base distinguishes nucleotide identity 4. Numbering scheme fo ...
Chemistry 160 Homework 1
... 4. Describe Hydrogen bonds. Give an example. 5. What is the velcro effect? 6. Using a diagram, show how sodium chloride dissolves in water. 7. Define amphipathic. Give an example of an amphipathic molecule. 8. Diagram and explain how soaps work. 9. Define chemical equilibrium. 10. Write equilibrium ...
... 4. Describe Hydrogen bonds. Give an example. 5. What is the velcro effect? 6. Using a diagram, show how sodium chloride dissolves in water. 7. Define amphipathic. Give an example of an amphipathic molecule. 8. Diagram and explain how soaps work. 9. Define chemical equilibrium. 10. Write equilibrium ...
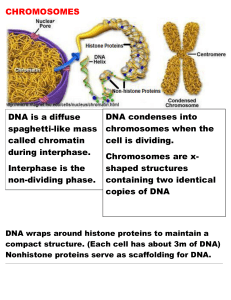
Chromosomes Notes
... chromosomes that have the same genes. However, they will be different versions of the gene (alleles) You get one chromosome of the pair from each parent. ...
... chromosomes that have the same genes. However, they will be different versions of the gene (alleles) You get one chromosome of the pair from each parent. ...
- David R. Liu
... has been to study nucleic acid duplex stability and the function of DNA and RNA polymerases, and has been reviewed recently (Hwang and Romesberg, 2006; Henry and Romesberg, 2003; Hirao, 2006; Jung and Marx, 2005; Kool, 2001). The discovery of novel, polymerase-compatible nucleic acid bases has creat ...
... has been to study nucleic acid duplex stability and the function of DNA and RNA polymerases, and has been reviewed recently (Hwang and Romesberg, 2006; Henry and Romesberg, 2003; Hirao, 2006; Jung and Marx, 2005; Kool, 2001). The discovery of novel, polymerase-compatible nucleic acid bases has creat ...
Recombinant DNA technology engineering) involves combining genes from genes.
... Enzymes are used to “cut and paste” DNA •Restriction enzymes were first discovered in bacteria in the late 1960s. •In nature, bacteria use restriction enzymes to cut up intruder DNA from phages and from other organisms into nonfunctional pieces. The bacteria first chemically modify their own DNA so ...
... Enzymes are used to “cut and paste” DNA •Restriction enzymes were first discovered in bacteria in the late 1960s. •In nature, bacteria use restriction enzymes to cut up intruder DNA from phages and from other organisms into nonfunctional pieces. The bacteria first chemically modify their own DNA so ...
DNA and Proteins - Furman University
... - Nitrogenous Base: each nucleotide has a single nitrogenous base attached to the 1' carbon of the sugar. This nitrogenous base may be a double-ringed structure (purine) or a single ringed (pyrimidine) structure. The purines are adenine (A) and guanine (G). The pyrimidines are thymine (T), cytosine ...
... - Nitrogenous Base: each nucleotide has a single nitrogenous base attached to the 1' carbon of the sugar. This nitrogenous base may be a double-ringed structure (purine) or a single ringed (pyrimidine) structure. The purines are adenine (A) and guanine (G). The pyrimidines are thymine (T), cytosine ...
Effect of vitamin E and beta-carotene on DNA strand
... The tobacco-specific nitrosamines (TSNAs), nitrosonornicotine (NNN) and 4-(N-methylN-nitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone (NNK), are metabolites of nicotine and are major carcinogens in cigarette smoke. Chronic inflammation may promote the carcinogenic effect of these nitrosamines through the gener ...
... The tobacco-specific nitrosamines (TSNAs), nitrosonornicotine (NNN) and 4-(N-methylN-nitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone (NNK), are metabolites of nicotine and are major carcinogens in cigarette smoke. Chronic inflammation may promote the carcinogenic effect of these nitrosamines through the gener ...
Biological Science, 4e (Freeman)
... color blind marries a man who also has normal color vision. He has brown eyes, but his mother had blue eyes. Which of the following do you expect to be true for their sons? A) One-half of their sons will have normal color vision and brown eyes; 1/2 of their sons will have normal color vision and blu ...
... color blind marries a man who also has normal color vision. He has brown eyes, but his mother had blue eyes. Which of the following do you expect to be true for their sons? A) One-half of their sons will have normal color vision and brown eyes; 1/2 of their sons will have normal color vision and blu ...
Insulin is a relatively small protein that in its final form consists of two
... 1. Insulin is a relatively small protein that in its final form consists of two polypeptide chains. The smaller of these two polypeptides consists of 21 amino acids and the larger consists of 30 amino acids. This is how insulin forms: In the beta cells within islets of Langerhans of the pancreas, in ...
... 1. Insulin is a relatively small protein that in its final form consists of two polypeptide chains. The smaller of these two polypeptides consists of 21 amino acids and the larger consists of 30 amino acids. This is how insulin forms: In the beta cells within islets of Langerhans of the pancreas, in ...
Chromosome, genes and DNA Task 1 chromos
... Teaching notes and answers This activity sheet can be used to introduce the topic of chromosomes, genes and DNA (with teacher explanation) or could be used as part of a recap lesson. It covers the basic structure of chromosomes, genes and DNA and some key facts. Task 3 is a dominoes game which could ...
... Teaching notes and answers This activity sheet can be used to introduce the topic of chromosomes, genes and DNA (with teacher explanation) or could be used as part of a recap lesson. It covers the basic structure of chromosomes, genes and DNA and some key facts. Task 3 is a dominoes game which could ...
Control of Eukaryotic Gene Expression (Learning Objectives)
... sequences (proximal and distal elements) 6. Compare and contrast pre and post transcriptional and translational controls of gene expression 7. Explain interference RNA and its role play in post-transcriptional and translational regulation of gene expression 8. Define ubiquitin and proteosome and exp ...
... sequences (proximal and distal elements) 6. Compare and contrast pre and post transcriptional and translational controls of gene expression 7. Explain interference RNA and its role play in post-transcriptional and translational regulation of gene expression 8. Define ubiquitin and proteosome and exp ...
1030ExamFinal
... 29. A sequence of DNA nucleotides coding for a specific protein or RNA molecule is a: A. Gene B. Genome C. Chromosome D. All of the above are correct E. None of the above are correct 30. Which phrase does not belong? The polymerase chain reaction: A. Is used to amplify minute quantities of DNA into ...
... 29. A sequence of DNA nucleotides coding for a specific protein or RNA molecule is a: A. Gene B. Genome C. Chromosome D. All of the above are correct E. None of the above are correct 30. Which phrase does not belong? The polymerase chain reaction: A. Is used to amplify minute quantities of DNA into ...
2- Tropical Course Biochemistry
... B- Intellectual skills B1. Integrate the basic science of biochemistry into clinical practice to explain the various phenomena of infectious disorders. B2- Integrate the biochemical aspects of enzymes and vitamins in diagnosis of infectious diseases B3- Relate principles of gene therapy to manageme ...
... B- Intellectual skills B1. Integrate the basic science of biochemistry into clinical practice to explain the various phenomena of infectious disorders. B2- Integrate the biochemical aspects of enzymes and vitamins in diagnosis of infectious diseases B3- Relate principles of gene therapy to manageme ...
Toxicity of benzo[a]pyrene occurs because of the formation of
... Toxicity of benzo[a]pyrene occurs because of the formation of covalent adducts with DNA guanines. In this work we report the attempt to detect this DNA-adduct using both an electrochemical assay based on gold nanoparticles and a surface plasmon resonance DNA sensor. Detection was achieved via inhibi ...
... Toxicity of benzo[a]pyrene occurs because of the formation of covalent adducts with DNA guanines. In this work we report the attempt to detect this DNA-adduct using both an electrochemical assay based on gold nanoparticles and a surface plasmon resonance DNA sensor. Detection was achieved via inhibi ...
O - IS MU
... Unfortunately, uric acid and its urate salts have a low solubility in water. The average serum concentrations in humans (normal range 100-400 µmol/l) is close to the solubility limit, above which the precipitation of needle-shaped monosodium urate crystals may begin. Excessive accumulation of urate ...
... Unfortunately, uric acid and its urate salts have a low solubility in water. The average serum concentrations in humans (normal range 100-400 µmol/l) is close to the solubility limit, above which the precipitation of needle-shaped monosodium urate crystals may begin. Excessive accumulation of urate ...
Zoo/Bot 3333
... blot analysis. The probe used in this instance hybridizes to a DNA fragment linked to the disease gene, which shows polymorphism for this restriction enzyme. The autoradiogram of this blot is shown above, aligned with the family pedigree. 5. In the above example, which of the following are likely t ...
... blot analysis. The probe used in this instance hybridizes to a DNA fragment linked to the disease gene, which shows polymorphism for this restriction enzyme. The autoradiogram of this blot is shown above, aligned with the family pedigree. 5. In the above example, which of the following are likely t ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.


















![Toxicity of benzo[a]pyrene occurs because of the formation of](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/021940064_1-8f197aea7df98d9d2658a5a3ca962b5c-300x300.png)



